Chapter 5, Part 3
advertisement

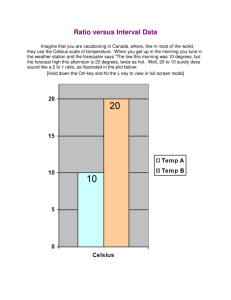
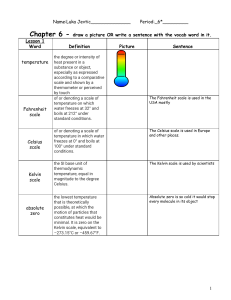
Chapter 5, Part 3 Measurements and Calculations 5.6 Dimensional Analysis 1 in. = 2.54 cm is an equivalence statement and can be turned into a conversion factor: 1 in./2.54 cm or 2.54 cm/1 in. Any equivalence statement can be used in this manner. Example: 62 cm = ? In. 62 cm x 1 in./2.54 cm = 24 in. (note sig figs) Example: 26.2 mi. = ? Km. 26.2 mi. X 1760 yd/1 mi. X 1 m/1.094 yd x 1 km/103 m = 42.1 km Embedded problem: (convert the speed of light from 3.00 x 108 meters per second to miles per hour.) 5.7 Temperature Conversions Fahrenheit Celsius Kelvin b.p. water 212 100 373 f.p. water 32 0 273 Absolute zero -460 -273 0 (note: no degree symbol “o” is used in the Kelvin scale. It is an absolute scale.) Conversions: Celsius to Kelvin: add 273 to Celsius Figure 5.6: The three major temperature scales. Figure 5.7: Converting 70 degrees Celsius to Kelvin units. Figure 5.8: Comparison of the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. Example: 70.oC = ? K 70.oC + 273 = 343 K Example: 77 K = ? oC 77 K - 273 = -196oC Problem: Which temperature is colder, 172 K or -75 oC? (172 K)(Why?) 5.8 Density- amount of matter present in a given volume of a substance. Density = mass/volume Mass = density x volume Volume = Mass/Density Specific gravity- ratio of the density of a given liquid to the density of water @ 4oC (has no unit) Example: 23.50 mL of a certain liquid has a mass of 35.062 g. Calculate density. D = M/V = 35.062 g/23.50 mL = 1.492 g/mL Problem: 35.8 mL of a cleaner has a mass of 28.1 g. Which of the four substances in the table on p. 144 is the major component? D = M/V = 28.1 g/35.8 mL = 0.785 g/mL Therefore, isopropyl alcohol. Example: V = M/D = 225 g/13.6 g/mL = 16.5 mL


![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)