Plant Water Potential: Salt, Equilibrium, & Calculations
advertisement

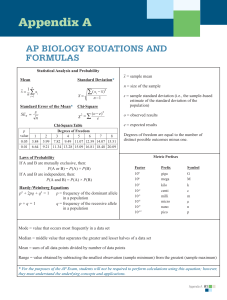
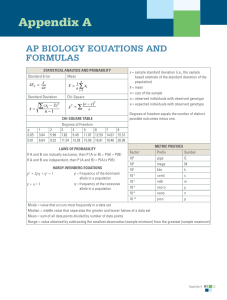
Why can salt cause a water deficit in plants even though the soil has plenty of water? Given that the plant cell in the picture is maintaining a constant volume, what can you deduce about the water potential of the plant cell and the solution in the beaker? Water Potential Plant cell in an aqueous solution. The water potential of the cell equals that of surrounding solution at dynamic equilibrium. From AP Biology Exam Equation Sheet Water Potential (Y) • Y = Yp + Y s • Yp = pressure potential • Ys = solute potential The water potential will be equal to the solute potential of a solution in an open container, since the pressure potential of the solution in an open container is zero. The Solute Potential of the Solution • Ys = –iCRT • i = ionization constant (for sucrose this is 1.0 because sucrose does not ionize in water) • C = Molar concentration • R = Pressure constant (R = 0.0831 literbar/moleK • T = Temperature Kelvin (273 + °C)