health ch 4
advertisement

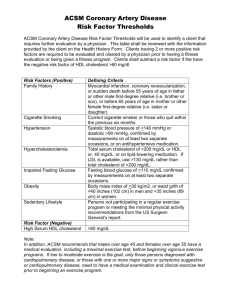
Nutrition 101 The process by which the body uses food for maintenance of life, growth, normal functioning of every organ and tissue and the production of energy. Food is Fuel • Countries other than the United States view food • • • • • as medicine or fuel for their bodies. We need to view food as a source of energy, fuel as well as medicine Each of our bodies are different and use food differently. We are all not the same. Hypoglycemics: 12 grams of protein in the morning Breakfast IS THE MOST IMPORTANT MEAL TOO MUCH CAFFEINE IS BAD FOR YOU. Six Essential Nutrients • • • • • • Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Minerals Vitamins Water What food provides to the body • Fuel (energy) in the form of calories for your physical activity • The stamina and vigor needed to enjoy daily activities • The basis for sound, healthy skin, teeth, hair , muscles and bones What is a calorie? • Each of the foods you eat contain calories. • 9 calories per gram of fat • 4 calories per gram of protein • 4 calories per gram of carbohydrate • You can eat twice the amount of protein and carbohydrates as compared to fat. That is why we encourage you to eat less fat and more protein and carbohydrates Carbohydrates are not BAD! • Carbohydrates supply energy to the body in the form of sugar. • 3 groups of carbs based on the number of sugars they contain: • Single Sugar: fruit sugar,glucose • Two Sugars: Sucrose, lactose, maltose • Multiple Sugars (polysaccharides): Starch – plant sugars Note on carbohydrates • Limit your intake of refined carbohydrates such as table sugar, sweets, pastries and soft drinks. • INCREASE you intake of complex carbohydrates such as grains, cereals and vegetables. • Stay away from prepacked food…read the label How to read a food label • Check out what the serving size is? • Ice cream example • Take total calories and divide them by calories from fat and you will get the percentage of fat for that item. DO NOT BELIEVE the outside packaging. • Total Cereal contains partially hydrogenated oil yet lists only 1g of fat. What is a serving size? • Three ounces of cooked meat, fish or poultry is the size • • • • • • of a deck of cards Two tablespoons of peanut butter is the size of a golf ball A medium piece of fruit looks like a baseball A medium bagel is the size of a hockey puck One ounce of cheese is the size of four dice A small baked potato is the size of a computer mouse The serving size for raw vegetables, yogurt and fruit is one cup – which will fit into an average woman’s hand. Fiber • Water-soluble fiber • helps lower cholesterol levels. It is found in citrus fruits and apples. Insoluble fiber protects against colon cancer. • Found in whole grain • products, especially bran. Recommended intake: 25-50 grams per day. Boost your fiber • • • • • • • • • Berries Beans Romaine lettuce or spinach Whole wheat or whole grain Brown Rice Skins of potatoes, fruits and other vegetables Hummus Oranges and grapefruit Foods high in fiber also contain nutrients that may help reduce the risk of chronic disease. Proteins • Importance for growth, maintenance, repair of • • • tissue Food Sources: Chicken, Fish meat and low fat diary products, eggs, dried peas, beans Recommended Percentage in Diet 10-12% BEWARE of enriched products: this means that the nutrients were destroyed during its processing and then added back to the product. Fats are not EVIL • Function: source of stored energy: provide and carry the fat soluble vitamins :A,D,E,K • Monounsaturated: olive oil, canola oil • Polyunsaturated: Safflower oil, corn oil, margarines • Saturated Fat: meat, butter, milk, solid shortenings • Recommended Percentages: 20-30% • Most people eat too MUCH fat. Minerals • Helps in activating numerous reactions in the body: building and regulating • Variety of food helps you obtain these minerals • Special note: the balance between minerals is important. If you take too much of one mineral you may offset the functioning of another. Where are minerals found? • Food and water • DID you know? Absorption of iron is tripled if it is consumed with vitamin C. • Minerals originate from the soil. The minerals in the soil are taken up by plants and then are passed on to humans and other animals who eat these plants. They cannot be made by people. Vitamins • Aid in absorbing and using the nutrients. Each vitamin helps one or more specific functions in the body. • Vitamins are organic substances from a living thing which are essential for the body to utilize and absorb nutrients. Vitamins and Superfoods • Garlic: one clove may contain more than 15 antioxidants • Onions: contain phosphorous and potassium: may help • • • • • • control high cholesterol Spinach: contains vitamin c, Vitamin E, folic acid, protein, calcium and beta carotene Strawberries: high in vitamin c, potassium and dietary fiber Carrots: full of beta carotene and fiber Fat free milk: loaded with calcium, protein and riboflavin Beans: contain protein, folic acid and fiber Broccoli: high in fiber, calcium, folic acid and vitamin C Vitamins and Mineral Superfoods • Sweet potatoes: rich in vitamin C, vitamin E, Beta • • • • • • carotene, fiber, potassium and iron Citrus fruits loaded with vitamin C Soy: contains iron, calcium, magnesium and fiber Tomatoes: contain fiber and vitamin C Cantaloupes: one cup provides 125% of the Daily value for vitamin C and more than 50% for vitamin A. Oatmeal: full of fiber, iron, copper, folic acid vitamin E and zinc. Brown Rice: one cup contains more than 20% of the Daily value for magnesium and selenium, plus fiber Free Radicals and Antioxidants • Free radical: a chemical that causes damage to the • cells. Cigarette smoke, exhaust fumes, radiation, excessive sunlight, certain drugs and stress can all increase the number of free radicals. Antioxidants: help prevent and possibly repair damage done to the body by the free radicals. Antioxidants are your body’s natural defense mechanism against free radicals. Antioxidants prevent the free radicals from causing the LDL cholesterol (bad) to damage the lining of the arteries and from allowing the buildup of plaque in the walls of the arteries. How do I read my cholesterol numbers? What are HDL,LDL and triglycerides? Stay away from partially hydrogenated oils • These are trans fatty acids which are bad for your system. These are shown to contribute to heart disease. • They help to slow down and even stop your metabolism • Ask my personal fitness class they know all about this. • Eat butter instead or use olive oil as substitutes. Foods rich in antioxidants • • • • • • • • • • • Mangoes Cantaloupes Tangerines Carrots Squash Green leafy vegetables Spinach Broccoli Green peppers Sweet potatoes Vitamin C is an antioxidant but getting it from foods is the best source. Water • Two to three quarts daily: • It is important to drink more than just to satisfy thirst. Those involved in strenuous exercise programs must drink enough water to programs must drink enough water to replace what is lost through perspiration. Drink water before, during and after exercise. Total Cholesterol • Total cholesterol HDL cholesterol is the "good" • • cholesterol carried on high-density lipoproteins. Having more of it means you're more likely to have a lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). LDL cholesterol is the "bad" cholesterol carried on lowdensity lipoproteins. You're better off with lower levels of LDL cholesterol, because it's associated with a higher risk of heart disease. Note that total cholesterol doesn't equal HDL cholesterol plus LDL cholesterol. This is because there are still more types of cholesterol, which we won't talk about here. What does the total number mean? • If your total cholesterol is: 200 mg/dl or less it is considered Normal • If your cholesterol level is between 200 and 239 it means you are borderline. • If your cholesterol is 240 or more then it is too high. What is my HDL number mean? • Less than 40mg/dl is too low. • More than 40mg/dl is beneficial • If above 60mg/dl then you are doing well • HDL is the good cholesterol. LDL the bad cholesterol • If you do not have any heart disease then these are the numbers to look at: • Less than 100 mg/dl is desirable • 100mg/dl -129mg/dl is near optimal/above optimal • 130-159mg/dl – borderline • 160-189mg/dl – high • 190mg/dl and above- very high Trigylcerides • are another fatty substance in the blood that affects your risk for heart disease. Most fat in food, as well as in your body, is present in the form of triglycerides. High levels of triglycerides are a matter of concern and are linked to the risk of heart disease, just as with cholesterol. Triglyceride numbers • Less than 150mg/dl is normal. • 150mg/dl-190mg/dl is borderline • 200mg/dl-400mg/dl is high • More than 500mg/dl is very high Cholesterol Ratio what your doctor doesn’t tell you. • Sometimes you'll be given your cholesterol results as a ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol. (This is the same thing as saying total cholesterol divided by HDL cholesterol.) According to the American Heart Association (AHA), the ratio should be below 5:1, with the optimal amount being 3.5:1 (3.5 to 1). • It's also possible to divide LDL cholesterol by HDL cholesterol to obtain a ratio. (This is the same thing as saying the ratio of LDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol.) In this case, the ratio should be below 3.5. • However, the AHA recommends using absolute numbers for cholesterol (as discussed above) rather than ratios. The reason is that the absolute numbers give physicians a better idea of what type of treatment is needed by the patient, than do ratios. Resources • Textbook: Personal Fitness for You, Second Edition, by Roberta Stokes and Sandra L. Schultz: Copyright 2002: Hunter Textbooks, Inc.: Winston Salem, NC.