Homework and Practice An Overview
advertisement

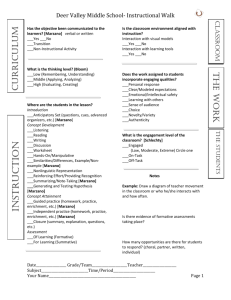
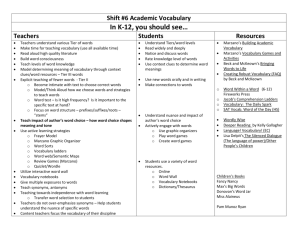
Homework and Practice An Overview Lake Norman High School 9-22-09 Introduction Video • http://teachertube.com/viewVideo.php?vid eo_id=1246&title=Welcome_Back_to_Sch ool Review of Previous Strategies • Marzano’s HYIS • For more information visit Mr. Gentle’s webpage on the LNHS website Learning About Homework & Practice – Fall ‘09 • Session 1 – Build shared knowledge – Reflect on our practice • Sessions 2 & 3 – Classroom application – Integration of resources, technology, & differentiation – Sharing our practice Self-Reflection Prior to Marzano Video Marzano’s Intro to Homework and Practice http://platform.teachscape.com/tsp/web/orgp review/oid/3995/asid/10457 Purpose of Homework and Practice • • • To deepen a student’s understanding To extend learning opportunities beyond the confines of the school day Two purposes 1. Practice 2. Preparation Source: Classroom Instruction that Works: Research-based Strategies for Increasing Student Achievement, Robert Marzano et.al – pp 60-71 Purposeful Homework • Is an appropriate amount • Requires minimal parental involvement • Clearly communicates to students the purpose for the Homework or Practice • Provides feedback to the student Amount of Homework Different levels require different amounts of homework and practice - elementary, middle, high school Cooper’s Study reported the following gains: – 24 percentile points: high school – 12 percentile points: middle school – 6 percentile points: elementary school Marzano et.al reported a 28 overall percentile gain from their meta-analysis study. NOTE: Although the percentile gain at the elementary is a single digit, other studies (Cooper and others) determine that purposeful homework at the elementary level is beneficial. It produces good study habits It fosters positive attitudes toward school Parent Involvement in Homework • Role of parent → minimal • Encourage independent solving of content problems by students • To facilitate homework, parents can: – Reinforce the purpose of homework – Provide a quiet and consistent place – Reinforce and recognize the effort Purpose of Homework Students need to know if the homework assignment is: •for practice •for preparation/elaboration For Practice • Structured around highly familiar content for the student • Reinforcing a familiar skill For Preparation or Elaboration • Preparing students for new content • Having students elaborate on new knowledge Articulate clear guidelines & expectations for the assignment Value, Benefit, Time-frame, Acceptable parent involvement Feedback on Homework Homework with feedback 30% gain Homework without feedback 11% gain • Vary the approach to feedback – – – – – Specific comments from teacher Peer feedback monitored by teacher Written Verbal Rubric • Let students know type of feedback to expect Purposeful Practice • While practicing, students should adapt and shape what they have learned. • Allowing students time to “shape” skills builds their conceptual understanding. • Mastery takes focused practice spread out over time. • Have students practice fewer examples to develop a deep understanding vs. many examples that create a shallow understanding. High School Scenarios High School Scenario #1 Homework Overload Mrs. Devlin feels it is important to give lots of homework in her 9th grade U.S. History class, usually consisting of worksheets related to the book chapters. She feels she has so much content to cover that she cannot afford to take time in class to discuss the homework with students. She spends hours each night grading the worksheets and returns them to students without comment. She assumes it is their responsibility to learn from the textbook on their own, and her lectures cover material that is not covered in the textbook. Several students are failing because they cannot complete the large amount of homework required. High School Scenario #2 Patrick is a very bright 10th grader taking chemistry, biology, and the highest-level math courses his school offers. He learns math quite easily, never does homework, and still makes As on all the tests. Luckily his science teacher, Mr. Richardson, does not count homework in Patrick’s grade. Other teachers believe that Mr. Richardson is wrong not to require Patrick to do the homework. Grading Homework Scenario What does grading homework mean for a student’s grade? Below is a chart where we have two 9th grade students whose teacher grades every homework assignment. Serena is a child who does well in school and has mastered many of her objectives. Unfortunately her homework doesn’t get finished because she has to help her mom take care of her two younger brothers. Her grades in (insert subject) have suffered because her homework isn’t always complete. Sarah is a girl who really struggles in school. She hasn’t mastered many objectives and has difficulty paying attention. When she goes home her mom tries to help her with her homework but gets frustrated with Sarah’s lack of attention. Sarah’s mom ends up telling Sarah most of the homework so she can get it done. Sarah’s final grade is increased because she turns her homework in everyday. Data of 2 students Assessment and Homework Assess #1 Asses s#2 Asses s#3 Asses s#4 HW #1 HW # 2 HW # 3 HW # 4 Final Grade w/HW Final Grade wo/HW Serena 92 93 96 89 0 0 100 0 58.75 92.5 Sarah 72 67 82 74 100 100 100 100 86.88 73.75 Are these grades really representations of how much the students know? Is the homework we assign purposeful? What are some other ways a teacher can keep students accountable for their homework? District HW Policy • ISS Board Policy 3135 Closing Activity Gallery Walk Read the research statements and place a colored dot on your top 3 statements that raise the biggest issue/concern/passion. Research Statements Sources • Classroom Instruction that Works: Researchbased Strategies for Increasing Student Achievement, Robert Marzano et.al • Teachscape – www.teachscape.com • Teacher Tube