Food chains and food webs
advertisement

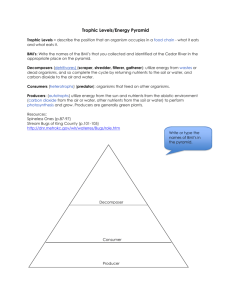
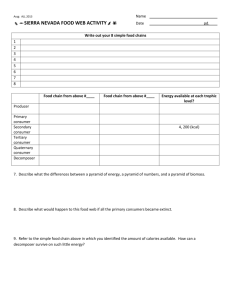
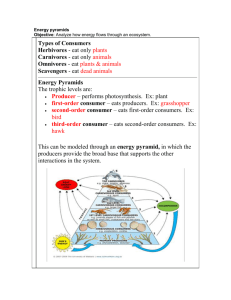
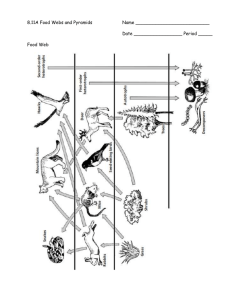
Food Chain/Food Webs • Learning Target • #5, #6, #13 All food chains start with ENERGY from the sun Feeding Relationships • A food chain shows a simple feeding relationship. Sun → •Plants are producers. They turn energy from the sun into sugars that animals can use Through Photosynthesis Because plants produce their own food, they are called ‘Producers’ Primary consumers eat plants. They are herbivores. Insects and other animals eat plants for energy. Secondary consumers are animals that eat other animals for energy. They are called carnivores or omnivores Decomposers are organisms that eat dead things for energy. Food Chains are connected to Food Webs • Combined food chains make food webs. • Food webs start with the sun • Food webs contain producers, consumers, and decomposers. • Are you part of food webs? Feeding Relationships • A food chain shows a simple feeding relationship. Sun → grass → Feeding Relationships • A food chain shows a simple feeding relationship. Sun → grass → rabbit → Feeding Relationships • A food chain shows a simple feeding relationship. Sun → grass → rabbit → fox The energy is then passed on to animals when they eat the plant. Animals of all shapes… …and sizes! Because these animals are the first to take the food energy from the plants, They are called primary consumers Some of these primary consumers have predators. Other animals that feed on them Aphids are eaten by…. Ladybugs Animals that eat primary consumers are called secondary consumers • So far this is a straightforward food chain • Sun → leaf aphid → ladybug But in reality it is more complicated than that This bird eats ladybugs and aphids This bird eats smaller birds, mice, and rabbits Mice and rabbits have other predators What will eat the frog? What do you think the frog eats? Sometimes it’s not entirely clear who eats who! We can show what goes on with the help of a Food Web What would happen if a disease killed off many of the hawks? There will be nothing to eat the snakes, so their numbers will increase. Many of the frogs get eaten No frogs. More crickets Most of the cattail gets eaten by the crickets Now the crickets don’t have enough food so their numbers go down ..and so on. Numbers of each species have an effect on the numbers of the other species in the web. • Use the food web worksheet to predict what might happen in the following situations: • A) There is very little rain and much of the Marsh Grass and Cattail die off. • B) Humans nearby bring cats into the area. • C) The frogs eats some poisoned slugs from a garden Transfer of Energy • When a zebra eats the grass, it does not obtain all of the energy the grass has (much of it is not eaten) • When a lion eats a zebra, it does not get all of the energy from the zebra (much of it is lost as heat) • No organism EVER receives all of the energy from the organism they just ate • Only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next – this is called the 10% law • Key Points to Remember… • Energy moves from one organisms to another when it is eaten • Each step in this transfer of energy is known as a trophic level – The main trophic levels are producers, consumers, and decomposers DDT affect on Food Webs http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2001_gbio/folder_structure/ec/m3/s4/ecm3s4_2.htm DDT: Used in the 40’s and 50’s as a pesticide . Outlawed in 70’s: collects in fats of organisms and cannot be broken down. Marine microorganisms greatly affected collected in plankton and green algae slows photosynthesis – not death Mostly noted in birds eggs thinning of eggshells Brown Pelican: 1970-550 nests only 1 chick survived Food Web Biomass • The total mass of the organic matter at each trophic level is called biomass • Biomass is just another term for potential energy – energy that is to be eaten and used. • The transfer of energy from one level to another is very inefficient (10% Law) Biomass Ecological Pyramid • An ecological pyramid shows the relationship between consumers and producers at different trophic levels in an ecosystem • Shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained at each trophic level • The Pyramid shows which level has the most energy and the highest number of organisms Ecological Pyramid Ecological Pyramid Ecological Pyramid • Which level has the most energy? • Which level has the most organisms? • Which level has the least organisms? • Which level has the least energy? This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.