Peripheral Nervous ppt
advertisement

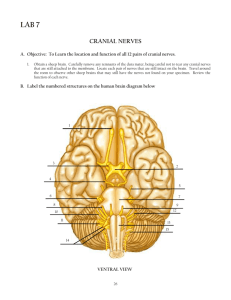
Peripheral Nervous System Ch. 13 Sensory receptors: Classified according to location and type of stimulation Location: Exteroceptors - stimulation arising outside of the body (touch, pain, and temperature) Interoceptors - stimulation arising inside the body (chemical messengers, stretching of tissue, and internal temperature) Proprioceptors - respond to internal stimuli, but located only in skeletal muscle, tendons, joints, and ligaments and C.T. covering bones and muscles. Stimulus detected: - Mechanoreceptors (touch, pressure, vibrations) - Thermoreceptors (temperature) - Photoreceptors (light) - Chemoreceptors (smell, taste, blood chemistry) - Nociceptors (pain) Nerves: Nerve consists of parallel bundles of peripheral axons enclosed by connective tissue coverings: - Epineurium - Perineurium (surrounds fascicle) - Endoneurium (surrounds axon) Direction of transmission: - Mixed nerves - contain both sensory and motor fibers and transmit to and away from CNS - Sensory nerves - contain sensory fibers carrying impulses toward the CNS - Motor nerves - contain sensory fibers carrying impulses away from the CNS PNS nerves classified as cranial or spinal 123- 45- Regeneration of a severed nerve: Separated ends seal off and swell Axon and myelin sheath (of injured site) disintegrates Schwann cells and macrophages migrate to site to phagocytize debris Neurilemma remains intact and schwann cells proliferate Axon "sprouts", guided by schwann cells, gap to original contact - Cranial nerves: 12 pairs Classified as sensory, motor or mixed First two pairs attach to the forebrain Remaining ten pairs attach to the brainstem Olfactory nerve (I) - - - Sensory Sense of smell Olfactory bulbs that terminate into filaments piercing the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. Clinical: person is asked to identify an odor Anosmia: lack of smell Optic nerve (II) - Sensory Vision Not a true nerve but an extension of the brain Begins at the retina, converges at the optic chiasma, partial crossing over of the fibers to enter the thalamus. Optic radiations take impulse to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe. Oculomotor Nerve (III) - - Motor Motor fibers to the 4 of the six eye muscles Eyeball movement Pupil constriction Trochlea Nerve (IV) - - Motor Movement of one eye muscle: superior oblique muscle Downward and lateral movement of the eyeball. Trigeminal nerve (V) - - Mixed Largest cranial nerve Sensory to the face, controls muscles of mastication (temporalis and masseter) Three divisions: V1- Ophthalmic division V2- Maxillary division V3- Mandibular division Nucleus located in the pons Abducens (VI) - - Motor Innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye Moves eyeball laterally Facial Nerve (VII) - - Mixed Exits at the stylomastoid foramen Controls muscles of facial expression Controls lacrimal and salivary glands Taste of anterior 2/3 of tongue Bell’s palsy; unilateral facial paralysis Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII) - Sensory Vestibulo branch: equilibrium Cochlear branch: hearing Travels through the internal acoustic meatus Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX) - - - Mixed Fibers emerge from medulla and exit the jugular foramen. Innervates part of the tongue and pharynx Taste for bitter on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue (Bitter Back 9) Swallowing and gag reflex Vagus (X) - - - - Mixed Only cranial nerve to extend below the head and neck into thorax and abdomen Heart rate, breathing and digestive function. Sensory from the viscera Recurrent laryngeal nerve branches innervate larynx (voice box) Spinal Accessory Nerve (XI) - - Motor Innervates trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscle Clinical: ask patient to shrug shoulders against resistance Hypoglossal Nerve (XII) - Motor Tongue movements: swallowing and speech. Oh, oh, oh, to touch and feel very green vegetables- AH Or On occasion our trusty truck acts funny- very good vehicle anyhow Spinal nerves - - 31 pairs of spinal nerves Mixed nerves (8) Cervical - cervical and brachial plexus (12) Thoracic - intercostal nerves and cervical and lumbosacral enlargement (5) Lumbar - lumbar plexus (5) Sacral - sacral plexus (1) Coccygeal - - Branches (one passing through intervertebral foramen): dorsal ramus: deep muscles and skin of the dorsal surface of the trunk ventral ramus: muscles and structures of the upper and lower limbs and the lateral and ventral trunk Formation of Spinal Nerves Formation of Spinal Nerves Brachial plexus Arises from spinal nerves C4-T1 Serves the arm and shoulder Median nerve: Flexor muscles of the anterior forearm and small muscle in hand (thenar eminence). Radial nerve: extensor muscle of posterior forearm and triceps brachii Musculocutaneous nerve: biceps brachii Axillary nerve: deltoid Lumbosacral plexus Lumbar plexus: Arises from spinal nerves L1- L4 Sacral plexus: L4-S4 - Innervates lower limb, buttocks and pelvic muscles - Femoral nerve: Quadriceps and sartorius - Obturator nerve: Adductor muscles Sciatic nerve: 2 nerves - tibial nerve - common fibular nerve Tibial: hamstrings Common fibular: anterior tibialis - Sacral Plexus