Howard Module 1 - The Study of Economics MAIN IDEA(s) Identify

Howard
Module 1 - The Study of Economics
MAIN IDEA(s)
Identify clear main ideas or purposes
1. Why is scarcity important in economics?
2. What is opportunity cost?
3. What is the difference between positive and normative economics?
4. What is studied in microeconomics?
5. What is studied in macroeconomics?
SUPPORTING DETAILS
Locate and interpret details. Understand the function of a part of a passage.
6. Individual Choice: The Core of Economics
A. Resources are Scarce
B. Opportunity Cost: The Real Cost of Something is What You Must Give Up to Get It
7. Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics
8. Positive vs. Normative Economics
9. When and Why Economists Disagree
SEQUENTIAL, COMPARATIVE, & CAUSE-EFFECT RELATIONSHIPS
Order sequences of events. Understand the subtleties in relationships between people, ideas, and concepts. Understand implied, subtle, or complex cause-effect relationships.
10. What could happen to the price of a scarce resource?
11. Why do so many people choose to give up earning more money at age 18 and head to college?
MEANING OF WORDS
Determine the appropriate meaning of context-dependent words, phrases, or statements.
12. Individual Choice
13. Economy
14. Economics
15. Market Economy
16. Resources
A. Land
B. Labor
C. Capital
D. Entrepreneurship
17. Scarce
18. Opportunity Cost
19. Microeconomics
20. Macroeconomics
21. Economic Aggregates
22. Positive Economics
23. Command Economy
24. Incentives
25. Property Rights
26. Marginal Analysis
GENERALIZATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS
Draw generalizations and conclusions about people, ideas, and variables.
27. How does understanding marginal analysis impact choices that people make?
28. How do markets impact the allocation of resources?
29. Why do economists have different views on the economy?
Howard
Module 3 - The Production Possibilities Curve Model
MAIN IDEA(s)
Identify clear main ideas or purposes
1. Why are trade-offs important in economic analysis?
2. How does a production possibilities curve explain efficiency, opportunity cost, and economic growth?
3. How do the factors of production & technology SHIFT the PPC outward creating long term economic growth ?
SUPPORTING DETAILS
Locate and interpret details. Understand the function of a part of a passage.
Trade-Offs: The PPC
4. Describe how the concept of scarcity from Mod 1 is related to the idea of trade-offs.
Efficiency:
5. Explain how an economy is efficient or inefficient.
6. Explain what the word “allocation” means and what efficient allocation is.
Opportunity Cost:
7. Describe the how opportunity cost is displayed on the PPC.
8. Explain the difference between constant opportunity cost and increasing opportunity cost.
Economic Growth:
9. Explain economic growth (a sustained rise in aggregate [total] output and why it is important to society.
SEQUENTIAL, COMPARATIVE, & CAUSE-EFFECT RELATIONSHIPS
Order sequences of events. Understand the subtleties in relationships between people, ideas, and concepts. Understand implied, subtle, or complex cause-effect relationships.
10. A graph that shows the trade-offs between the production of two goods is called a
(a)__________ curve. A production point is feasible if it lies (b) _____________ or
(c) ____________ this curve, but not feasible if it lies (d) ____________ this curve.
If a production point lies on this curve, there are no missed opportunities and production is (e) ____________.
11. If the PPC moves outward over time, the economy has been experiencing (f)
____________. This can be caused by advance in (g) ____________ or an increase in the economy’s (h)____________.
12. Because the PPC has a negative slope, producing more of one good means less of the other good can be produced. Therefore, a movement from point on the PPC to another point on the PPC illustrates the concept of (i) ____________.
MEANING OF WORDS
Determine the appropriate meaning of context-dependent words, phrases, or statements.
13. Trade-off
14. Production Possibilities Curve
15. Efficient
16. Factors of Production
17. Technology
GENERALIZATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS
Draw generalizations and conclusions about people, ideas, and variables.
18. The PPC is...
19. Efficiency to me means....
20. Opportunity cost in my personal life would be...
21. Economic growth can impact my family by...
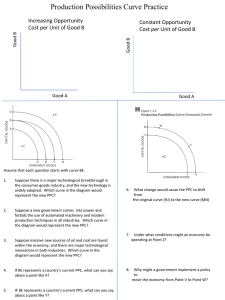
Practice:
Draw a PPC showing each of the following.
-A labeled X & Y Axis
-A negatively sloped curve showing increasing opportunity cost
-Label a point labeled A is an inefficient allocation of goods
-Label a point labeled B as an efficient point
-Label a point labeled C as unattainable at present
-Create a new curve showing economic growth with arrows showing clearly the shift.
Howard
Module 4 - Comparative Advantage & Trade
MAIN IDEA(s)
Identify clear main ideas or purposes
1. Explain how specialization and trade lead to gains for an individual or economy.
2. Describe the difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage, and how to determine each using tables of data or PPC models for two countries.
3. Explain how comparative advantage leads to increased gains from trade.
SUPPORTING DETAILS
Locate and interpret details. Understand the function of a part of a passage.
Gains from Trade
4. Why is it important that people specialize in a skill and then trade for the other items they may want or need?
5. Why are markets important for the concept of specialization and trade?
Comparative Advantage
6. Explain how comparative advantage and specialization are related.
7. Examine Figure 4.1 in the text. Explain why Tom should specialize in the production of fish and Hank should specialize in the production of coconuts.
8. Examine Figure 4.2 in the text. Explain the gains from trade for BOTH Tom and Hank.
How is specialization related to a “major” in college?
9. Germany, the United States, and Japan have an ablsolute advantage in most types of production. Should they trade with any other nations? Why?
Comparative Advantage and International Trade
10. Examine Figure 4.3 in the text. Explain how specialization, trade, and comparative advantage positively impact international trade.
SEQUENTIAL, COMPARATIVE, & CAUSE-EFFECT RELATIONSHIPS
Order sequences of events. Understand the subtleties in relationships between people, ideas, and concepts. Understand implied, subtle, or complex cause-effect relationships.
11. When people divide tasks among themselves and each person provides a good or service that other people want in return for different goods and services that he or she wants, it is called (a) ________________. This is a key to a much higher standard of living for everyone because it allows for a division of tasks, called
(b) ________________.
12. If the opportunity cost of production is lower for one person (or country) than it is for other people (or countries), then that person has a (n) (c) ________________ advantage. If an individual (or country) can produce more output with a given amount of input than another person (or country), then that person (or country) has a(n)
(d) ________________ advantage. (e) ________________ advantage is the basis for mutual gains from trade.
MEANING OF WORDS
Determine the appropriate meaning of context-dependent words, phrases, or statements.
13. Trade
14. Gains from Trade
15. Specialization
16. Comparative Advantage
17. Absolute Advantage
GENERALIZATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS
Draw generalizations and conclusions about people, ideas, and variables.
18. People gain from specialization and trade because...
19. Comparative advantage is an important economic concept because...
20. International trade is efficient and advantageous to society because...
REVIEW:
Go to: http://ebooks.bfwpub.com/krugman_ap_econ.php