Bonding and Naming Honors Supplement
advertisement
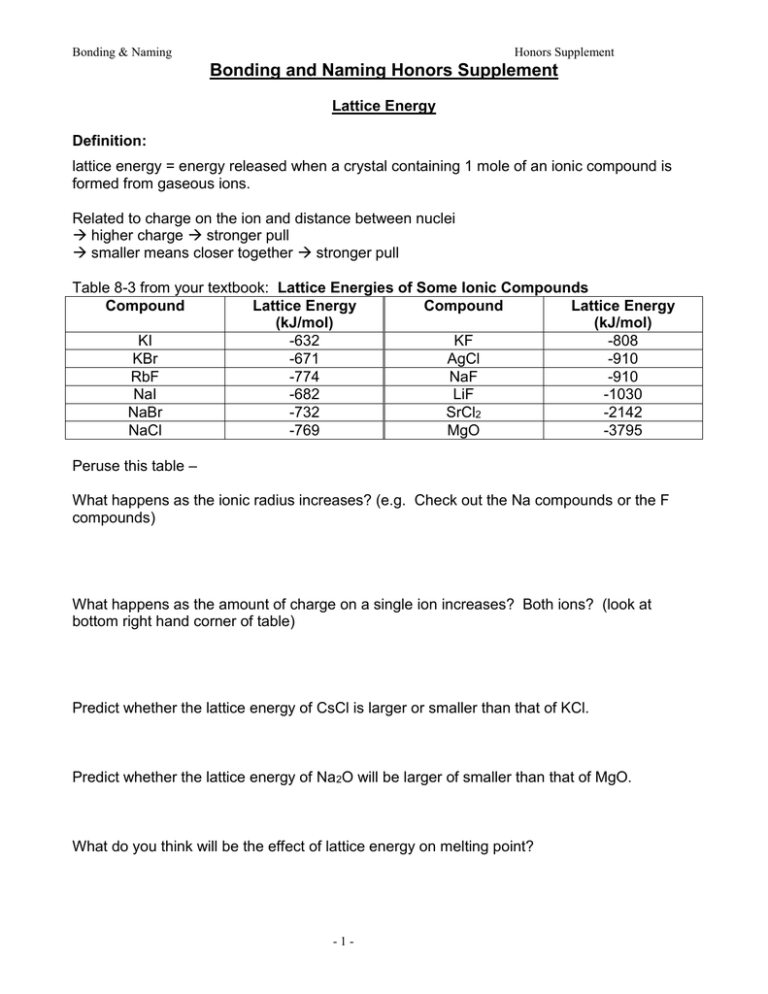
Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement Bonding and Naming Honors Supplement Lattice Energy Definition: lattice energy = energy released when a crystal containing 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from gaseous ions. Related to charge on the ion and distance between nuclei higher charge stronger pull smaller means closer together stronger pull Table 8-3 from your textbook: Lattice Energies of Some Ionic Compounds Compound Lattice Energy Compound Lattice Energy (kJ/mol) (kJ/mol) KI -632 KF -808 KBr -671 AgCl -910 RbF -774 NaF -910 NaI -682 LiF -1030 NaBr -732 SrCl2 -2142 NaCl -769 MgO -3795 Peruse this table – What happens as the ionic radius increases? (e.g. Check out the Na compounds or the F compounds) What happens as the amount of charge on a single ion increases? Both ions? (look at bottom right hand corner of table) Predict whether the lattice energy of CsCl is larger or smaller than that of KCl. Predict whether the lattice energy of Na2O will be larger of smaller than that of MgO. What do you think will be the effect of lattice energy on melting point? -1- Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement Oxidation Numbers Oxidation number = the charge on an ion e.g. K+ has an oxidation number of 1+ O2- has an oxidation number of 2We use oxidation numbers to figure out the formulas of ionic compounds. The sum of oxidation numbers for the formulas of an ionic compounds must = 0. Oxidation Numbers Practice Problems The oxidation number of an atom is the apparent charge assigned to it in a particular molecule or ion. Certain rules are followed in assigning oxidation numbers. The oxidation number of: an element in the uncombined state is 0. a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. hydrogen is generally +1; in hydrides, -1. oxygen is generally -2; in peroxides, -1. the more electronegative element in a binary covalent compound is negative, while that of the other element is positive. elements other than oxygen and hydrogen in a neutral compound is such that the sum of the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the compound is 0. elements other than oxygen and hydrogen in a polyatomic ion is such that the sum of the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the ion equals the charge on the ion. Use these rules to assign oxidation numbers to each element in each of the given formulas. e.g. H2O +1, -2 N2 0 1. Cl2 2. Cl3. Na 4. Na+ 5. KCl 6. H2S 7. CaO 8. H2SO4 9. NO310. Cr2O7211. NH4Cl 12. NH3 13. NO2 14. CaH2 (calcium hydride) 15. Na2O2 (sodium peroxide) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Prentice Hall Inc. -2- Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement -3- Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement Sigma Bonds and Pi Bonds • Sigma () bonds: electron density lies on the axis between the nuclei. • • All single bonds are bonds. What about overlap in multiple bonds? • Pi () bonds: electron density lies above and below the plane of the nuclei. • A double bond consists of one bond and one bond. • A triple bond has one bond and two bonds (above and below the plane of the nuclei; in front of and behind the plane of the nuclei). Compare C2H6, C2H4, C2H2. Formation of a Double Bond -4- Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement Double Bond (C2H4) Triple Bond (C2H2) -5- Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement Naming Molecular Compounds B. Stock system oxidation numbers Treat molecular compounds (esp. those with polar covalent bonds) as if they are ionic: 1. Use electronegativities to determine which atom is more electronegative negative (-) oxidation number (usually = ionic charge) 2. Assign positive oxidation number to other element. Note: Sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound = 0. Practice: CCl4 CO CO2 As2S3 P2O5 P4O10 -6- Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement Hybridization (Honors only) Atomic orbitals are mixed new, identical hybrid orbitals Helps to explain VSEPR # of hybrid orbitals = # atomic orbitals mixed, including lone pairs -7- Bonding & Naming Honors Supplement Hybrid Orbital Summary Electron-domain geometry must be known before hybridization is assigned. • To assign hybridization: • Draw a Lewis structure. • Assign the electron-domain geometry using VSEPR theory. • Specify the hybridization required to accommodate the electron pairs based on their geometric arrangement. • Name the geometry by the positions of the atoms. -8-