SKIN STRUCTURE
advertisement

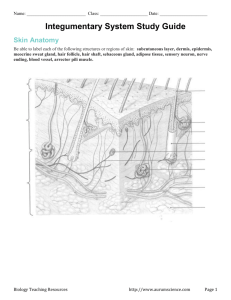
SKIN STRUCTURE Skin is a living, largest organ of the body. It weight around 3kg. 6.6 pounds. It thickness varies from about 1.5-4 mm. Thickest on the back, thinnest on the eye lids. Skin is the largest organ of the immune system (uklad odpornosciowy). Skin consists of 3 layers: 1. EPIDERMIS (NASKOREK) 2. DERMIS (SKORA WLASCIWA) 3. SUBCUTANEOUS LAYER (TKANKA PODSKORNA) The EPIDERMIS (outer skin) consists of 5 layers: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. STRATUM STRATUM STRATUM STRATUM STRATUM CORNEUM LUCIDUM GRANULOSUM SPINOSUM GERMINITIVUM (basal layer) (warstwa rogowata) (warstwa przezroczysta) (warstwa granulowata) (warstwa kolczasta) (warstwa podstawowa—zawiera melanin) EPIDERMIS has no blood supply and virtually no nerve endings. EPIDERMIS 1. STRATUM CORNEUM Is the outer layer. Composed of flat, scale like cells which are constantly being shed and replaced from beneath. The cells contain fatty materials forming a tough, waterproof coat which prevents the skin from cracking and stop bacteria invading. The cells are dead (keratinised- already changed from leaving cells into dead flat cells). Cells are flat, hard, dry and non- leaving. There is no nucleus. Cells are renewed daily. The corneum layer is completely renewed about every 15 days. This process is called proliferation. This layer varies in depth from 10-15 cells. Thinnest -on the eye lids and thickest- on the soles. 2. STRATUM LUCIDUM – transparent layer (e.g palms of the hands, soles of the feet ) It’s a few cells deep and is controlling the transmission of water through the skin. The cells have no nucleus. They are dead. 3. STRATUM GRANULOSUM (warstwa granulowana) In this layer the cells begin to keratinise- changed from leaving cells into dead flat cells. This layer contains cells with granules which are visible in healing tissue after trauma. 4. STRATUM SPINOSUM (warstwa kolczasta) Cells are living. Cells are egg shaped. Small hairs/spines are attached to the cells which disappear when the cells move upwards. This layer is connected with the germinativum layer which is where mitotic activity takes place. 5. STRATUM GERMINITIVUM (basal layer) Deepest layer of epidermis. Cells are made here, and they are living. Its takes about 28-30 days for the cells to move up to the first layer-to stratum corneum. Pigment called MELANIN which determinates colour of the skin and protects from UV rays is produced in this layer- in stratum GERMINITIVUM. The cells that produce MELANIN are called MELANOCYTES. DERMIS (active) The dermis is skin supportive tissue. It is composed of connective tissue (tkanka laczna) containing cells and collagen and ellastin fibres responsible for skin elasticity and firmness. The dermis contains a number of structures which have grown down into it from the epidermis. These are: Hair follicles (mieszki wlosowe) Sebaceous glands (gruczoly lojowe) Sweat glands (gruczoly potowe) Blood vessels (naczynia krwionosne) Nerves Muscles HAIR FOLLICLES Downwards growth of epidermis cells into the dermis. At the base of the hair follicle is the cluster of the cells called the bulb from which the hair grows. Hair is formed by multiplication of cells from the bulb and as they are pushed up and away from the nutrience, the cells die and turn into keratin (hard protein). Within the follicle there is a muscle called ARRECTOR PILI. If one feels cold the muscle receives a massage from the brain to contract, which pulls the hair upright and causes the skin to dimple.( goose pimples). SEBACEOUS GLANDS (gruczoly lojowe) Present all over body except: palms of the hands and soles of the feet Found on scalp, forehead, nose, chin, armpits, and groin area Most sebaceous glands open inside the hair follicle via a duct Sebaceous gland secrets SEBUM SEBUM prevents skin and hair from becoming dry SEBUM provides a waterproof coat on the skin SWEAT GLANDS (gruczoly potowe) 2-3 million sweat gland in the body They regulate body’s temperature Cool the body down through evaporation of sweat We have 2 types of sweat glands: APOCRINE and ECCRINE APPOCRINE (odoriferous) sweat glands Develops in puberty Produces milky fluid containing fats, sugars and pheromones Found in: armpits, pubic area Brake down of appocrine sweat glands produces an unpleasant smell. ECCRINE GLANDS (sudoriferous ) sweat gland Are all over body Very large numbers of pores occurs on palms of hands and soles of the feet Sweat secreted in eccrine glands is composed of 99% of water, 1% milk plus other materials SUBCUTENEOUS LAYER (adipose tissue, fat layer) This layer provides the plump look of youth and health Adipose tissue reduces heat loss through the skin Subcutaneous layer has got network of blood vessels, nerve endings and fat cells BLOOD SUPPLY- a system of blood vessels and small capillaries. LYMPHATIC CAPILLARY SYSTEM- work in conjunction with blood supply. FUNCTION OF THE SKIN S—SENSORY ORGAN Skin contains various nerve endings for heat, cold, touch, pain pressure H—HEAT REGULATION Body temperature is maintained at 36.8C. A fine balance is maintained between heat loss and heat production. Heat is lost by allowing more blood to come to the surface, controlled by vasodilatation-vessels expands, and by reliving sweat onto the surface of the skin which evaporates, cooling the body. Heat is produced by restricting blood flow to the surface controlled by vasoconstriction-vessels contract. A—ABSORPTION (wchlanianie) Skin is capable of absorbing small amount of oily substances and some water soluble substances through the opening of the hair follicles and sebaceous gland. Natural oils are absorbed into first layer of epidermis-stratum corneum like: almond oil, sunflower oil, jojoba, vitamin E and aromatherapy oils are the best. P—PROTECTION Stratum corneum- protects against injury Subcutaneous layer and the fat cells – protects from knocks Acid mantle ph- protects against invasion of bacteria Melanin formed in the melanocytes –protects against the harmful effects of sunlight E—EXCRETION (removal of waste products) Sweat glands excrete (wydala) sweat, which contains 99% of water and 1% waste products (salt, urea) S—SECRETION (wydzielanie loju) Sebaceous glands secrete (wydziela) sebum –which helps to keep the skin and hair soft and protect the skin from harmful bacteria. Formation of vitamin D. Ultra violet radiation from the sun changes a chemical in the skin calledDEHYDROCHOLESTEROL into VITAMIN D –which passes into the blood and is important for the healthy growth of bones and teeth. Production of melanin. MELANIN is produced in 5th layer of Epidermis- stratum germinitivum (basal layer) by cells called melanocytes Pigment –MELANIN protects the skin from UV rays