Cell Processes Test Review
advertisement

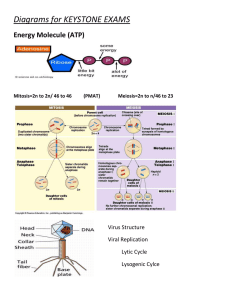
Name:________________ Date:________________ Cell Processes Test Review Part 1: The cell cycle 1. Eukaryotic things do the cell cycle, which consists of three general phases: __Interphase___, ____Mitosis__, and then ____Cytokinesis_____. 2. What happens in each of the three general phases? a. __Interphase__- Cell grows and DNA is copied b. ___Mitosis___- the nucleus’ DNA divides and two nuclei are formed c. __Cytokinesis___- cytoplasm splits and two new daughter cells are created. 3. Mitosis has four phases- draw and label them: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 4. Bacteria don’t do the cell cycle- instead, they do __binary___ _fission__. 5. Why do we need to make more cells? List 3 reasons 1) To replace worn out cells 2) To replace damaged cells 3) Growth and development 6. What can happen if your cells do not divide correctly? Mutations or cancer can oocur Part 2: Cell transport 7. When must a cell use active transport? (Be very descriptive and complete) a) When moving particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration b) When bringing in, or getting rid of, large particles that cannot fit through the cell membrane. 8. When there is a higher concentration of water outside of the cell than inside of the cell, which way will the water move and why? The water will move into the cell. Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. 9. A cell engulfs large particles by ___endocytosis______. 10. The diffusion of water, which is called ___osmosis____, involves movement of water from a __high__ concentration to a _low__ concentration without any energy. 11. The movement of particles from a low to a high concentration is called ___active_____ ___transport____. 12. Explain why red blood cells shrivel when they are exposed to salt water. There is more water inside the red blood cell than there is outside of the red blood cell. The water will leave the cell in order to balance the amount of water inside and outside. 13. When plants do photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters the plant because there is more carbon dioxide in the air than in the plant- this is an example of __diffusion____. Part 3: Cell energy processes 14. What are the possible products of fermentation? - lactic acid (animals) - alcohol (bacteria and yeast) - ATP 15. Write out the photosynthesis equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 16. Write out the cell respiration equation: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP 17. How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related? (Be thorough in your answer) The products of one process are the reactants of the other. In other words, what is produced during photosynthesis is then used during cellular respiration. (and vice versa) 18. Why is cellular respiration better than fermentation for our cells? Cellular respiration produces more ATP. Fermentation produces lactic acid which builds up in our cells. 19. What are the three products of cellular respiration? CO2, H2O, and ATP 20. Cellular respiration happens in the ___mitochondria_____. 21. The pigment involved in photosynthesis is ___chlorophyll____ and it is found in the __chloroplast____. 22. What is the chemical formula for glucose? C6H12O6 23. What organelle does photosynthesis occur in? chloroplast 24. What is the ultimate source of all the energy used by plants and animals? Sun 25. The main goal of photosynthesis is to make ___glucose (food)__, while the main goal of cell respiration is to make _____energy (ATP)_____.