Document
advertisement

Thermodynamics
Tutorial 4
26 February 2016
Electrochemistry
Electrochemical cells
Nernst Equation
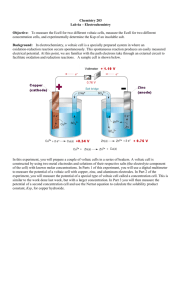
Electrochemical cell
∆rG = -νF∆Ecell
p,T constant:
ν : number of transferred electrons
(according to the chemical equation)
F : Faraday constant = 96 485 C/mol
∆Ecell : electromotive force of the cell
If a process is spontaneous then:
∆rG ≤ 0 (p,T constant)
So for a battery:
∆Ecell ≥ 0 (p,T constant)
Standard conditions
∆rGƟ = -νF∆EcellƟ
Redox table T=298 K, p = pƟ and all activities a = 1
oxidizing
agent
reducing
agent
EƟ(V)
Cu2+ + 2 e-
→ Cu
+ 0.34
2 H+ + 2 e-
→ H2
0.000000
Zn2+ + 2 e- → Zn
- 0.76
Standard Daniell cell: Zn(s) | Zn2+ || Cu2+ | Cu(s)
∆EcellƟ = 0.34 – (– 0.76) = 1.10 V
∆rGƟ = – 1.10·2· 96485 = – 2.12·105 J mol-1 < 0
Non-standard conditions
If p ≠ pƟ and/or a ≠ 1 ,
apply a correction:
RT
For overall potential: Ecell E
ln Q
F
Q : reaction quotient
(similar to concentration quotient)
Θ
cell
For each electrode:
Ox + ν e- → Red
RT
Θ
EE
ln Q
F
E : potential of the electrode
Q refers to the half-reaction of the cell
Example: the nickel chromium battery
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni
3x
Cr
→ Cr3+ + 3e2x
3 Ni2+ + 2 Cr → 3 Ni + 2 Cr3+
ν = 6 and Q
aCr2 3
aNi3 2
If the activities are known you can calculate the
potential by:
Ecell E
Θ
cell
RT
ln Q
F
see last slide for explanation
Answers
Question 1
1.14 V
Question 2
2.33 V
Question 3
a. 12.246 V
b. 0.946
Question 4
pH = 0.86
explanation for nickel chromium battery
RT
ln Q Ecell E pole E pole
F
RT ared
RT
1
E pole Epole
ln
0
.
25
ln
F aox
2F a
E E
fill in for the
reduction
reaction:
the
together
and(b/c)
because
a·ln terms
(b) – a·ln
(c) = a·ln
2) –
By
changing
quotients
{Fill
a·ln(x)
in: ΔE
=cel
a/2·ln(x
=the
E+ pole
} E- pole the
– ln becomes a + ln
Ni2+ + 2e- ⇄ Ni
Ni 2
E pole E
pole
RT ared
RT
1
ln
0.74
ln
F aox
3F a 3
Cr
Ecell
RT
1
RT
1
0.25
ln
0.74
ln
2 F a Ni 2
3F aCr 3
Cr3+ + 3e- ⇄ Cr
RT
RT
Ecell 0.25
ln aNi 2 0.74
ln aCr 3
2F
3F
RT
RT
2
3
Ecell 0.25 0.74
ln aCr 3
ln aNi 2
6F
6F
2
RT aCr 3
Ecell 0.49
ln 3
6F aNi 2
RT
Θ
Ecell Ecell
ln Q
F
3x
Ni2+ + 2e→ Ni
Cr
→ Cr3+ + 3e- 2x
3 Ni2+ + 2 Cr → 3 Ni + 2 Cr3+