simple present- present progrissive
advertisement

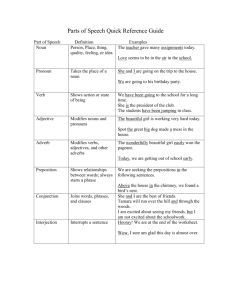
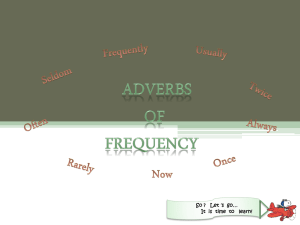
Section 3:The Simple Present By: Areej Dawoud Examples 1. 2. 3. 4. I play tennis every day. The sun rises from the east. The train leaves at 6 PM. They like apples. The simple present is a verb. It has only two forms: the simple form without an –s (sleep). the simple form + s (sleeps) with third person singular subjects. Forming the simple present Subject Verb I You We They Subject Verb He Work She It Works Usages of the simple present USE 1 Repeated Actions Use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is repeated or usual. The action can be a habit, a hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. E.g. She walks to school. Usages of the simple present USE 2 Facts or Generalizations The Simple Present can also indicate the speaker believes that a fact was true before, is true now, and will be true in the future. It is used to make generalizations about people or things. E.g. Cats like milk. Usages of the simple present USE 3 Scheduled Events in the Near Future Speakers occasionally use Simple Present to talk about scheduled events in the near future. This is most commonly done when talking about public transportation, but it can be used with other scheduled events as well. E.g. The party starts at 8 o’clock. Adverbs of frequency Examples 1. I always brush my teeth before I go to bed. Ann usually has toast for breakfast. Mr. Smith often goes to the park with his dog. We sometimes see Susan down at the shops. They rarely smoke cigars. He never works on the weekend. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Adverbs of frequency Adverbs of frequency Adverbs of frequency tell us how many times something happens. Always = every day Usually = happens most days Often = many times Sometimes= at particular occasions but not all the time Rarely = it is not common Never = not at any time or not on any occasion Adverbs of frequency come between the subject and the main verb. Subject I Adv. Of frequency Simple present always do my home work Adverbs of frequency with to be Examples Tom is usually very friendly. Ramon and Frank are often hungry. Ted is rarely late. We put adverbs of frequency after the verb to be (is / are). subject Simple present to be Peter is Adverb of frequency always nice 3.4 spelling of final -s & -es Verb The verb ends in the sounds /f/, /k/, /p/, /t/ ends in the sounds /b/, /d/, /g/, /l/, /m/, /n/, /r/, /v/ or in a vowel ends in /ch/, /sh/, /s/, /x/, /z/. ends con. + y ends in a vowel+ y Spelling Examples Pronunciation +s He likes coffee.. It sleeps. /s/ +s He swims. She reads. /z/ +es She watches TV. It finishes at 10 p.m. /iz/ Drop y, add -ies He worries a lot. /z/ She stays at home. /z/ +s 3.5 Irregular verbs I have a job. He She It has a problem. I do the work. He She It does the work. I go to work. He She It goes outside. 3.6 have (got) & has (got) We use have (got) & has (got): For things we possess or own. I have got a car. To describe people, places, animals, and things. She has (got) black hair. For our families and people we know. I have (got) a son. With some expressions like the following: have got (a cold, the flu, temperature, headache, toothache, a problem) 3.6 have (got) & has (got) Singular I, you have (got) He, she, it has (got) a book Plural You, we, they have (got) books. 3.8 The simple present: yes / no We use do or does to make questions in the simple present. We always use the base form after do and does. do/does subject Do Does Base v. Affirm. Neg. I, we, you, Work? they Yes, I do. You do. No, they don’t We don’t He, she, it Work? Yes, he does No, it doesn’t The simple present:whquestions Where does he live? What do they do? We put question words (what, where, when, why, who,…) before do or does. Frequency adverbs comes after the subject in the question. When do you usually get up? 4.1 The present continuous We form the present continuous with the present of verb to be (am, is, are) and the base verb + ing. subject To be I am He, she, it is They, we, you are Base v. + ing working 4.2 The spelling of verbs ending in -ing Verb ending Rule example Consonant + e Drop the e, add -ing dance, come 1 vowel + consonant fitting Verbs end in w, x, y Double the con., sit add –ing Do not double show the con. fix say 2 vowels + 1 con. Do not double, add -ing eat sleep eating sleeping All other verbs Add -ing talk read talking reading dancing coming showing fixing saying 4.3 The present continuous negative To form the negative of the present continuous, we use not after the verb to be and the verb with –ing. He is not working. You are not sleeping. 4.4 The present continuous: yes/ no questions To be subject Am I Is he, she, it Are you, we, they Base v. + ing Working? 4.5 The present continuous: wh- questions Where, What, Why, When, How, Who I am drinking tea. What am I drinking? 4.6 Verbs not used in the present continuous Non action verbs (describe a state or condition): Believe hate have hear know like remember think see smell taste think understand want Julia has a car. Julia is having a cup of tea. Conclusion 1. 2. 3. The simple present has two forms. Adverbs of frequency usually come with the simple present between the subject and the verb. Adverbs of frequency come after verb to be. To practice more www.englischhilfen.de/en/exercises/adverbs_of_freque ncy.htm www.english-zone.com/verbs/freq-adv01.html http://esl.about.com/library/grammar/blgr_adverbs_freq uency.htm Thank you