Accounting Equation
advertisement

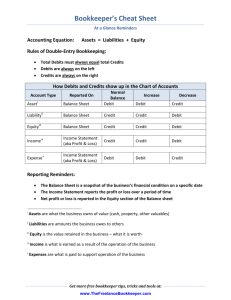
ACCOUNTING CHAPTER 2 USING “T” ACCOUNTS Mr. Khatcheressian 09/17/2013 WELCOME!!!! In Chapter One, transactions that affect owner’s equity on the accounting equation were analyzed. In today’s lesson, the relationship of a “T” account to the accounting equation will be shown. Preview the accounting terms and definitions introduced in this lesson: T account, debit, credit and normal balance. OBJECTIVES Students will define accounting terms related to analyzing transactions into debit and credit parts Identify accounting practices related to analyzing transactions into debit and credit parts. Bank Debits (dr) Credits (cr) AGENDA Objectives Direct Instruction Chapter 2 Aplia Practice Complete Web-Site Assignments Closure ACCOUNTING EQUATION AND T ACCOUNT Accounting Equation: an equation showing the relationship among assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity T ACCOUNT The process of using debits and credits creates a ledger format that resembles the letter "T". The term "T-account" is accounting jargon for a "ledger account" and is often used when discussing bookkeeping. The left side (column) of the "T" for Debit transactions and the right side (column) of the "T" for Credit transactions. T ACCOUNT The T account is the foundation of transaction analysis Debits and Credit will now be introduced Debits and Credits are neither Good or Bad. Debit means left and credit means right Bank Debits (dr) Credits (cr) MORE ON T ACCOUNTS The equations again must always have equal amounts on each side. Accounts on the left side of the equation have a left side normal balance and accounts on the right have a right side normal balance. Bank Debits (dr) Credits (cr) NORMAL BALANCE The side of the account that is increased. EXAMPLE Account balances increase on the normal balance side of an account Account balances decrease on the side opposite the normal balance side of an account. INCREASES AND DECREASES IN ACCOUNTS 11 http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=DfX_mbbBsYo LES SON 2-1 CLOSURE Account balances increase on the normal balance side of the account. Account balances decrease on the side opposite the normal balance side of the account. QUICK REVIEW Draw the accounting equation on a T account What are the two accounting rules that regulate increases and decreases of account balances. Assets=Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Account balances increase on the normal balance side of an account/Account Balances decrease on the side opposite the normal balance side of an account. LESSON 2-2 Analyzing How Transactions Affect Accounts RECEIVED CASH FROM OWNER AS AN INVESTMENT page 32 August 1. Received cash from owner as an investment, $5,000.00. 15 2 1 2 1 4 4 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? 3 LES SON 2-2 PAID CASH FOR SUPPLIES page 33 August 3. Paid cash for supplies, $275.00. 16 1 2 1 4 4 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? 3 LES SON 2-2 PAID CASH FOR INSURANCE page 34 August 4. Paid cash for insurance, $1,200.00. 17 1 2 1 4 4 3 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? LES SON 2-2 BOUGHT SUPPLIES ON ACCOUNT page 35 August 7. Bought supplies on account from Supply Depot, $500.00. 18 2 1 2 1 4 4 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? 3 PAID CASH ON ACCOUNT page 36 August 11. Paid cash on account to Supply Depot, $300.00. 19 2 1 1 4 4 3 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? 2 LES SON 2-2 APLIA CHAPTER TWO Work Together 2-1 On Your Own 2-1 Application Problem 2-1 Application Problem 2-2 21 TERM REVIEW page 37 chart of accounts LESSON 2-2 LESSON 2-3 Analyzing How Transactions Affect Owner’s Equity Accounts RECEIVED CASH FROM SALES page 38 August 12. Received cash from sales, $295.00. 23 2 1 2 1 4 4 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? 3 LES SON 2-3 SOLD SERVICES ON ACCOUNT page 39 August 12. Sold services on account to Oakdale School, $350.00. 24 2 1 2 1 4 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? 4 3 LES SON 2-3 PAID CASH FOR AN EXPENSE page 40 August 12. Paid cash for rent, $300.00. 25 1 2 3 2 4 3 1 4 1. Which accounts are affected? 3 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? LES SON 2-3 RECEIVED CASH ON ACCOUNT page 41 August 18. Received cash on account from Oakdale School, $200.00. 26 2 1 4 1 4 3 1. Which accounts are affected? 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? 3 LES SON 2-3 PAID CASH TO OWNER FOR PERSONAL USE page 42 August 12. Paid cash to owner for personal use, $125.00. 27 2 1 3 4 3 1 2 4 1. Which accounts are affected? 3 2. How is each account classified? 3. How is each classification changed? 4. How is each amount entered in the accounts? LES SON 2-3