Heat Unit Test: High School Physics/Chemistry
advertisement

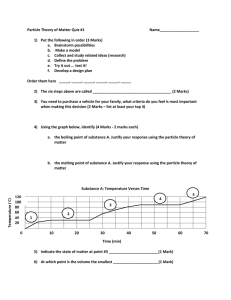
Unit Test – Heat Name __________________________ ___ Volume A. Energy transferred via special waves (ex. UV and electromagnetic) B. The temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid C. Heat is created when a solid resists the flow of electrons D. A substance that inhibits or slows the transfer of heat E. The amount of space matter occupies F. Heat is created by bending and twisting G. When a liquid becomes a gas H. A device used to measure temperature I. Heat is released by breaking the bonds between atoms J. The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid K. Energy transfer through a fluid (gas/liquid) L. Heat is created as a result of motion and position M. Heat produced by breaking apart (spitting) an atom N. A form of energy O. The temperature when a liquid becomes a gas P. A device that regulates heat by monitoring temperature Q. The transfer of heat through solids R. The measurement of heat S. Heat produced by squeezing a fluid T. Allows heat transfer to occur easily U. The movement of particles suspended in a solution V. An electrical device that responds to a difference in temperature by producing an electric current. W. Heat produced by pounding on a surface X. When a gas becomes a liquid Y. Heat produced due to force acting in the opposite direction (rubbing) ___ Thermometer ___ Mechanical Energy ___ Heat ___ Radiation ___ Boiling Point ___ Distortion ___ Thermostat ___ Insulator ___ Electrical Energy ___ Temperature ___ Conductor ___ Percussion ___ Freezing Point ___ Nuclear Energy ___ Convection ___ Chemical Energy ___ Melting Point ___ Compression ___ Thermocouple ___ Brownian Motion ___ Vaporization ___ Friction ___ Conduction ___ Condensation Circle the glass that has more energy? Use the particle theory to explain your choice. (2 Marks) 200 mL @ 40 C⁰ 100 mL @ 40 C⁰ Answer the following questions using the graph provide. (1 Mark each) Heating Substance A 140 100 60 20 10 20 30 40 50 Time (min) What is the boiling point of substance A? What is the melting point of substance A? After 30 minutes, what state of matter is substance A? 60 70 80 90 Short answer- (2 Marks each) Is it possible to add heat to a substance without changing its temperature? Explain What happens to the average energy of the particles of milk when taken from the refrigerator and left of the counter? Explain using particle theory and heat transfer. A boy feels ill and touches his forehead to see if he as a fever; can he tell? Explain. Use particle theory to explain expansion and contraction of a solid when the temperature is changed. Give two examples of materials that slow heat transfer. Choose one and state an example where it is used. Bonus: Use particle theory, heat transfer, and states of matter to explain why a hot glass won’t crack when adding ice until you add water. (2 Marks)