Understanding Annual Rates
advertisement
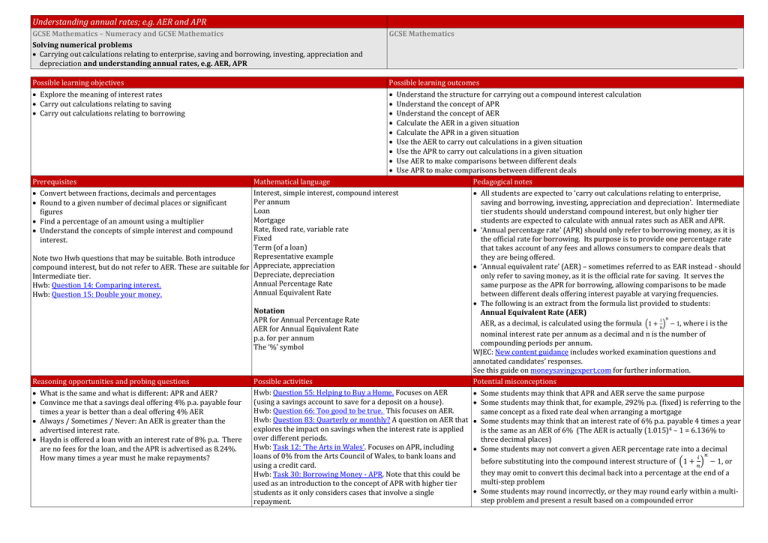
Understanding annual rates; e.g. AER and APR GCSE Mathematics – Numeracy and GCSE Mathematics Solving numerical problems Carrying out calculations relating to enterprise, saving and borrowing, investing, appreciation and depreciation and understanding annual rates, e.g. AER, APR Possible learning objectives Explore the meaning of interest rates Carry out calculations relating to saving Carry out calculations relating to borrowing GCSE Mathematics Possible learning outcomes Understand the structure for carrying out a compound interest calculation Understand the concept of APR Understand the concept of AER Calculate the AER in a given situation Calculate the APR in a given situation Use the AER to carry out calculations in a given situation Use the APR to carry out calculations in a given situation Use AER to make comparisons between different deals Use APR to make comparisons between different deals Prerequisites Mathematical language Pedagogical notes Interest, simple interest, compound interest Convert between fractions, decimals and percentages All students are expected to ‘carry out calculations relating to enterprise, Per annum saving and borrowing, investing, appreciation and depreciation’. Intermediate Round to a given number of decimal places or significant Loan tier students should understand compound interest, but only higher tier figures Mortgage students are expected to calculate with annual rates such as AER and APR. Find a percentage of an amount using a multiplier Rate, fixed rate, variable rate ‘Annual percentage rate’ (APR) should only refer to borrowing money, as it is Understand the concepts of simple interest and compound Fixed the official rate for borrowing. Its purpose is to provide one percentage rate interest. Term (of a loan) that takes account of any fees and allows consumers to compare deals that Representative example they are being offered. Note two Hwb questions that may be suitable. Both introduce Appreciate, appreciation ‘Annual equivalent rate’ (AER) – sometimes referred to as EAR instead - should compound interest, but do not refer to AER. These are suitable for Depreciate, depreciation only refer to saving money, as it is the official rate for saving. It serves the Intermediate tier. Annual Percentage Rate same purpose as the APR for borrowing, allowing comparisons to be made Hwb: Question 14: Comparing interest. Annual Equivalent Rate between different deals offering interest payable at varying frequencies. Hwb: Question 15: Double your money. The following is an extract from the formula list provided to students: Notation Annual Equivalent Rate (AER) n APR for Annual Percentage Rate AER, as a decimal, is calculated using the formula (1 + ni ) − 1, where i is the AER for Annual Equivalent Rate nominal interest rate per annum as a decimal and n is the number of p.a. for per annum compounding periods per annum. The ‘%’ symbol WJEC: New content guidance includes worked examination questions and annotated candidates’ responses. See this guide on moneysavingexpert.com for further information. Reasoning opportunities and probing questions Possible activities Potential misconceptions Hwb: Question 55: Helping to Buy a Home. Focuses on AER What is the same and what is different: APR and AER? Some students may think that APR and AER serve the same purpose (using a savings account to save for a deposit on a house). Convince me that a savings deal offering 4% p.a. payable four Some students may think that, for example, 292% p.a. (fixed) is referring to the Hwb: Question 66: Too good to be true. This focuses on AER. times a year is better than a deal offering 4% AER same concept as a fixed rate deal when arranging a mortgage Hwb: Question 83: Quarterly or monthly? A question on AER that Always / Sometimes / Never: An AER is greater than the Some students may think that an interest rate of 6% p.a. payable 4 times a year explores the impact on savings when the interest rate is applied advertised interest rate. is the same as an AER of 6% (The AER is actually (1.015)4 – 1 = 6.136% to over different periods. three decimal places) Haydn is offered a loan with an interest rate of 8% p.a. There Hwb: Task 12: ‘The Arts in Wales’. Focuses on APR, including are no fees for the loan, and the APR is advertised as 8.24%. Some students may not convert a given AER percentage rate into a decimal loans of 0% from the Arts Council of Wales, to bank loans and 𝑖 𝑛 How many times a year must he make repayments? before substituting into the compound interest structure of (1 + 𝑛) − 1, or using a credit card. they may omit to convert this decimal back into a percentage at the end of a Hwb: Task 30: Borrowing Money - APR. Note that this could be multi-step problem used as an introduction to the concept of APR with higher tier Some students may round incorrectly, or they may round early within a multistudents as it only considers cases that involve a single step problem and present a result based on a compounded error repayment.