File
advertisement

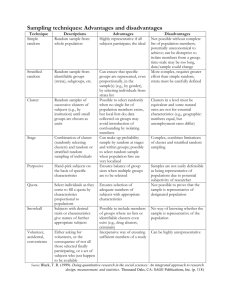
20 minutes to complete Assignment #1.10, pgs 10-11 [#s 1-13 all] Pass back papers Check in A#1.10 Work on completing definitions sheet for Section 1.2, pages 12 –17 Begin discussion on Sampling Techniques Section 1.2 Random Samples * Sampling Techniques Bell Ringer Worksheet – Review from Sec. 1.1 Notes & Assignment – Section 1.2 Explain the importance of random samples Describe the following samplings: Stratified Cluster Systematic Multistage Convenience Construct a simple random sample using random numbers Simulate a random process Use your handout and textbook (pages 12 – 17) and write out the definitions. Read pg. 12 A simple random sample of n measurements from a population is a subset of the population selected in a manner such that every sample of size n from the population has an equal chance of being selected. Important to remember: One of the most important sampling techniques Not only does every sample of the specified size have an equal chance of being selected, but also every individual of the population has an equal chance of being selected. SRS video explanation Guided Exercise #3 on page 12. WEDNESDAY, SEPT 11 PATRIOT’S DAY Calculator Pre-Test Finish notes and discussion of section 1.2 (Random Samples) Begin Assignment for section 1.2 Assignment: - Due Thursday (9/12): Pages 17-18 [#s 1 - 10] - QUIZ FRIDAY (9/13), Sections 1.1 - 1.2 1. Number all members of the population sequentially. 2. Use a table, calculator, or computer to select random numbers from the numbers assigned to the population members. 3. Create the sample by using population members with numbers corresponding to those randomly selected. A numerical facsimile or representation of a real-world phenomenon. Simulations are useful in the study of: Nuclear Reactors Shipbuilding Cloud Formation Airplane Design Medical Science War Games Highway Design Economics Production Control Electronics Although a number is selected for a sample, it is not removed from the population. Simulations often use this. Strata: groups or classes within a population that share a common characteristic. Plural of stratum Characteristics can be age, income, education level, etc. 1. Number all members of a population sequentially. 2. Then, from a starting point selected at random, include every kth member of the population in the sample. Advantage: easy to get Problems: If the population is repetitive or cyclic in nature, do not use this sampling technique. Used by government agencies and certain private research organizations 1. Begin by dividing the demographic area into sections. 2. Randomly select sections or clusters. 3. Every member of the cluster is included in the sample. Used when population is very large or geographically spread out. This method uses a variety of sampling methods to create successfully smaller groups at each stage. The final sample consists of clusters. Uses results or data that are conveniently and readily obtained. Runs the risk of being severely biased. The list of individuals from which a sample is actually selected. Best case is that it includes the entire population Undercoverage happens when a sample frame does not match the population. The difference between measurements from a sample and corresponding measurements from the respective population. It is caused by the fact that the sample does not perfectly represent the population. THESE ARE NOT MISTAKES! The result of poor sample design, sloppy data collection, faulty measuring instruments, bias in questionnaires, etc. A#1.2 Pages 17 – 18 #s 1 – 9 all – DUE THURS QUIZ ON FRIDAY, Sections 1.1 – 1.2