Drugs
advertisement

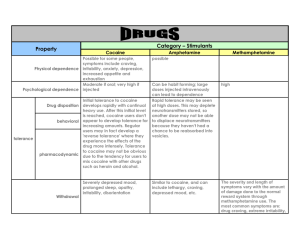
the federal drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use and distribution of certain substances is regulated Categorized certain drugs into 5 classes high addictive potential – not considered of medicinal value There is a lack of accepted safety for use of the drug or other substance under medical supervision No prescriptions may be written for Schedule I substances, and such substances are subject to production quotas by the DEA. ◦ mescaline, lysergic acid diethylamide, heroin, and marijuana, gamma hydroxy butyrate (GHB), ibogaine Drugs with a high abuse risk, but also have safe and accepted medicinal uses Abuse of the drug or other substances may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence stimulants, opiates, methadone, codeine, methylphenidate (Ritalin), mixed salt amphetamine (Adderall), less abuse potential than Schedule I or II has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States. abuse of the drug may lead to moderate or low physical dependence or high psychological dependence.“ ◦ – includes barbiturates, anabolic steroids, ketamine (?), buprenorphine, marinol (synthetic THC) medical use, less abuse liablity, less risk of physical dependence ◦ benzodiazepenes (?) – although n of prescriptions is controlled ◦ some barbiturates Schedule V ◦ cough suppressants with small amounts of codeine History ◦ Cocaine ◦ Source: leaves of E. coca (indigenous to western South America ◦ word spread through explorers, naturalists, botanists History ◦ Cocaine ◦ Source: leaves of E. coca (indigenous to western South America ◦ word spread through explorers, naturalists, botanists 1860’s – a variety of medicinal uses History ◦ Cocaine ◦ Source: leaves of E. coca (indigenous to western South America ◦ word spread through explorers, naturalists, botanists 1860’s – wine tonics Launched in 1863- European success; the world's most popular prescription Some of its advocates; Henrik Ibsen, Jules Verne, Alexander Dumas, Robert Louis Stephenson, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, Queen Victoria; King George 1 of Greece; King Alphonse XIII of Spain; the Shah of Persia; William McKinley, President of the United States. Sears and Roebuck, 1900 "...sustains and refreshes both the body and brain....It may be taken at any time with perfect safety... it has been effectually proven that in the same space of time more than double the amount of work could be undergone when Peruvian Wine of Coca was used, and positively no fatigue experienced....." History ◦ Cocaine ◦ Source: leaves of E. coca (indigenous to western South America ◦ word spread through explorers, naturalists, botanists 1860’s – wine tonics 1884 - Freud as a mental stimulant as a possible treatment for digestive disorders as an appetite stimulant in case of wasting diseases as a treatment for morphine and alcohol addiction as a treatment for asthma as an aphrodisiac as a local anaesthetic mid 1880’s – ◦ Atlanta druggist John Pemberton – devised a patent medicine that contained two naturally occurring stimulants; cocaine and caffeine Coca-cola – advertised as an intellectual beverage a temperance drink; a brain tonic Pemberton sold 2/3 of his interest in 1887 for $283.29 late 1800’s until 1903 ◦ Coca Cola had ~ 60 mg/ 8 ounces ◦ 1903 Coca Cola stopped having cocaine 1914 – Harrison Narcotic Act – ◦ listed cocaine as a narcotic synthesized in the lab (in early 1900’s) first marketed in 1927 drug has been abused since its introduction benzedrine inhalers used by a wide segment of population during 1930’s amphetamines and war amphetamines and weight reduction ◦ 1967 – estimates of 23,000,000 prescriptions in US for weight reduction Cocaine use still rose during the 1920’s but then decreased in 1930’s because amphetamines became available (and at the time cost less, were more easily available AND the euphoria lasted longer) Amphetamine took over in popularity during the 1940’s – 1960’s. In 1970’s restrictions on amphetamine tightened ◦ made amphetamine a schedule II drug so…. some estimate 1.8 million Americans users of cocaine in 1998; majority between 18 and 34 ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ males more likely than females males more likely to use higher amount males more likely to use for longer duration significant proportion met criteria for ADHD coca leaves ◦ leaves can be soaked and mashed to form coca paste oral – 70 – 80% broken down by liver biotransformation cocaine hydrochloride coca paste treated to form salt water soluble and can be taken intranasally or injected IV snorting – not very efficient because cocaine hydrochloride is ionized; also cocaine has vasoconstrictive properties (so it limits its own passage into blood vessels) IV – onset is rush ~ 30 – 45 secs freebase- extracted from crystalline from with either ether or sodium hydroxide ◦ duration lasts 10 – 20 min; ◦ 100% reaches circulatory system ◦ vaporized at lower temps than cocaine hydrochloride and so can be inhaled crack – freebase but extracted with alkaline water and premade (or prepackaged) smoking not really efficient for delivering cocaine to body because significant portion is lost to pyrolysis – but remaining dose produces intense effect originally regional specificity spreading across nation (ease of production although dangerous- explosions, toxic substances, etc) illicit amphetamine production estimated to be in the billions/year methamphetamine ◦ made in growing numbers of clandestine labs ◦ produces greater cortical stimulation than some other amphetamines ◦ huge profit margin ice – free base form of amphetamine Estimated that for each pound of methamphetamine produced, between five and six pounds of highly toxic waste is generated. amphetamine ◦ causes release of newly synthesized monoamines ◦ also blocks reuptake of monoamines cocaine ◦ blocks reuptake of monoamines stereotypic behavior ◦ high doses result in stereotyped behaviors representative for respective species in rat, can be sniffing, licking, biting or gnawing Appetite suppression ◦ weight loss Aggression ◦ several descriptions of murder and other violent offenses attributed to amphetamine intoxication cardiovascular ◦ ◦ ◦ heart disease increased risk for CVA cardiac arrhythmia increased blood pressure respiratory ◦ ◦ chest pain respiratory complications difficulty breathing neurotoxic ◦ seizures intracranial hemorrhages ◦ cocaine or amphetamine induced psychosis ◦ formication methylphenidate (Ritalin) ◦ causes release of newly synthesized DA ◦ also blocks reuptake of DA “Adderall” Strattera –atomexetine HCl ◦ first non stimulant pharmacotherapy for ADHD ◦ blocks reuptake of NE instead of DA methylated amphetamine – text covers this in chapter with hallucinogens (affects 5HT as well) UNTIL RECENTLY - sold in health food stores and on internet Now – no longer on US market! ◦ ephedra – also known as ma huang; herb ◦ FDA received many reports from doctors, government health authorities and others about adverse-based ephedrine based products Currently – OTC subject to FDA regulations HOWEVER herbal supplements currently are essentially unregulated – may soon change! ◦ either decreased effectiveness or potency of a drug How does tolerance occur? Data is mixed acute tolerance acute tolerance animal models – ◦ sensitization Psychological dependence – very strong! Physical dependence – WD? ◦ Cocaine crash operant performance animals will self administer in absence of tolerance, physical dependence, withdrawal or prior drug taking history two bar test variation in extent and rate of self administration depends on drug being administered ex. opiates – uniform and constant administration (moderate and measured with voluntary abstinence) cocaine – frenzied intake followed by abstinence enhances basal neuronal firing or basal NT release in “reward circuit” 1. dose-response rates at fixed ratios 2. progressive ratio schedule ◦ how hard is the animal willing to work for drug drug discrimination – ◦ 2 bar discrimination ◦ what does this tell us? initially trained to self administer drugs followed by extinction priming or nondrug stimuli good predictive validity - reinstate heroin and cocaine seeking in laboratory animals including as drug reexposure, drug cues, and stress (Self and Nestler, 1998; Shaham et al., 2000a; Stewart, 2000) 1. 2. non specific drug effects only test the rewarding component of drug during “intoxicated” state rewarding stimulus is repeatedly paired with neutral environmental stimulus food, water, brain stimulation, sexual partner drugs 1. 2. can study reinforcing effects of a drug in drug free state can sometimes see CPP in one trial (IV particularly) Animals find amphetamine and cocaine highly rewarding