Name: Social Psychology, Guided Notes #2 Cooperation
advertisement

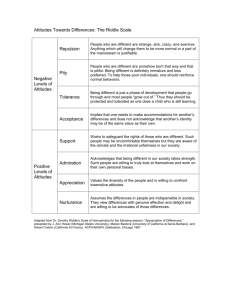
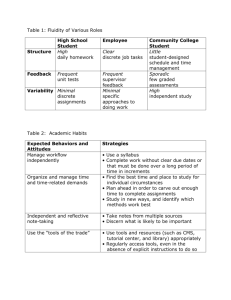
Name:_______________________________________ Social Psychology, Guided Notes #2 Cooperation, Competition and Conflict I. Cooperation vs. Competition A. Cooperation involves people working together to reach a goal. Example: B. Competition involves working toward a goal while denying access to that goal to others. Can be between individuals or groups. Example: II. Social Dilemmas A. Definition – Individual or group behavior that leads to a short-term gain for the individual or group, can lead to ______________________ for all if everyone (or all groups were to engage in the same behavior. B. ___________________ ______________________ ________________ - Two people are separated immediately after being arrested for a serious crime. They are believed to be guilty, but the evidence to convict them is lacking. Each prisoner can confess or not confess to committing the crime. If neither prisoner confesses, each will be given a lesser punishment (1 year in jail). If both prisoners confess, each will receive a moderate sentence (5 years in jail). If one prisoner confesses and the other does not, the prisoner who confesses will go free and the other will receive a more severe sentence (10 years in jail). The best mutual outcome is for both prisoners to cooperate, but there is a strong tendency for people to compete rather than to work toward a mutually beneficial goal. Summarize how the game could have turned out better that we played as a class: C. _____________ _______________ - When individuals share a common resource they all want and there is a scarcity of that resource (or the perception of a scarcity), individuals sometimes take more than their fair share and use the resource up quickly. Example: D. Social dilemmas reflect _____________________ ________________ between an individual and others (or groups) and between short-term and long-term interests. Example: III. Interpersonal Conflict A. Definition – An interpersonal conflict occurs if a person believes that another stands in the way of something of ________________. B. Causes 1. Competition for scarce resources Example: 2. Revenge Example: 3. Attribution of selfish or unfriendly motives to others. Example: 4. Misperceived or faulty communication or misperceptions. Example: IV. Managing Conflict A. __________________________ is the term used when each side offers and counteroffers until a mutually agreeable solution is found. Example: B. _____________-_______________ _______________________ take place when an outside, objective source helps find a workable solution. Example: C. __________________________ ______________ are shared goals that can only be achieved through cooperation. Example: D. Communication and trust underlie these methods of reducing conflict. Attitude Formation and Change; Conformity, Obedience, and Prosocial Behavior I. Attitudes Attitudes are _______________________ (i.e. positive or negative) judgments about people, objects, events and thoughts. Attitudes can be formed through ___________________ and ___________________. A. Attitudes can serve two functions: to enable us to rapidly evaluate objects as good or bad (the object appraisal function of attitudes) and to express values and convey a person’s ____________________ (the value-expressive function of attitudes. B. Attitudes are often measured using self-report techniques. Example: II. The ABCs of Attitudes A. Components of Attitudes A for __________________________ (emotional) component. B for __________________________ (action) component, and C for ___________________________(belief) component. B. Example – Attitude toward pizza a. Affective: b. Behavioral: c. Cognitive: C. Attitudes can be ___________________(attitudes that can be reported consciously) or ___________________ (attitudes that are automatic responses, possibly unconscious) III. Attitude – Behavior Link A. Attitudes and behaviors have a dual relationship. Our current attitudes are influenced by ______________ behaviors, and yet our _________________ behavior is predicted by our current attitudes. Attitudes often guide rational choices we make (we believe dirt is bad so we wash dirty clothes), and attitudes can also influence what we pay attention to in the world around us and therefore affect our behavior. Example: B. IV. Attitudes tend to predict behaviors when the attitude is strong. Example: Attitudes also predict behaviors when we are free to behave in a variety of ways. Example: Understanding Attitudes A. ________________________ _____________________ ________________ There are two routes of persuasion. 1. _________________ _______________ - Attitude change involves carefully processing a message’s content. The message is important (strength of arguments). This route usually requires motivation and ability to process. (systematic processing) Example: 2. __________________________ ________________ - This route devotes little attention to the actual content of the message and tends to be affected by persuasion cues such as confidence, attractiveness, or other characteristics of the person delivering the message. Example: B. The _____________________ ________________________ _________________ is the tension resulting from the lack of consistency in a person’s attitudes or beliefs and behaviors. Cognitive dissonance generally occurs when the ABCs of attitudes are inconsistent. We often bring our attitudes in line with our actions, when we are aware that out attitudes and actions don’t coincide. In other words, we rationalize our behavior. Example: C. V. ______________ - ____________________ ____________________, people infer their attitudes from their behavior. This is most likely to happen when our internal attitudes are weak or ambiguous. Example: Conformity Conformity is following a group’s standards, methods, or behavior as a result of unspoken group pressure, real or imagined. Example. Reasons for Conformity 1. _______________________ _______________ _____________________ is a person’s desire to gain group approval and avoid disapproval. Example: 2. ________________________ _________________ _________________ is a person’s willingness to accept others’ opinions regarding reality. Example: 3. Cultural effects – Some cultures value conformity; others value individualism. a. Example of a collectivist culture: b. Example of a individualistic culture: c. Individuals living in collectivist cultures tend to conform more than individuals living in individualistic cultures because they more often look out for the good of the group and allow individual ideas to be stifled if it benefits the group. Individualistic cultures like the U.S. generate individuals who are more concerned with personal opinion and gain. 4. Ambiguity of the situation – people rely more on the opinions and behaviors of others in certain situations. Example 5. Individual differences exist with conformity. Individuals who are highly motivated to achieve have high self-esteem, are less concerned with the approval of others, and are less likely to conform. D. Conformity includes both compliance and obedience. Conformity refers to any behavior that occurs as a result of outside influence. VI. Compliance Compliance is obeying a direct request or giving in to overt ____________ _____________. A. The ________________ in the ___________________ effect is the concept that if people first agree to a small request, they are more likely to comply with a larger request later. Example: B. The _____________ in the ____________ effect is if people are asked for a large favor first (which they deny) they are more likely to comply with a subsequent smaller request. If a person has already said no, but wants to be perceived positively, the person is more likely to say yes to a more reasonable request. Example: C. Other forms of compliance 1. Free gift technique: 2. Scarcity technique: 3. Liking technique: VII. Obedience Obedience is a form of _________________ that occurs when people follow direct commands, usually from someone in a position of authority. A. Summarize the Milgram experiment: B. Cults and Propaganda 1. Summarize what happened in Jonestown 2. Summarize what happened with Heaven’s Gate Cult 3. _____________________________ is a persuasive attempt that is purposefully biased, motivated by a specific idea or ideology. Propaganda can range from persuasive attempts used by Hitler in Nazi Germany to the messages we see every day in commercials. C. Influences on obedience include: 1. The prestige of _________________________ 2. The presence of others who _________________/____________________ 3. Personality characteristics (a) High authoritarianism (b) ____________________ _____________ _____ _________ is the phenomenon that results when people believe that they cannot control their environment, rather it controls them. Example: