Biological Diversity
advertisement

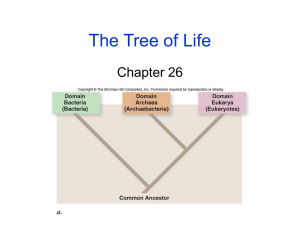
Classification is the grouping of living organisms according to similar structures and functions Aristotle grouped animals according to the way they moved Today’s system developed by Carolus Linnaeus Organization of Biological Diversity: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Domain (often not even used) Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species A taxonomic category that is based on fundamental differences among organisms Three main domains: ◦ Bacteria ◦ Archaea ◦ Eukarya Taxonomic category made up of related phyla Six kingdoms currently recognized for living organisms ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Animalia Fungi Prokaryotes (lack nucleus) Unicellular (one cell) Heterotrophic (most)-eat other organisms for energy All bacteria are in the same domain and kingdom, which is not true for a lot of organisms! Examples: E. Coli, Streptococcus Prokaryotes Unicellular Live in extreme environments Ex: Sulfolobus acidocaldarius(grow in volcanos), Methanogens (produce methane) Eukaryotes (contain nuclei) Multicellular (multiple cells making up organism) Four kingdoms in this domain ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Protista Animalia Fungi Plantae Mainly unicellular Heterotrophic or Photosynthetic (use light as energy) Ex: Protozoa, slime molds Heterotrophic Contain a nervous system Ex: Us!!, Fish, Bats, Snakes (lots of examples!) Heterotrophic Absorb nutrients Contain cell walls of chitin (distinguishes them from plants!) Ex: mushrooms, truffles “The latest auction was for two truffles weighing just under 3 lbs total. $330,000 was paid for the fungal delicacy.” Photosynthetic Cell walls made with cellulose Ex: Trees, Mosses, Ferns Now that we know how living organisms are organized, let’s look at the differences in the microscope! While looking at the samples, I would like you to note: ◦ Differences between organisms/cells in different kingdoms ◦ Differences in organisms/cells in similar kingdoms ◦ Common features in plant slides