Valuation of Leases
advertisement

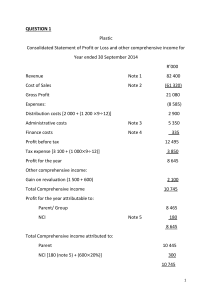
VALUATION A. Valuation steps 1. 2. 3. B. Estimate future cash flows Determine required rate of return (discount rate k) Find present value of cash flows Applications of valuation 1. 2. 3. 2. Bonds and stocks Capital budgeting Leasing Mergers and acquisitions Methods of evaluating projects 1. Net Present Value (NPV) n CF t (where the initial cash flow is usually negative) t t 0 1 k 2. Internal Rate of Return (IRR) n CFt CF0 t t 1 1 IRR 1 TAXES AND LEASES Because of tax laws, we have to worry about whether certain effects are taxable and how much tax they incur. We also have to worry about whether a lease qualifies for the tax benefits (especially if it is leveraged). The differences in tax rates between the lessee and the lessor is typically why it is beneficial for both to enter into a leasing arrangement. One example is depreciation, which is a charge to earnings (a quasi-expense), but not an actual cash flow. With qualified leases, assets can be depreciated faster for tax benefits. Another example is the sale of the asset. Whenever you sell an asset, you pay taxes on any "profit" from the sale. Uncle Sam defines profit as: Profit = Selling Price - Book Value (where Book Value = Installed Cost of Asset Accumulated Depreciation) Ex: If you sell an asset for $10,000, the book value is $6,000, and your tax rate is 40% then: Profit = $10,000-$6,000=$4,000 and your net cash inflow is: $10,000-.40($4,000)=$8,400. 2 A Typical Profile of Lessor’s Cash Flows: Initial outlays or cash flows Intermediate cash flows Terminal cash flows Purchase of assets – the net cash Lease payments net of tax Proceeds from sale of assets net outlay or “net capitalized cost” if effects of tax effects lease is not leveraged Maintenance costs net of The owner’s equity invested in tax savings the purchase of the asset Depreciation tax shields Financing costs net of tax savings on interest 3 COMPUTING THE LEASE PAYMENT TO MAKE NPV=0 1. NPV = 0 when: Net Capitalization Cost C0 + PV(After-Tax Residual Value of Asset) = -PV(intermediate CF) 2. To calculate n equal intermediate monthly after-tax CF payments, use Excel’s pmt function: =pmt(k/12, n, C0 + PV(After-Tax Residual Value of Asset)) 3. After-Tax Monthly CF payment = Depreciation tax shield + Lease payment * (1-T) And therefore the Lease Payment = (After-Tax Monthly CF payment – Depreciation tax shield)/(1-T) 4