final exam review - Iowa State University
advertisement
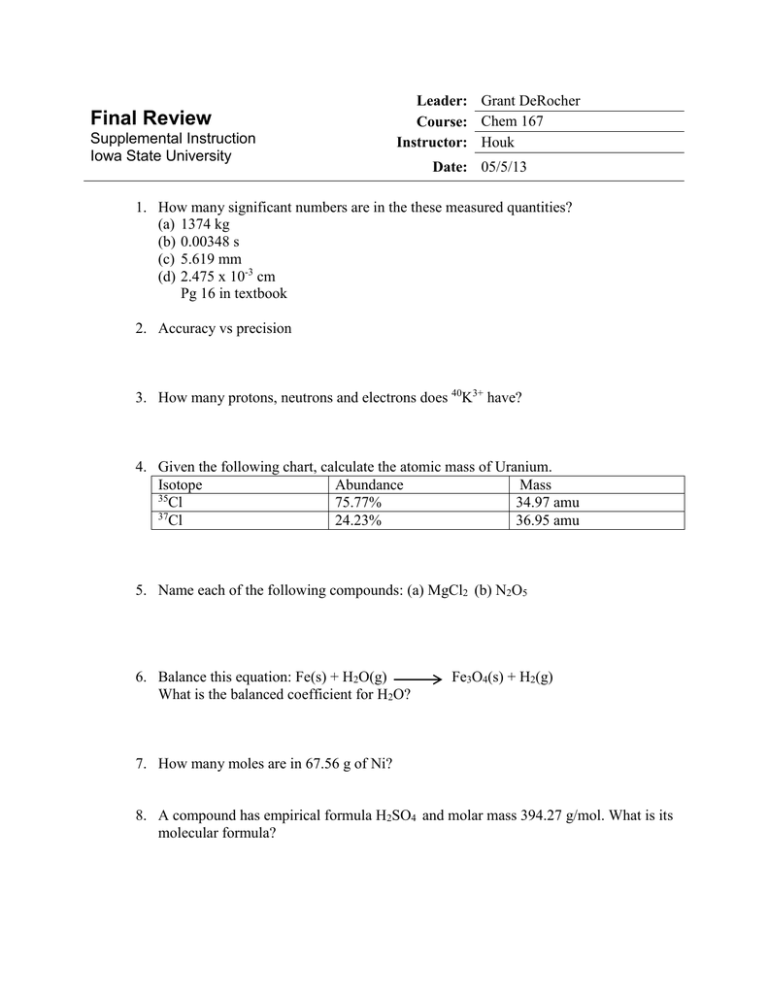
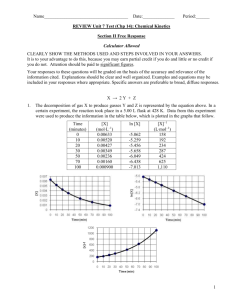
Final Review Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Grant DeRocher Course: Chem 167 Instructor: Houk Date: 05/5/13 1. How many significant numbers are in the these measured quantities? (a) 1374 kg (b) 0.00348 s (c) 5.619 mm (d) 2.475 x 10-3 cm Pg 16 in textbook 2. Accuracy vs precision 3. How many protons, neutrons and electrons does 40K3+ have? 4. Given the following chart, calculate the atomic mass of Uranium. Isotope Abundance Mass 35 Cl 75.77% 34.97 amu 37 Cl 24.23% 36.95 amu 5. Name each of the following compounds: (a) MgCl2 (b) N2O5 6. Balance this equation: Fe(s) + H2O(g) What is the balanced coefficient for H2O? Fe3O4(s) + H2(g) 7. How many moles are in 67.56 g of Ni? 8. A compound has empirical formula H2SO4 and molar mass 394.27 g/mol. What is its molecular formula? 9. If 522.82 g of disiline, Si2H6, is combined with 483.2 g O2, which is the limiting reagent? Si2H6 + O2 SiO2 + H2O NOT BALANCED 10. If 2.70 mL of 12.0M NaOH is diluted to a volume of 150.0 mL, what is the final concentration? 11. A sample of CO2 gas has a pressure of 56.5 mm Hg in a 125 mL flask. The sample is transferred to a new flask where it has a pressure of 62.3 mm Hg at the same temperature. What is the volume of the new flask? 12. Methanol, CH3OH, is used in racing cars because it is a clean-burning fuel. It can be made by this reaction: CO(g)+ 2H2(g) CH3OH(l) 23 What is the percent yield if 5.0x10 g H2 reacts with excess CO to form 3.5x103 g CH3OH? 13. What is the total pressure(in atm) of a 15.0-L container at 28.0 degrees C that contains 3.5g N2, 4.5 g O2, and 13.0 g Cl2? 14. Write the ground state electron configuration for (a) B (b) Ba (c) Be. 15. When light with a wavelength of 58.5 nm strikes the surface of tin metal, electrons are ejected with a maximum kinetic energy of 2.69 x 10-18 J. What is the binding energy of these electrons to the metal? 16. Arrange the following set of anions in order of increasing atomic radii: (a) Cl- , P3-, S2- 17. Which of the following represent valid sets of quantum numbers? (a) n=3, l=3, ml=0 (b) n=2, l=1, ml=0 (c) n=6, l=5, ml= -1 (d) n=4, l=3, ml=-4 18. Arrange the following atoms in order of increasing ionization energy: Li, K, C and N. 19. Indicate which species in each pair has the more favorable (more negative) electron affinity. (a) Cl or S (b) S or P 20. Draw the Lewis dot structure of the following species and identify the number of pi bonds in each: (a) CS2 (b) CH3Cl 21. Predict the geometry of the following species: (a) SO2 (b) BeCl2 (c) SeCl4 22. Predict the shape of each of the following molecules or ions: (a) IF3 (b) ClO3- 23. Based on the positions in the periodic table of the following pairs of elements, predict whether bonding between the two would be primarily ionic or covalent. (a) Ca and Cl (b) Ba and F (c) Br and I 24. What hybrid orbitals would be expected for the central atom of GeCl4? 25. Identify the kinds of intermolecular forces that are most important in methanol, CH3OH. A. London dispersion B. H-Bonding C. Covalent bonding D. Dipoledipole 26. Write a formation reaction for C8H10O. 27. What is the symbol for giving off heat? 28. For the reaction N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g) ∆H=180.5kJ, how much energy is required to generate 1050.35 grams of NO? 29. How fast (in meters per second) must an iron ball with a mass of 56.6 g be traveling in order to have a kinetic energy of 15.75 J? The density of iron is 7.87 g/cm3. 30. The first order rate constant for the photodissociation of A2 is 0.231 s-1. How much time is needed for the concentration of A2 to decrease to one-fifth (20%) of its initial concentration? A) 10.3 s B) 6.97 s C) 3.45 s D) 0.179 s 31. A metal radiator is made from 26.0 kg of iron. The specific heat of iron is 0.449 J/g*degreesC. How much heat must be supplied to the radiator to raise its temperature from 25 degrees C to 55 degrees C? 32. For the reaction 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) N2(g) + 2H2O(l) AT 1100 degrees C, the following data have been obtained. [NO](mol L-1) [H2](mol L-1) Rate=-[NO]/∆t (mol L-1 s-1) -3 5.0x10 0.32 0.012 1.0x10-2 0.32 0.024 -2 1.0x10 0.64 0.096 Describe the rate law for the reaction, and determine the value of the rate constant. 33. HBr is oxidized in the following reaction: 4HBr(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) + 2Br2(g) A proposed mechanism is HBr + O2 HOOBr HOOBr + HBr 2HOBr HOBr + HBr H2O + Br2 (slow) (fast) (fast) (a) Identify all intermediates in this mechanism (b) Identify the rate determining step 34. The following reaction is at equilibrium: HF(g) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + F-(aq) If water is added to the system, what will happen? A. [F-] will increase B. [H3O+ ] will decrease C. [HF] will decrease D. Concentrations will not change We won’t have time to cover everything from chapters 13 and 14 but since those are the most recent chapters they should be more fresh in your mind. Refer to www.si.iastate.edu and go to Chem 167 to find my SI worksheets over these chapters. Sessions 33 and after. I will post the solutions to these lessons on the website but you need to try them on your own first or you won’t be doing yourself any favors. Go through the chapters since the last test and make sure you have the new equations that will be important on your periodic table. This is the last time you will need it to don’t hold back. Fill up all of your space. But make sure you can find it come test time.



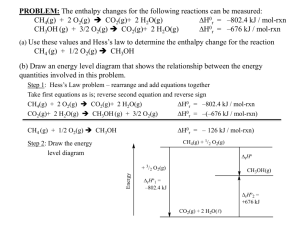


![Homework V solution [ ][ ] [ ]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/013607381_1-076372d3d646781c8f0a3a6699d59ec5-300x300.png)