Nutrients worksheet fill in chart
advertisement

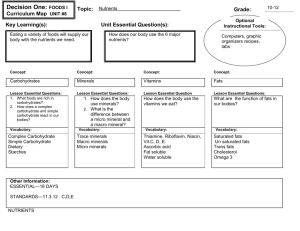
Nutrients HFN1O/2O Mrs. G. Bethune Name ______________________ Date _________________ Read Chapter 11. 1. Define the following terms: a) nutrients – b) calories – c) nutrient deficiency – d) antioxidantse) phytochemicals - 2. Compare the calories provided by each of the following nutrients and their DRI: Nutrient carbohydrates proteins fats calories per gram recommended daily % 3. List the six main nutrients, their functions and main foods by completing the following chart: Nutrient Function 1. Carbohydrates - the body’s main source of energy - most easily digested source of energy a) Complex: - large molecules of simple carbohydrates joined together - take longer to digest and provide your body with a steady supply of energy Starches: b) Complex: Dietary Fibre: - the only form of carbohydrate that does not provide energy - consists of non-digestible plant matter - promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation - may lower risk of colon cancer may reduce blood cholesterol levels c) Simple: - also called sugars - quickly broken down into a useable form by the body - naturally occurring 2. Proteins - used mainly to help the body grow and repair and replace worn-out or damaged parts - provide energy - maintain your hair, eyes, skin, muscles and bones which contain protein - regulate important body processes such as fighting disease a) Complete: - supply all 9 essential amino acids (building blocks that make up body proteins) Main Foods b) Incomplete: - lack one or more essential amino acids - must be combined with other foods to produce body proteins 3. Fats - provide heat and energy for the body -promote healthy skin and normal cell growth - supports function of the kidneys and eyes - carries fat-soluble vitamins A,D,E, K - acts as a cushion around vital organs such as the heart and liver - forms protective coverings around nerves (especially in the brain) - moves slowly through the digestive system making you feel full longer - eating too much increases the risk of illnesses such as heart disease and cancer, overweight and obesity a) Cholesterol: - is not a fat - a fat-like substance that is present in all body cells and needed for essential body processes - helps in the digestion of fat and the production of vitamin D - adults manufacture all the good cholesterol (HDL) their bodies need so do not require any in their diet - bad cholesterol (LDL)can build up on artery walls increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke b) Saturated: - solid at room temperature - raises levels of bad cholesterol c) Unsaturated: - liquid at room temperature - help to reduce bad cholesterol levels - help to increase good cholesterol levels e) Trans Fats - hydrogenated oils that make unsaturated fats solid at room temperature - reduce good cholesterol - increase bad cholesterol 4. Vitamins - keep your body tissues healthy and body systems working properly - assist carbohydrates, proteins and fats in their roles in the body - help to protect the body from disease - some vitamins may be dissolved in cooking water 5. Minerals - most minerals become part of your body ie. teeth, bones or are used to make substances your body needs - some minerals are needed in large amounts such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus some minerals are needed in small amounts such as iron, copper, zinc, iodine, selenium b) Electrolytes: - minerals that work together to maintain your body’s fluid balance - potassium, sodium, chloride 6. Water - essential for human survival - your body is 50-60 % water - your blood is 80% water - critical for chemical reactions that occur in the body - allows the body to regulate its temperature through perspiration - aids in digestion