location factors
advertisement

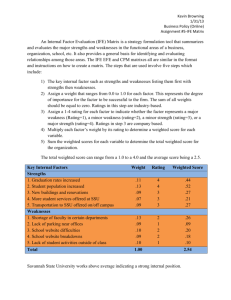
Starbuck focuses on densely populated areas for its 10,000 stores, e.g. it has 124 stores in 24 square mile area of Manhattan, NYC. Toyota has Manufacturing and assembly plant in 12 different countries. 3M has moved a part of it manufacturing unit including R&D in Texas where temperature is more. Toys ‘R’ Us open a new store in Tokyo Japan. Disney world chooses Paris, to start its operations in France. National Bank of Pakistan has more than 900 branches in Pakistan. BMW has 16 manufacturing facilities all around the world, 5 in the US. Refers to the process of determining geographic sites for a firm’s operations. Location choice can be critically important for firm’s performance. Location choice have a profound impact on the firm’s ability to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Improve productivity and quality Reduce costs Identify quality materials and vendors Identify required Technology Serve customers in a better way Find required labor skills Location decisions affect processes and departments › Marketing › Human resources › Accounting and finance › Production & Operations › Research & Development › International operations Location decisions vary over industry type and nature of business. E.g. Choice of location has different implications for: Manufacturing Firms Service & Retailing Firms Please see page 424 (book-1)for details Favorable labor climate Proximity to markets Quality of life (for staff & workers) Proximity to suppliers and resources Proximity to the parent company’s facilities Utilities, taxes, and real estate costs Other factors • Investment requirement for Construction & Set-up • Available Technology • Available modes of Transportation & Infrastructure • Community attitude • Local & regional Laws & legislation Please see page 426 (book-1)for details › Proximity to customers › Transportation costs and proximity to markets › Location of competitors › Site-specific factors Traffic flows & visibility Availability of parking facility Population density • • GIS is a system of computer software, hardware, and data Use to manipulate, analyze, and present information relevant to a location decision • Create a visual representation of a firm’s location choices • Useful decision-making tool Step 1:Identify the important location factors and categorize them as dominant or secondary Step 2:Consider alternative regions; then narrow to alternative communities and finally specific sites Step 3:Collect data on the alternatives Step 4:Analyze the data by quantitative Factors Evaluation Matrix or Preference Matrix Step 5:Bring the qualitative factors pertaining to each site into the evaluation Five-Step process: 1. 2. 3. List key factors (10-20) Assign weight to each showing relative important of each factor over others (0 to 1.0) › Sum of all weights = 1.0 Assign a Rating (1-4) to each factor based on the attractiveness or the suitability of each factor for the firm. 1 = not attractive at all 2 = Average attractiveness 3 = Above average attractiveness 4 = very attractive 4. Multiply each factor’s weight by its rating Produces a weighted score 5. Sum the weighted scores for each Determines the total weighted score for each site. • Highest possible weighted score for the organization is 4.0; the lowest, 1.0. Average = 2.5 Weight Site – A Rating Weighted score Site – B Rating Weighted score Total patients per month .25 4 1 3 .75 Facility distance from city center .20 3 .60 2 .40 Average time per emergency trip .20 3 .60 3 .60 Access ease .15 3 .45 2 .30 Land and construction costs .10 2 .20 3 .30 Employee preferences .10 2 .20 2 .20 Location Factor 3.05 2.55