Towards Civilization
advertisement

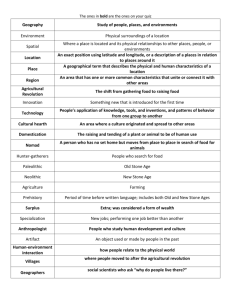
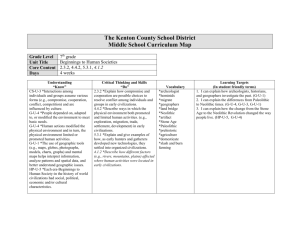
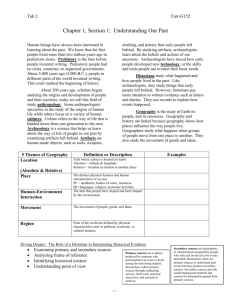
Towards Civilization Prehistoric-3000B.C. Stone Age period Unit I Creation vs Evolution Big Bang Theory Paleolithic Man 2million BC-10,000BC Survival depended on people meeting basic needs food, water and shelter Majority were nomadic following game animals and seasonal fruit and plants Except for necessary organization (no judges, doctors, etc) Paleolithic –Man begins to learn tool technology; sharpened 2mil BC sticks, grinding stones, stone scrapers and points -tools made of stone, wood or bone -Ice Ages caused use of animal hides for warmth and protection from cold 10,000BC -Man continues to evolve as toolmaker Page 2 Paleolithic cont. 30000BC people begin to show interest in spiritual matters -Early beliefs, animism: belief spirits and forces reside in animals, objects or dreams -Carving of stone figurines particularly female; “mother earth” deity provider of life and renewal 11000BC -2 events mark change - Beginning of belief in life after death-burials with preparation for afterlife -About the same time man begins to domesticate crops Ice Ages created stable climate and allowed people to see seasonal changes and winter plant cycles(death/renewal) 10000BC Neolithic Stone Age Beginning of the Agricultural Revolution Many nomadic groups developed farming techniques so were able to begin settling in villages Instead of worrying about game shortage they did have crops to help Man also realized he could control some of the more docile animals. Decreased the risk of hunting Also settlements decreased risk of travel particularly on young and old. Time to improve tools, clothing, shelters and other aspects of life People also traded with other villages. People grouped together for various needs People accumulated possessions so difference in wealth levels begin to appear Advanced settlements **writing Spoken lan. Record keeping Specialized workers Characteristics of civilization Advanced technology Complex institutions Government Religion economy Beginning of Civilizations First major civilizations were river based Tigris/Euphrates Nile River Indus River Huang He (Yellow River) In the Americas civilizations developed in high plains of Mexico and South America Aztecs, Inca, Maya North America Anasazi, Pueblo cultures, Mound builders Eight basic features of early civilizations •Primary feature of early civilizations was the growth of cities •Organized government • someone to coordinate large scale activities-I.e. farming, religious • enforce rules and make laws to promote group survival • earliest leaders were religious • later leaders were warrior kings who created family dynasties based on divine ordination •Complex religion • polytheistic worship specialized Gods and Goddess for specific functions and concerns • lead people in appropriate religious ceremonies, rituals and sacrifices if needed •Social class • people begin to be ranked usually based on their jobs. Also power and religious duties •Job specialization • each person begins to specialize in work activities, artisan class; toolmakers, hide workers, carvers, metal workers • bricklayers, soldiers, merchants, farmers •Arts and Architecture • belief system guided people in these areas • buildings designed to reassure people of power of their political and religious leaders • statuary, palace, wall carvings and paintings, jewelry and other adornments show high degree of sophisticated workmanship •Public works-gov. created • irrigation systems, roads, bridges and defensive walls • coordinate military offenses or defenses as needed ***Writing •True stepping stone from chaos to modern development •Confined to upper classes •Used to create legal and business transactions •Helped societies establish written history to replace oral records •Scribes trained sole function was to create written records •Able to evaluate past cultures by written documents Test Unit 1 Picture A-Paleolithic Picture B- ancient Egypt Man’s Record We Have Uncovered