Cell Growth and Reproduction

Cell Growth and
Reproduction
Cell Size Limitations
Most cells are 2-200 µm (micrometer) in diameter
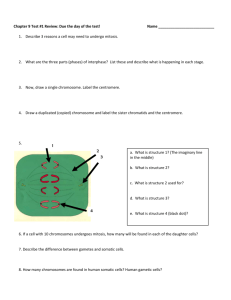
1) Diffusion limits cell size
If larger, cell can not diffuse substances in & out efficiently
2) DNA limits cell size
Only so much protein can be made at one time from DNA
3) Surface Area to Volume Ratio limits size
If cell size increases, cell membrane can not keep up with needs
Cell Division
“All cells are made from preexisting cells through cell division” (Cell Theory)
Cell division results in 2 new cells, identical to the original
Helps organisms grow larger, develop, change, heal, etc
DNA
DNA:
Deoxyribonucleic
Acid
In nucleus of eukaryotes
Contains genetic info
Composed of nucleotides
(monomers)
Chromosomes
When cells divide, chromosomes develop from DNA
Chromosome: DNA & protein in a coiled, rod-shaped form
Histones: proteins that help DNA form chromosomes
Together, DNA & a histone form a unit called a
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Structure
Chromosome Structure
Chromosomes have
2 identical parts called sister chromatids
Chromatid →
Connected by a centromere
Centromere
Chromatid
↓
The Cell Cycle
Cell Cycle: the repeating set of events that make up the life of a cell
Interphase: time between divisions
(G
1
, S, G
2 phases)
M phase: when division occurs
(Mitosis)
Phases of Cell Cycle
Interphase: most of cell’s lifetime
1) G
1
: cell growth
2) S: DNA replication (copied)
3) G
2
: centrioles form & cell prepares to divide
Mitosis: division of nucleus
1) Prophase
2) Metaphase
3) Anaphase
4) Telophase
5)Cytokinesis
Pre-Mitosis Cell
Mitosis
Phases of Mitosis
1) Prophase
Chromosomes form
Nuclear membrane breaks down
Centrioles and spindle fibers appear
Prophase
The arrow is pointing to the dark region, which is condensing chromatin
Phases of Mitosis
2) Metaphase
Spindle fibers move chromosomes to the center of the cell
Fibers attach to each sister chromatid at the centromere
Metaphase
Ch = chromosome,
S = spindle
Phases of Mitosis
3) Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite sides of cell
once apart, are considered individual chromosomes
Anaphase
Cell in mid anaphase
Phases of Mitosis
4) Telophase
Spindle fibers dissolve and nuclear membrane reforms
Chromosomes unwind back into chromatin
Telophase
Cell in early telophase. The arrow points to the formation of a cell plate.
Phases of Mitosis
5) Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
Cleavage Furrow: area that pinches in to form 2 separate cells in animals
Cell Plate: forms cell walls around each new cell
The arrow is pointing to the cell plate, which divides the cell into two new cells.
Live Mitosis!!
Mitosis
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_pla ce/biocoach/mitosisisg/process.html
Control of the Cell Cycle
Cell cycle is controlled by genes (DNA)
If genes become damaged, cells undergo mitosis uncontrollably!!
Sudden growth & reproduction of cells creates tumors
Benign Tumor: non-harmful; stays in place
Malignant Tumor: harmful b/c spreads throughout body
Causes of Cancer
1) Genetics: inherit from parents
2) Chemicals: cigarette tar, food preservatives, pollution
3) UV Radiation: overexposure to sunlight
4) Viruses: herpes, HIV
Skin Cancer
Most common form
Caused by overexposure to UV rays
Types:
1) Basal Cell: most common form; easy to treat
2) Squamous: affects upper layers of skin
3) Malignant: most deadly and fastspreading; found in moles
Meiosis
Chapter 8
Meiosis
“Sexual reproduction”
Produces Gametes : human reproductive cells (sperm/egg)
Cells begin with 2 sets of chromosomes
Must divide twice to become 4 single cells
Occurs in 2 stages:
1) Meiosis I
2) Meiosis II
Types of Chromosomes
2 Types:
Sex Chromosomes: determine sex of organism (male/female)
Male: XY
Female: XX
Humans have 1 pair
Autosomes: all others
Humans have 22 pairs
Homologous Chromosomes
Organisms produced by sexual reproduction
(2 parents) have
2 copies of each autosome
Homologous Chromosomes: carry genes for same traits
1 from each parent
same size & shape
Karyotypes
Karyotype: a picture of an individual’s chromosomes
May be used to identify genetic disorders
Humans:
22 autosome pairs
1 sex chromosome pair
Homologous
Chromosomes
↓
Sex Chromosomes
↑ ↑
Phases of Meiosis I
1) Prophase I Prophase I
Same as Mitosis, except …
Homologous chromosomes pair up to form a tetrad
Chromatids twist around each other & exchange info
Crossing-over: creates new mixture of genetic material
Maternal & Paternal DNA exchanged
Crossing Over
Tetrad →
Phases of Meiosis I
2) Metaphase I
Tetrads line up randomly along center of cell
Metaphase I
Phases of Meiosis I
3) Anaphase I
Each homologous chromosome moves to either side of cell
Independent Assortment: random separation of homologous chromosomes to opposite sides of cell
Creates genetic variation
Anaphase I
Phases of Meiosis I
4) Telophase I & Cytokinesis I
Same as Mitosis, except…
New cells contain 1 chromosome from each homologous pair
Different genetic material than original
Telophase I & Cytokinesis I
Phases of Meiosis II
1) Prophase II
Chromosomes form and spindles attach
Prophase II
Phases of Meiosis II
2) Metaphase II
Chromosomes move to center of cell
Metaphase II
Phases of Meiosis II
3) Anaphase II
Chromatids separate and move to either side of cell
Anaphase II
Phases of Meiosis II
4) Telophase II & Cytokinesis II
Nuclear membrane reforms
4 new cells form (gametes)
Telophase II & Cytokinesis II
Results of Meiosis
After meiosis has occurred, 4 new cells are created
All genetically different
Will become 4 new sperm or 1 new egg
Eukaryotic Cell Division
Mitosis: results in new cells with identical genetic material as original
Used for growth, repair, etc.
Meiosis: cuts chromosome # in half (to 23)
2 different cells must later join to form 1 whole cell
“sexual reproduction”
Diploid & Haploid Cells
Diploid Cells: cells with 2 sets of chromosomes - Mitosis
Describes all human cells except sperm & egg
Abbreviated “2n”
i.e.: Human 2n = 46
Haploid Cells: cells with 1 set of chromosomes - Meiosis
Describes human sperm & egg cells
Abbreviated “1n”
i.e. Human 1n = 23
Binary Fission
Binary Fission: division of a prokaryotic cell into 2 identical offspring cells
Steps:
1) Cells makes copy of DNA
2) Cell grows to 2x’s normal size
3) Cell wall forms, splitting into 2 cells, each with own copy of DNA
Binary Fission (con’t)
Chromosome #’s
Different species have different #’s of chromosomes inside their nucleus
Humans have 46
Lettuce only has 18
But, dogs have 78!!
(more chromosomes ≠ more complex!!)