uses for subjunctive
advertisement

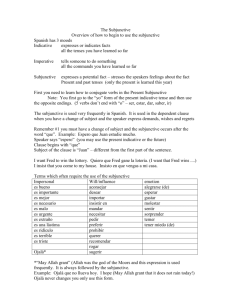
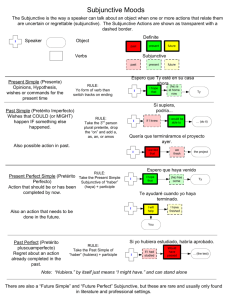
Subjunctive Notes 1. The subjunctive is not a tense; rather, it’s a mood. _________ refers when an action takes place (past, present, future), while __________ merely reflects how the speaker feels about the action. The subjunctive mood is rarely used in English, but it is widely used in Spanish. So far in Spanish, you have studied the verb tenses in the indicative mood. The indicative mood is used to express ___________________, ____________, and ______________. Ex. Ella va a Perú en diciembre. She is going to Peru in December. The above sentence merely reports the fact that you are going to Peru in December, so the indicative mood is used. Let’s change the above example slightly: Ex. Dudo que ella vaya al Perú en diciembre. I doubt that she is going to Peru in December. In the above sentence, the clause “dudo” introduces the quality of uncertainty, the speaker does have a doubt so here the subjunctive mood is used in the second clause (vaya). Subjunctive implies subjectivity. If there exists the possibility that the action about which I am speaking has not or may not take place it is necessary to use the subjunctive. If, however, it is a realized fact that the action has taken or definitely will take place the indicative is used. Consider the following examples: John is going to the store. John went to the store. Indicative Indicative I want John to go to the store. I tell John to go to the store. I hope John goes to the store. I prefer that John go to the store. It is necessary for John to go to the store. It is possible that John will go to the store. Subjunctive Subjunctive Subjunctive Subjunctive Subjunctive Subjunctive 2. How to conjugate: 1. Go to _________ (present tense) 2. Drop the ______ 3. Add the ____________ endings Verbs that end in “ar” *Think about your rules for formal commands. Verbs that end in “er/ir” ____e______emos__ ____a______amos___ ___es_______éis___ e en ___as_______áis____ a an Examples: Hablar Hable Hablemos Hables Habléis Hable Hablen Comer Coma Comamos Comas Comáis Coma Coman Vivir Viva Vivamos Vivas Viváis Viva Vivan 4. Don’t forget the irrefular “yo”s: Hacer, Poner, Salir, Decir, Caer, Traer, Venir, Tener, Ver, Conocer. Hacer- yo hago Haga Hagamos Hagas Hagáis Haga Hagan Traer- yo traigo Traiga Traigamos Traigas Traigáis Traiga Traigan Conocer- yo conozco Conozca Conozcamos Conozcas Conozcáis Conozca Conozcan 5. Super-Irregulars: The following 6 verbs are irregular and need to be memorized. Saber Ser Haber _sepa____sepamos ___sea_____seamos __haya_____hayamos _sepas___sepáis__ sepa sepan ___seas____seáis__ sea sean __hayas____hayáis__ haya hayan Dar Estar Ir __dé_____demos_ __esté ___estemos__ __vaya_____vayamos __des____deis___ dé den __estés____estéis____ esté estén __vayas____vayáis__ vaya vayan ** Hand clap- sepa, sea, haya, dé, esté, vaya 6. –ar and –er stem-changing verbs. For verbs that end in ar or er, if they are stem-changing verbs in the present tense, they are also stem-changing verbs in the subjunctive mood. * Think shoe verbs. They change in all forms except __________ and __________. Remember that in the present tense, you have the following changes: o _____, e ______, and e______. Pensar Volver __piense___pensemos_ __vuelva_____volvamos__ __pienses__penséis___ piense piensen __vuelvas____volváis____ vuelva vuelvan 7. –ir stem changing verbs. For verbs that end in ir, still make the same present tense change to all forms except nosotros and vosotros. Nosotros and vosotros however also have changes. * Think preterit stem changes. o _____ and e ______. Pedir __pida______pidamos_ Sentir __sienta_____sintamos_ Dormir _duerma______durmamos __pidas_____pidáis___ pida pidan __sientas____sintáis___ sienta sientan _duermas_____durmáis__ duerma duerman 8. Orthographic Changes: These are spelling changes that help preserve the rules of sound when pronouncing words. * Think formal commands Verbs that end in car, gar, zar, ger/gir, guir, uir. car- ______ ger/gir- _______ gar- ______ guir- _______ zar- ______ uir_______ Buscar Pagar Empezar busque____busquemos_ pague_______paguemos_ empiece______empecemos_ busques___busquéis___ busque busquen pagues______paguéis___ pague paguen empieces_____empecéis___ empiece empiecen Escoger Seguir Huir escoja____escojamos_ siga________sigamos__ huya_________huyamos__ escojas___escojáis___ escoja escojan sigas_______sigáis___ siga sigan huyas________huyáis____ huya huyan 9. Rules for using the subjunctive: 1. When using the subjunctive there will almost always be __________ Ex. I hope that he calls me. 2. The reason for using the subjunctive will be found in the ________ clause Ex. I hope that he calls me. 3. The subjunctive is used in the ___________ or subordinate clause Ex. I hope that he calls me. 4. The subjunctive is used after the conjunction “______” Ex. I hope that he calls me. 5. There is a subject change between the main clause and the subordinate clause Ex. I hope that he calls me. 6. *If there is no change in subject an infinitive follows the verb in the main clause. Ex. I hope that I play. Espero que jugar. To use the subjunctive you must have: 1. a trigger phrase (see attached sheet) 2. two clauses usually joined by the conjunction “que” 3. A change in subject USES FOR SUBJUNCTIVE ** Remember: U WEIRDO*S U- unknown/nonexistent W- wishing/wanting E- emotions I- impersonal expressions R- recommendations/ advice D- doubt/denial O- opposition *S- subject change 1. Unknown/Nonexistent - when the speaker doesn’t know “what is” or “what is not”. The speaker may be looking for someone or something with certain qualities, without having anyone or anything particular in mind. (the antecedent is unknown) Trigger phrases: No hay nadie que... – No hay nada que... – There isn’t anything that... Buscar Necesitar- to need Ex. No hay nadie que confíe en Marcos. Ex. Yo busco un novio que sea honesto y leal. Ex. Ella necesita un médico que hable español. There isn’t anyone that confides in Mark. I am looking for a boyfriend who is honest and loyal. She needs a doctor who speaks spanish. 2. Wishing/Wanting - when the speaker expresses a desire, hope, or a wish/want Trigger phrases: Querer- to want Preferir Esperar- to hope insistir en- to insist necesitar ojalá- God willing; I strongly hope Ex. Quiero que tú trabajes mañana. Ex. Ellos insisten que nosotros comamos. I want you to work(that you work) tomorrow. They insist that we eat. 3. Emotions -The subjunctive is used in the subordinate clause alter certain expressions of feelings. However, there of course has to be a subject change. Trigger phrases: me gusta que- I like that me molesta queme frustra que- It frustrates me that me sorprende que- It surprises me that Me preocupa queSiento que- I feel that Me irrita que- Ex. Me sorprende que vengan mis amigos a la fiesta. Ex. Me molesta que tú llegues tarde. It surprises me that my friends come to the party. It bothers me when you arrive late. **If the clause states a fact or belief then the indicative is used. Ex. Pienso que mi novia va a romper conmigo. I think that my girlfriend is going to break up with me. **If there is no change in subject then an infinitive is used. Ex. Me molesta llegar tarde. It bothers me when I arrive late. 4. Impersonal expressions - There are many expressions that convey a level of uncertainty that require the use of subjunctive. Trigger phrases: es necesario que- it’s necessary that es posible quees imposible que- it’s impossible that es probable que- it’s probable that es importante que- Es mejor que- it’s better that Es buena idea que- It’s important they bring a jacket. It is necessary that he writes it./ He needs to write it. Ex. Es importante que ellos traigan una chaqueta. Ex. Es necesario que él la escriba. 5. Recommendations/Advice -Use subjunctive to express advice or recommendations you have for someone * recomendar que- to recommend that * aconsejar que* sugerir que- to suggest that Ex. Te recomiendo que tú pruebes el pescado. Ex. Ellos sugieren que estudiemos para la clase de español. I recommend that you try the fish. They suggest we study for Spanish class. 6-7. Doubt/Denial/Opposition - The subjunctive is used in situations of doubt or with certain negative expressions. Trigger phrases: no es verdad que- It’s not true that no es cierto queno creer que- to not believe that no estar de acuerdo (en) que- to not agree that negar quedudar que- to doubt that Ex. Ella no cree que Juan tenga el dinero. Ex. Yo dudo que él sea honesto. She doesn’t believe that John has the money. I doubt that he is honest. ** If phrases express affirmation then the indicative is used. Ex. Ella cree que Juan tiene el dinero. Ex. Yo no dudo que él es honesto. **Trigger phrases for indicative: Es verdad que- It’s true that Creer queEs cierto que- It’s certain that Estar de acuerdo (en) queNo dudar que- to not doubt that She believes that John has the money. I don’t doubt that he is honest.