Vertebral Column
advertisement

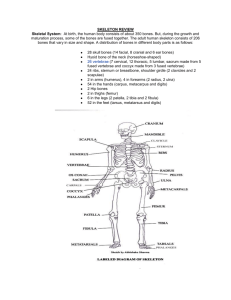
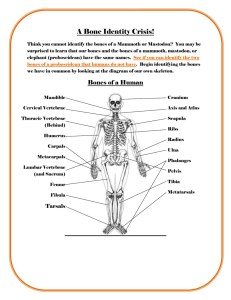
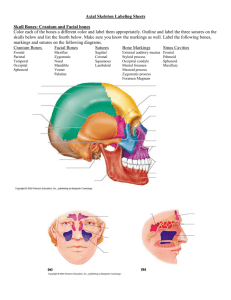
The body’s main axis Supports the head Protects the spinal cord Site of attachment for limbs and muscles Consists of a column of 33 irregular bones called vertebrae Curved when viewed from the side ◦ Differences in structure and size by region 5 anatomical regions Cervical (neck) – 7 vertebrae Thoracic (chest) – 12 Lumbar (lower, “small” of the back) – 5 Sacral (sacrum/upper pelvic) – 5 fused Coccogeal (tailbone) – 4 fused (vestigial tail) Strong impact can compress an intervertebral disc forcing the soft center to balloon outward, press on spinal nerves causing severe pain = herniated or slipped disc Occurs most often in lumbar vertebrae Can rupture releasing pulpy contents Surgery can relieve pain/pressure against the nerve – disc must be fused w/ adjacent vertebrae and limits flexibility Repetitive motions – carpel tunnel syndrome Connective tissue sheath holds the carpel bones of the wrist together Carpel tunnel delivers blood vessels, nerves and tendons to the carpel bones Overuse causes swelling and inflammation of the tendons causing them to press against the nerve supplying the hand numbness of wrist and hand Mild cases = pain relievers, severe = surgery to relieve pressure Imbalance of the activities of osteoclasts and osteoblasts Caused by inactivity & poor diet Hunched posture Post menopausal women at higher risk due to decreased estrogen General term for joint inflammation Most common – osteoarthritis – degenerative wear and tear – 20 million Americans >45 Bony spurs form as cartilage wears away and bones thicken Increased friction causes painful inflammation OTC meds can help, surgical joint replacement in severe cases; injections of hyaluric acid (a component of hyaline cartilage) can reduce knee pain temporarily Also causes joint inflammation but it is caused by the body’s own immune system (autoimmune disorder) which mistakenly attacks the joint tissues