Let's Talk About Cholesterol
advertisement

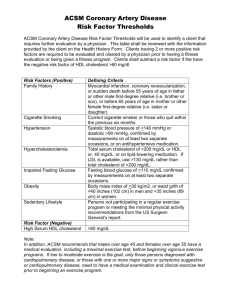
Let’s Talk About Cholesterol Emily Lundstrom, R.Ph., Pharm.D. Melissa Kalb, RD, LD August 8, 2007 Outline • Discuss the different types of cholesterol • Identify healthy cholesterol levels • Provide an overview of medications used to treat abnormal cholesterol levels • Discuss options for a low cholesterol diet What is cholesterol? • Fat-like, waxy substance • Cholesterol comes from two sources • The food you eat and your liver Why do we need cholesterol? • Some is needed for bodily functions • To make cells and some hormones • Too much cholesterol • Clogs arteries • Causes heart attack or stroke Types of Cholesterol • LDL Cholesterol-”Lousy” Cholesterol • HDL Cholesterol-”Happy” Cholesterol • Triglycerides • Which is the most important? • LDL • HDL & Triglycerides are a close 2nd and 3rd LDL—The “Lousy” Cholesterol • Contributes to build up of fat deposits in arteries • Decreases blood flow to the heart • Want this to be low • Lowered by diet, exercise, and most medications HDL—The “Happy” Cholesterol • Helps carry “bad” cholesterol away from arteries to liver • The higher the better! • How can you raise your HDL? • Exercise • Some medications help • Eating properly may help Triglycerides • Most common type of fat in the body • Comes mostly from diet Things that increase triglycerides What Level of Cholesterol is good? • • • • Total cholesterol Triglycerides HDL—”Happy” Cholesterol LDL—”Lousy” Cholesterol <200 <150 >40 <100? * LDL goal depends on other health conditions or risk factors Medications • • • • • • “Statins” Bile acid binders Nicotinic acid (“Niacin”) Fibric Acids Cholesterol absorption inhibitors Fish Oil “Statins” • Lipitor® (atorvastatin) • Zocor® (simvastatin)* • Pravachol® (pravastatin)* • Crestor® (rosuvastatin) • Lescol® (fluvastatin)* • Mevacor® (lovastatin)* *Indicates generic available “Statins” LDL Triglycerides HDL • Well tolerated • Could experience headache, constipation, stomach cramps or gas • A small number of patients experience muscle pain or weakness • Will require liver tests • Most need to be taken before bed Bile Acid Binders • LDL Triglycerides • Mix powders with water, juice, or food • Space from other medications • Side effects: • Constipation, nausea, gas HDL • Questran® (cholestyramine)* • Colestid® (colestipol) • Welchol® (colesevelam) *Indicates generic available Nicotinic Acid (Niacin) HDL Triglycerides LDL • Vitamin B3 • May cause flushing and itching • Take with food • Niacor®*, Niaspan®*, Slo-Niacin®* OTC *Indicates generic available Fibric Acids Triglycerides HDL LDL • Lopid® • Take with food • Side effects: (gemfibrozil)* • Nausea, diarrhea, • Tricor® or Triglide® constipation (fenofibrate) • May cause muscle pain or weakness *Indicates generic available Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors • Zetia® (ezetimibe) • Stops cholesterol absorption from food • Does not have to be taken with food • Often combined with a “statin” LDL • Side effects: • headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea Fish Oil Triglycerides Omacor® • • • * Omega-3 Supplement Rx only • Over-the-counter FDA Approved • Not FDA Approved • Inexpensive $$ Expensive $$ Now called Lovaza® Two-In-One • Combination medications available: • Vytorin® • (simvastatin + ezetimibe) • Advicor® • (lovastatin + Niaspan) • Pravigard PAC® • (pravastatin + aspirin) References • American Heart Association. Accessed at http://www.americanheart.org • National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Accessed at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/ • Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III. JAMA. 2001; 285:2486-97. References • Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation. 2004; 110: 227-39. Low Cholesterol Diet Melissa Kalb, RD, LD Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes (TLC) • • • • • • • • Limit saturated fats and trans fats Limit cholesterol Eat more omega-3 fats Monitor total fat intake 25-35 grams of fiber per day Include meat alternatives Weight loss Exercise Saturated Fats • Generally from animal or dairy sources • Also from coconut and palm oils • Items to limit = marbled meat, poultry skin, bacon, sausage, whole milk, cream, butter Trans Fats • Process that turns an unsaturated (healthier fat) into saturated fats • Items to limit = stick margarine, shortening, some fried foods, and packaged foods made with hydrogenated oils Cholesterol • TLC goal = 200 milligrams per day • American Heart Association = 300 milligrams per day • Items to avoid – egg yolks, fatty meat, whole milk, cheese, shrimp, lobster, and crab. Omega-3 Fats • These fats may help to reduce your risk of heart disease • Good sources = salmon, tuna, mackerel, walnuts, canola soybean and flaxseed oil. Total fat intake • 25% to 35% of total calories • Including heart-healthy fats Fiber • Goal = 20 – 30 grams per day • Soluble fiber – helps to lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol • Sources: oats, beans, peas, citrus fruits, strawberries, apple pulp • Insoluble fiber – helps to decrease your cardiovascular risk • Sources: whole wheat bread, wheat cereals, cabbage, carrots, cauliflower, apple skin Meat Alternatives • Meat and cheese can be high in saturated fats • Items to try = soy burgers, and beans in casseroles Weight Loss and Exercise • Following lifestyle changes • Speak with your health care team to determine an exercise plan Healthy Lifestyle and Medication • Do I need to follow a healthy lifestyle if I am taking my medication? Questions??? Emily Lundstrom, Pharm.D. emily.lundstrom@osumc.edu Chris Green, Pharm.D. christopher.green@osumc.edu Melissa Kalb, RD, LD melissa.kalb@osumc.edu