Integumentary System
advertisement

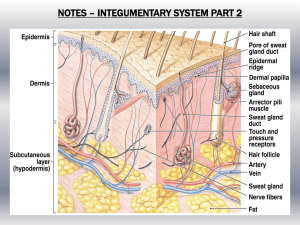
Integumentary System Your skin is the human body’s largest organ. It is the first line of defense against pathogens disease-causing agents such as bacteria, viruses and fungi. Your skin helps regulate your body temperature, removes waste products through your sweat glands, and provides protection from UV radiation. The skin has 3 main layers. 1. Epidermis – This is the outermost layer of skin. The epidermis contains 5 layers. The top or uppermost layer is called the stratum corneum which means “horny layer”. It is a flattened layer of dead cells that are typically sloughed off every few days. This allows for a new layer of skin cells to emerge from beneath the stratum corneum. The epidermis contains no blood vessels which is why you don’t bleed when you get a paper cut. 2. Dermis – The dermis lies beneath the epidermis. The dermis contains 2 layers. It contains blood vessels, sweat glands, sensory receptors, nerves, smooth muscle and hair follicles. 3. Hypodermis – The hypodermis is a fatty layer located beneath the dermis. It acts as a foundation or support for the layers above it. Along with fat, it contains blood vessels and nerve fibers. Fat is also called “adipose tissue”. ~Why do we need to have fat on our body? 1. protection (of internal organs) 2. insulation (from temperatures) 3. stored energy Keratin – This is a tough, fibrous protein. Hair, skin and nails are composed of keratin. Hair and nails contain no nerves, which is why cutting them isn’t painful! Gross Fact: Your skin weighs 8 pounds! During your entire lifetime, you will shed approximately 40 pounds of skin. So keep vacuuming all the places your spend the most time in such as your house and car. And don’t forget to change the sheets on your bed! Sweat glands remove water and salts through pores in your skin. This ensures that your body can excrete toxins and cool you off at the same time. The average human has over 2.6 million sweat glands, and approximately 650 sweat glands in 1 square inch of skin. What causes sweat to have an odor? Bacteria on your skin mixes with your sweat causing an odor. Sebaceous glands surround a hair follicle. They provide the skin with much-needed oil to naturally keep the skin moisturized and supple. However, anywhere there is a sebaceous gland, there is also the potential for acne. Arrector pili muscles are connected to hair follicles. When this muscle is engaged, it causes the hair shaft to stand on end, causing “goose bumps.” Stratum corneum Hair shaft Sebaceous gland dermis epidermis Arrector pili muscle Hair follicle Nerve fibers Sweat gland Blood vessels hypodermis