energy level
advertisement

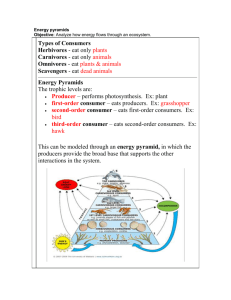
Trophic Levels, Energy transfer and Pyramids Trophic Levels – is the position an organism occupies in a food chain. It refers to food or feeding. Food Chain Food Chains The energy flow from one trophic level to the other is know as a food chain Producers are at the first ENERGY LEVEL Primary Consumers are the SECOND ENERGY LEVEL Secondary consumers are at the THIRD ENERGY LEVEL Trophic Levels (feeding levels) 3 2 1 Food Web Food webs are multiple food chains. Food Webs Food webs show ALTERNATIVE PATHWAYS other possible pathways through which an organism can obtain energy Food webs Energy Level Grass Mouse Grasshopper Frog Owl Hawk 1st 2nd Producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer? producer Primary consumer Energy Level Producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer Producer Grass 1st Mouse 2nd Primary consumer Grasshopper 2nd Primary consumer Frog 3rd Secondary consumer Owl 3rd and 4th Hawk 3rd Secondary and tertiary consumer Secondary consumer Transfer of Energy Energy lost from chain “link” to “link” is significant! from grass to sheep, loss is about 90%! HEAT 90% HEAT 90% 100% Energy Available 10% Original Energy! 1% Original Energy! Energy lost from one trophic level (energy level) to the next level can be represented by a pyramid 4⁰ CONSUMERS 3 CONSUMERS 2 CONSUMERS 1 CONSUMERS PRODUCERS Each level above only gets 10% of the energy from below Ex: 10,000 J of producers (plants) only give 10% of energy to primary consumers 1,000 J to primary consumers (snails, minnows, dragonflies) 100 J to secondary consumers (small fish) 10 J to tertiary consumers (big fish) 1 J to quaternary consumers (fish hawk) ENERGY PYRAMID 1J 10 J 100 J 1,000 J 10,000 J Usually no more than 5 trophic levels since 6th level would have very little energy to keep it alive Ecological Pyramid • • • • Which Which Which Which level level level level has has has has the the the the most energy? most organisms? least organisms? least energy?