The Atmosphere
advertisement

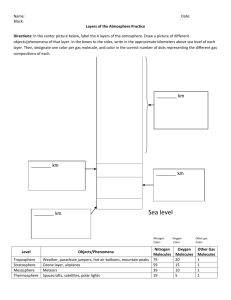
Today’s agenda 1.Peer Tutoring a. Post assessment – Pressure, Air Pressure, Altitude, Density, Atmosphere, Weather) . B. Pre assessment – Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Ionosphere, Exosphere) 2. Notes taking from PowerPoint (Layers of the Atmosphere) http://www.timeanddate.com/eclipse/lunar/2014-october-8 Q1. Why do we see the red color of the moon during Lunar Eclipse? A. All the light from the sun is blocked by the earth. The earth has an atmosphere. The light when escapes from Earth’s atmosphere bends and orange/red light bends the most. The Atmosphere Q2. What are the properties of air? Ans. 1. Air has mass. 2. Air occupies space, or has volume. 3. Air has density. 4. Air exerts pressure. Composition of the Atmosphere • Nitrogen makes up 80% of our atmosphere • Oxygen makes up 21% • Argon makes up almost 1% • All other gases have only trace amounts Atmospheric Pressure – The atmosphere exerts pressure on the Earth that decreases with increasing altitude • This is due to the fact that with increasing altitude, there is a decrease in the column of gases above the Earth’s surface • At greater altitudes, the same volume contains fewer molecules of the gases that make up the air. This means that the density of air decreases with increasing altitude. Trace elements/compounds • Carbon dioxide: plants use to produce food. Plants take in CO2 and give off oxygen as a waste product. • Animals take in oxygen to make energy and give off CO2 as a waste product. • Fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) give off CO2 when they are burned. Rising CO2 levels can cause global warming. Water Vapor • Water Vapor is water in the form of a gas. • It is invisible, not the same thing as steam. Steam is water vapor condensing back into a liquid. • The amount of water vapor in the air varies, from 0% in an arid environment, to 5% in tropical rain forests. Ozone • Ozone is a molecule of oxygen with 3 oxygen atoms instead of 2. • Often formed when lightning interacts with oxygen in the air. • Forms a layer in the atmosphere that absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Without this layer life might not be possible on the surface of the planet. What is the atmosphere? • The layer of gases that surrounds our planet. • Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a certain place and time. • Our atmosphere makes life possible on our planet. • Provides us with oxygen. • Keeps surface warm so water can exist as a liquid. • Protects the surface from dangerous radiation from the sun. Layers of Atmosphere video • http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/ jams/science/weather-and-climate/earthsatmosphere.htm Why is the atmosphere divided into four layers? Temperature variations in the four layers are due to the way solar energy is absorbed as it moves downward through the atmosphere. The boundaries between each layer are known as the pauses. The tropopause, stratopause, and mesopause mark the increase or decrease in temperature. Troposphere • Troposphere – “ Tropo” means changing or turning • As altitude increases, temperature decreases. • -60 degrees Celsius at the boundary of Troposphere. Stratosphere • “Strato” means layer or spread out • Has ozone ( three atom oxygen ) layer – protects the earth from harmful UV radiation coming from the sun • As altitude increases the temperature increases Mesosphere • “Meso” means middle • Meteor showers happens in this layer • As altitude increases the temperature decreases to – 90 degrees Celsius Thermosphere • “Thermo” means heat • Outermost layer which blends with outer space • Very hot temperatures (1800 degrees Celsius ) Two layers of Thermosphere • Lower layer – Ionosphere • Auroras happens here • Upper layer – Exosphere • Satellites are stationed here. • The structure of the atmosphere based on temperature differences. Note that the "pauses" are actually not lines, but are broad regions that merge. Rap • http://www.watchknowlearn.org/Video.asp x?VideoID=26842