Poetic Devices for Close Reading
advertisement

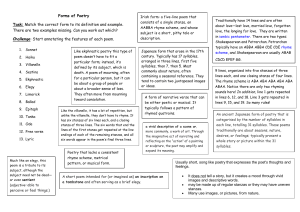
By Monday of Friday be able to match the word with its definition 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. Speaker- an imaginary voice created by the poet (or performer) to tell the poem Voice- speaker, mask, or persona (Latin for mask) Tone- attitude projected toward the subject and audience Formal Tone- features standard English and formal grammar Informal Tone- may feature colloquial language, local idioms or slang Denotation- word’s literal definition Connotation- emotional associations the word evokes Sensory Details- details appealing to sight, sound, hearing, taste, and or touch Figurative language- words and phrases not meant to be taken literally that draw comparisons between ideas and images Simile- make direct comparisons using as or like Metaphor- make direct comparisons by stating that one thing is another Personification- gives human qualities to nonhuman things Hyperbole- an extreme exaggeration Free Verse- does not follow a fixed pattern but may use rhyme, sound devices, meter, and varied stanzas Formal verse- follows established patterns regarding rhyme scheme, meter, and line or stanza structure Narrative- tells a story, has a plot, characters, and a setting Epic poem- long narrative poem about gods or heroes Ballad- describes a single event and may be set to music Dramatic- tells a story using characters own thoughts or spoken statements Lyric- expresses feelings of a single speaker using melodic language, imagery, rhythm, and sound devices Odes- poems of praise often exhibiting complex metrical patters Elegies- poems of loss expressing both praise for the dead and an element of consolation Sonnets- 14 line poem in which lines consist of 5 iambic feet Haiku- a form of Japanese poetry that consists of three unrhymed lines of 5, 7, and 5 syllables Tanka- form of Japanese poetry consisting of 5 unrhymed lines consisting of 5, 7, 5, 7 and 7 syllables Shakespearean sonnet- three stanzas, four lines a piece with an abab, cdcd, efef, rhyme scheme followed by a rhyming (gg) couplet Petrarchan sonnet- eight line stanza with an abbaabba rhyme scheme followed by a six line stanza with a cdecde rhyme scheme Alliteration- repetition of initial consonant sounds Assonance- repetition of vowel sounds within stressed syllables Consonance- repetition of consonant sounds within stressed syllables Onomatopoeia- invented word imitating the sound it describes