File - phsapstatistics
advertisement
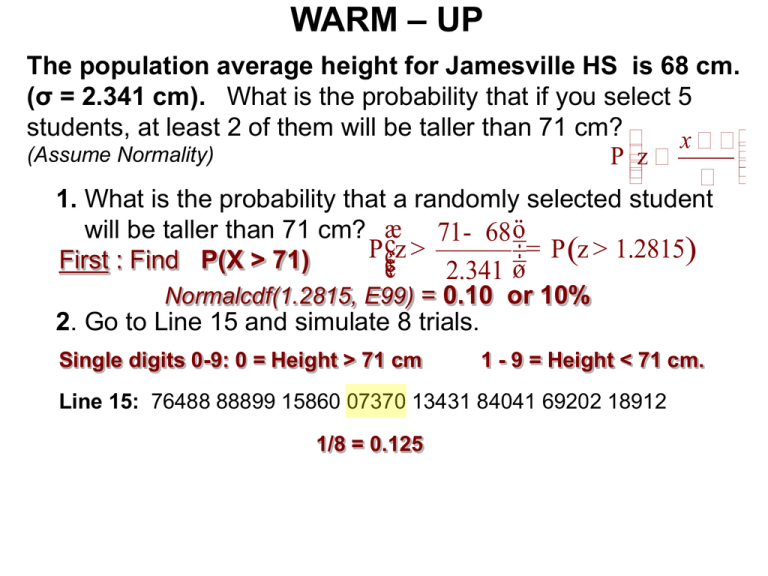
WARM – UP The population average height for Jamesville HS is 68 cm. (σ = 2.341 cm). What is the probability that if you select 5 students, at least 2 of them will be taller than 71 cm? x (Assume Normality) P z 1. What is the probability that a randomly selected student ö will be taller than 71 cm? æ 71- 68 ÷ P ççz > = P (z > 1.2815) ÷ First : Find P(X > 71) ÷ çè 2.341 ø Normalcdf(1.2815, E99) = 0.10 or 10% 2. Go to Line 15 and simulate 8 trials. Single digits 0-9: 0 = Height > 71 cm 1 - 9 = Height < 71 cm. Line 15: 76488 88899 15860 07370 13431 84041 69202 18912 1/8 = 0.125 Identify the type of sampling used in each example. A researcher randomly selects 8 schools from one school district with 38 schools and interviews all the teachers at each of the 8. Cluster sampling At a college there are 120 freshmen, 90 sophomores, 110 juniors, and 80 seniors. A school administrator selects a random sample of 12 of the freshmen, a random sample of 9 of the sophomores, a random sample of 11 of the juniors, and a random sample of 8 of the seniors. She then interviews all the students selected. Stratified sampling At the local college a survey was being done on whether or not the students liked the cafeteria food. The survey was located in the college newspaper and was to be filled out and sent to the editing office. Voluntary Response sampling At the end of each semester a local college requires a teacher's evaluation. An evaluation survey is given to all students to fill out. “Attempted” Census Identify the type of sampling used in this example. During a particular weekend, a reporter who manages many apartment buildings, interviews almost everyone in his building. The reporter finds that everyone, including himself, is satisfied with the conditions with the apartment building. Convenience sampling A new clothing store in town emphasizing mainly children clothing. Before opening, management had to decide whether to only carry either men's, women's, boys', girls', or infants' clothing. After performing representative sampling of potential customers from each of these groups, it was decided to carry only children’s clothing. Stratified sampling The human resources department of a large firm is behind schedule in sampling the job satisfaction of the company's employees. In an effort to catch-up, the HR manager quickly goes down an alphabetical list of employees and e-mails a survey to every tenth employee. Systematic sampling Identify the type of sampling used in this example. The human resources department of a large firm is behind schedule in sampling the job satisfaction of the company's employees. In an effort to catch-up, the HR manager numbers the alphabetical list of employees and uses a random number generator to select 20 employees Simple Random Sample WARM - UP You want to conduct a survey about the opinions students have with regards to AP Statistics. Describe the Bias the may result from… Voluntary Response, Undercoverage, Nonresponse , Response, or Poor Wording of the Question 1. Putting an ad in the Pony Express asking students to go to a website and fill out a survey. Voluntary Response Bias 2. Asking the first 5 students who enter B211. 3. Randomly selecting 5 students and asking…“Everyone I have asked just loves AP Stats, you would have to be dumb not too. How do you feel about Stats? Poor Wording Bias 4. Randomly selecting 5 students who made 5 (100%) on the AP Statistics exam. 5. Randomly selecting Statistics students from FACEBOOK. Chapter 12 (continued) Randomization • Randomizing protects us from the influences of all the features of our population, even ones that we may not have thought about. – Randomizing makes sure that on the average the sample looks like the rest of the population. • Bias: Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent the entire population. • Randomization REDUCES Bias! Simple Random Samples • Samples drawn at random generally differ from one another. – Each draw of random numbers selects different people for our sample. – These differences lead to different values for the variables we measure. – Sample-to-sample differences are called Sampling Variability. Cluster and Multistage Sampling (cont.) • Sometimes we use a variety of sampling methods together. • Sampling schemes that combine several methods are called Multistage Samples. • Most surveys conducted by professional polling organizations use some combination of stratified and cluster sampling as well as simple random sampling. Populations and Parameters A value that represents a characteristic of a population is called a population parameter. (μ = Population Mean p = Population proportion.) A value that is CALCULATED from sample data is called a Statistic. ( x = sample mean, p̂ = sample proportion.) HW Page 290 11-17, 21, 27, 28 Cautions in Sampling 1. Voluntary Response Bias: Individual with strong opinions choose themselves 2. Undercoverage occurs when some groups in the population are left out of the process of choosing the sample. 3. Nonresponse occurs when an individual chosen for the sample can’t be contacted or refuses to cooperate. 4. Response Bias occurs when the behavior of the respondent or interviewer leads to a systematic favoring of one response. Respondents may lie or give an “expected” answer. 5. Poor Wording of the Question Bias occurs when the question is confusing or leading. Warm-Up: You invent a new chocolate bar and you want to gather information about it’s likeability from the population of US consumers. Using Undercoverage, Nonresponse, Response Bias, Poor Wording, or Voluntary Response, describe what is wrong with the following sampling methods? A. You randomly select 10 households. Six are not home and 4 slam the door in your face. Nonresponse B. You randomly select 10 individuals who all happen to be new employees that work under you. Response Bias C. You randomly select 10 individuals who are all in the Weight Watchers program. None of them have had chocolate for 5 years but agree to eat yours. Response Bias Undercoverage, Nonresponse, Response Bias, Poor Wording, or Voluntary Response D. You randomly select 10 individuals from the Richardson Phone Book and ask them to come in for a taste test. Undercoverage E. You put the bars along with a questionnaire next to a time clock. Voluntary Response F. You explain how extremely beneficial the candy is to general health. You then ask them to taste it and comment on its manifestation, its majestic consistency, and its astounding eminence. Poor Wording of the Question Example You want to conduct a survey about the opinions students have with regards to AP Statistics. How would you select 5 individuals from this previous year statistics. 1. DARAIS, NATHAN A 2. DAVIS, MADISEN E 3. FARAGO, PETER 4. GOODWIN, JONATHAN J 5. GUNTER, AUSTIN S 6. KAWALSKY, ERIC M 7. LOEWENSTEIN, BEN N 8. MANDELBAUM, CAREN L 9. MICHELL, ANDREW R 10.MILLER, TYLER L 11.PIERCE, TAYLOR 12.REDLINGER, JOHN L 13.ROBINSON, CHAD B 14.SCHUTZA, EVAN J 15.SLATE, LEE 16.SMEJDIR, ANDREW D 17.STEPHENS, JOHN-MICHAEL 18.STIEG, ANNE M 19.WHALEY, CHLOE 20.WINER, LEMORE P 21.YANG, MATTHEW 22.ZACK, AARON E • Work hard to avoid influencing responses. Cluster and Multistage Sampling • Sometimes stratifying isn’t practical and simple random sampling is difficult. • Splitting the population into similar parts or clusters can make sampling more practical. – If we select one or a few clusters at random and perform a census within each of them, this sampling design called Cluster Sampling. – If each cluster fairly represents the full population, cluster sampling will give us an unbiased sample.









