Digestion
advertisement

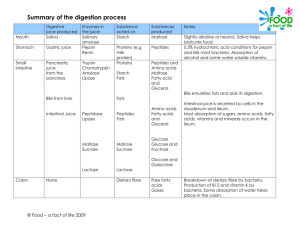
Function of Digestive System: Break down carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (polymers) into small molecules. Allows absorption of nutrients (ions and molecules) into bloodstream. Alimentary canal Accessory glands Mouth Mechanical digestion: teeth! pH: 7.0 Chemical digestion: saliva • amylase (salivary glands) • mucin (mucins + H2O = mucous) Saliva also regulates pH in mouth. Esophagus • Peristalsis: wave of muscular contractions (reflex) Stomach • Mechanical & chemical: reduce food to uniform consistency and osmolarity. • Gastric juice = HCl (parietal cells) + pepsin (chief cells) • Mucus (goblet cells) protects stomach from HCl pH: 2.0 Small intestine Functions: • Digestion of lipids and carbohydrates • Protein processing • Absorption of nutrients and water. pH: 7.8 Carbohydrate digestion • Starts in oral cavity with salivary amylase (ptyalin). • Continues in small intestine with pancreatic amylases. • Polysaccharides / disaccharides >> monosaccharides. • Types of carbs? Plants >> starch, cellulose Animals >> glycogen Protein digestion • Starts in stomach: – Chief cells secrete pepsinogen – Pepsinogen + HCl = pepsin – Proteins denatured by HCl; broken down by pepsin • Then small intestine: – digested by trypsin and other pancreatic enzymes • Proteins >> peptide chains >> amino acids Lipid digestion Small intestine: – bile salts from gall bladder emulsify lipids. – pancreatic lipase digests smaller droplets. – NaHCO3 from pancreas increases pH. Lipids >> glycerol, fatty acids, & glycerides. Hormones Molecules (e.g. peptide or steroid) produced in one part of an organism that trigger a specific cellular reaction in target tissues. Exocrine glands: secrete enzymes that are transported through ducts. (e.g. sweat glands, salivary glands) Endocrine glands: secrete hormones into circulatory system (no ducts). (e.g. pituitary gland, adrenal gland) Pancreas: “mixed” gland Exocrine products: • sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) • digestive enzymes (acinar cells) – lipase – lipids – trypsin – proteins – amylase – starches Pancreas: “Islets of Langerhans” vascularized clusters of endocrine cells. Regulate carbohydrate metabolism (glucose levels in blood). Islets of Langerhans: alpha cells = glucagon beta cells = insulin Glucagon: • Promotes the release of glucose from glycogen stores. • This causes blood glucose levels to increase (hyperglycemia). • Typically released during fasting. Insulin: • Glucose is stored in liver (hepatic tissue) and fat (adipose tissue) as glycogen. • When insulin is released, these tissues uptake glucose from the bloodstream. • This causes blood glucose levels to decrease (hypoglycemia). • Typically released after feeding. Diabetes mellitus • characterized by hyperglycemia. • 20.8 million people, or 7% of US population Type I Diabetes • • • • • Insulin deficiency Autoimmune disorder Islet cells destroyed by immune system Treat by injection Not hereditary Type II Diabetes • • • • • • Insulin resistance “adult-onset” diabetes Over 90% of diabetes Gradual onset Hereditary Associated with age, obesity, physical , ethnic background and inactivity • Treated by diet Mouth Esophagus Carbohydrates Lipids Amylase Lipase Stomach Lumen of small Proteins Pepsin (Polypeptides) Amylase (Monosaccharides) (Disaccharides, Trisaccharides) Bile salts & lipase (Monoglycerides & Fatty acids) Trypsin, et al.! (Short peptides & amino acids) intestine Monoglycerides & Fatty Acids Epithelium of small intestine Monosaccharides Triglycerides Chylomicrons Amino acids Mouth Esophagus Carbohydrates Lipids Amylase Lipase Stomach Lumen of small Proteins Pepsin (Polypeptides) Amylase (Monosaccharides) (Disaccharides, Trisaccharides) Bile salts & lipase (Monoglycerides & Fatty acids) Trypsin, et al.! (Short peptides & amino acids) intestine Monoglycerides & Fatty Acids Epithelium of small intestine Monosaccharides Triglycerides Chylomicrons Amino acids Mouth Esophagus Carbohydrates Lipids Amylase Lipase Stomach Lumen of small Proteins Pepsin (Polypeptides) Amylase (Monosaccharides) (Disaccharides, Trisaccharides) Bile salts & lipase (Monoglycerides & Fatty acids) Trypsin, et al.! (Short peptides & amino acids) intestine Monoglycerides & Fatty Acids Epithelium of small intestine Monosaccharides Triglycerides Chylomicrons Amino acids Mouth Esophagus Carbohydrates Lipids Amylase Lipase Stomach Lumen of small Proteins Pepsin (Polypeptides) Amylase (Monosaccharides) (Disaccharides, Trisaccharides) Bile salts & lipase (Monoglycerides & Fatty acids) Trypsin, et al.! (Short peptides & amino acids) intestine FACILITATED DIFFUSION & TRANSPORT Monoglycerides & Fatty Acids Epithelium of small intestine Monosaccharides Triglycerides Chylomicrons Amino acids Mouth Esophagus Carbohydrates Lipids Amylase Lipase Stomach Lumen of small Proteins Pepsin (Polypeptides) Amylase (Monosaccharides) (Disaccharides, Trisaccharides) Bile salts & lipase (Monoglycerides & Fatty acids) Trypsin, et al.! (Short peptides & amino acids) intestine Monoglycerides & Fatty Acids Epithelium of small intestine Monosaccharides Triglycerides Chylomicrons Amino acids Mouth Esophagus Carbohydrates Lipids Amylase Lipase Stomach Lumen of small Proteins Pepsin (Polypeptides) Amylase (Monosaccharides) (Disaccharides, Trisaccharides) Bile salts & lipase (Monoglycerides & Fatty acids) Trypsin, et al.! (Short peptides & amino acids) intestine Monoglycerides & Fatty Acids Epithelium of small intestine Monosaccharides Triglycerides Chylomicrons BLOODSTREAM Amino acids