Overview of Domains and Kingdoms
advertisement

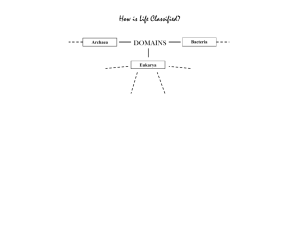
Overview of Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. There are three Domains: Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Organisms are classified into domains according to cell type and structure. What are the two basic cell types, and how do they differ? If the organisms have a cell wall, it might be made of peptidoglycan, cellulose, or chitin Organisms may exist as either Unicellular, Colonial, or Multicellular To get much-needed nutrition, organisms might be Autotrophs, or Heterotrophs Within the Domain Bacteria, there is one Kingdom: Eubacteria Characteristics of Kingdom Eubacteria include… What is the cell type? Is a cell wall present? If a cell wall is present, does it have peptidoglycan, cellulose, or chitin? Are the organisms unicellular, colonial, or multicellular? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs? Find some pictures of Eubacteria and paste them here (e.g. Pseudomonas, tuberculosis, and anabaena). Within the Domain Archaea, there is one Kingdom: Archaebacteria Characteristics of Kingdom Archaebacteria include… What is the cell type? Is a cell wall present? If a cell wall is present, does it have peptidoglycan, cellulose, or chitin? Are the organisms unicellular, colonial, or multicellular? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs? Find some pictures of Archaebacteria and paste them here (e.g. Staphylothermus and Methanopyrus) Within the Domain Eukarya, there are four Kingdoms: Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Characteristics of Kingdom Protista include… What is the cell type? Is a cell wall present? If a cell wall is present, does it have peptidoglycan, cellulose, or chitin? Are the organisms unicellular, colonial, or multicellular? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs? Find some pictures of Protists and paste them here (e.g. algae like kelp, protozoans like Amoeba, and other protists like mildew and Euglena) Characteristics of Kingdom Fungi include… What is the cell type? Is a cell wall present? If a cell wall is present, does it have peptidoglycan, cellulose, or chitin? Are the organisms unicellular, colonial, or multicellular? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs? Find some pictures of Fungi and paste them here (e.g. mushrooms, yeast, molds, and those that cause athletes foot and ringworm) Characteristics of Kingdom Plantae include… What is the cell type? Is a cell wall present? If a cell wall is present, does it have peptidoglycan, cellulose, or chitin? Are the organisms unicellular, colonial, or multicellular? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs? Find some pictures of plants and paste them here (e.g. moss, fern, and types of flowers, bushes, and trees) Characteristics of Kingdom Animalia include …. What is the cell type? Is a cell wall present? If a cell wall is present, does it have peptidoglycan, cellulose, or chitin? Are the organisms unicellular, colonial, or multicellular? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs? Find some pictures of animals and paste them here (e.g. worms, coral, fish, insects, spiders, and various types of amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) Check your knowledge by studying the chart below. Try covering parts of it and see if you remember the characteristic. You can also make your own Jeopardy-style game Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell type Cell walls Number of cells Nutrition Eukarya Protista Prokaryote peptidoglycan Plantae Animalia Eukaryote no peptidoglycan unicellular Fungi some with cellulose chitin unicellular and multicellular most are multicellular autotroph or heterotroph heterotroph cellulose no cell walls multicellular autotroph heterotroph