Metformin by Dr Sarma
advertisement

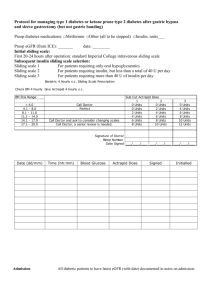
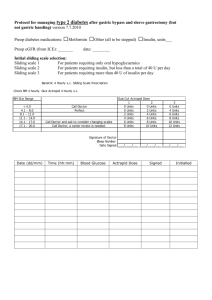
Metformin Revisited A comprehensive review by Dr. R.V. S. N. Sarma, M.D., M.Sc., Dr.Sarma@works Diabetes Mellitus 1. Type 2 DM (NIDDM) 2. Not merely “ SUGAR DISORDER” 3. Multi system disease – A syndrome 4. Metabolic – endocrine – vascular – 5. Cardiac – cerebral – renal – ophthalmic From blood sugar to blood vessel Dr.Sarma@works Prevention of Diabetes • How we have grown ? • Prevention holds the key – no users ? • Diabetic care is Life long – • Nutrition – Excercise – Education - DM • How about NOW – or never ? • 1,49, 806 studied – 1 kg - 9% DM Dr.Sarma@works Should we wait ? and • Pay heavily on • ICUs, transplant units, amputation units • Laser therapy, physio therapy units • Or pay very little now • By preventing the epidemic rise in DM Clinical diabetes – ADA – Apr/June 2001 Dr.Sarma@works Mandatory Examinations 1. H/o Smoking 1. Fasting and PP BG 2. H/o IHD 2. GHb A1c periodically 3. Family H/o DM 3. Microalbuminuria 4. H/o Hypoglycemia 4. Lipid profile 5. Exam for all pulses 5. ACR 6. B.P recording 6. ECG for LVH, IHD 7. Foot exam - Trophic 7. Echo for LV Dysfun. 8. Autonomic neuropathy 8. Stress test – ST Seg. 9. Fundus exam for DR Dr.Sarma@works Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Dr.Sarma@works The questions ? 1. Does the patient have Diabetes Mellitus ? 2. If so, what is the type of DM ? Dr.Sarma@works Does the Patient have Diabetes ? “POLYS” Loss of weight Asymptomatic Symptomatic + Unequivocal Hyperglycaemia on more than one occasion + No unequivocal Hyperglycaemia Diabetes Abnormal GTT Normal Follow up Dr.Sarma@works Diagnosis – O-GTT DM DM 126 200 IGT 140 IFG 110 Normal Normal FPG PPG 75g of oral glucose – 2 hrs. after Dr.Sarma@works Diagnosis – Criteria R B G > 200 mg % on 2 occasions or F B G > 126 mg % on 2 occasions or P P B G > 200 mg % on 2 occasions Never make a diagnosis on single test Never diagnose based on glycosuria Glucometer is not ideal for diagnosis Screening, Diagnosis and Monitoring Dr.Sarma@works Diabetes Mellitus in India 20 40 IDDM Type - 1 DM NIDDM Type - 2 DM ? IRDM Type - 1½ Dr.Sarma@works Hyperglycemia Blood sugar rises above normal if 1. ↓ in insulin secretion (endogenous) 2. ↓ in insulin sensitivity (non-response) 3. ↑ increased hepatic production 4. ↓ decreased peripheral utilization 5. Excessive CHO consumption 6. A combination of any of the above Dr.Sarma@works Hyperglycaemia Acute Chronic / Sustained Stress Hyperglycaemia Diabetes Mellitus Insulin 120 mg % 80 Glucagon GH Cortisol Catacholamines Differentiation: HbA1C / Fructosamine / Follow up Dr.Sarma@works Diagnosis - Practical Points 1. Do not label one a diabetic by glycosuria alone For, one may have renal glycosuria 2. Benedict’s shows any reducing substance. Glucose oxidase test strips confirm glucosuria 3. Do not neglect urine test for acetone 4. Never base Dx on a single blood sugar test 5. O-GTT is the gold standard for diagnosis DM 6. HbA1C - of use in DD of stress hyperglycemia 7. All diabetics need not be symptomatic One may present first time with complications Dr.Sarma@works Diagnosis – New concept Syndrome X Metabolic syndrome Insulin Resistance Syndrome Pre CHD + Pre Diabetic state It is very common in USA - > 24% above 20 years of age. Childhood overweight / obesity PCOD is common association Dr.Sarma@works Metabolic Syndrome NECP ATP III criteria – 3 or more below 1. Abdominal obesity –W.C (cm) > 88 ♀, 102 ♂ 2. ↑ in Triglycerides > 150 mg% 3. ↓ in HDL < 50 mg% for ♀, < 40 mg% for ♂ 4. Blood pressure > 130 / 85 mm Hg 5. IFG = FPG > 110 or IGT = PPBG > 140 mg% WHO criteria (in addition to above) 1. ACR > 30 mg/g 2. Micro-Albuminuria > 20 μgs / min Dr.Sarma@works Dr.Sarma@works Treatment Strategies Dr.Sarma@works Treatment Strategy Defect in insulin sensitivity 1. Exercise - aerobic 2. Weight reduction – Diet, drugs 3. Thiazolidinediones - Glitazones 4. Metformin Defect in insulin secretion 1. βcell stimulation - SU, Repaglinide 2. Insulin exogenous supplimentation Dr.Sarma@works Treatment Strategy Increased hepatic glucose output 1. Metformin > Glitazones 2. Insulin supplimentation, SU Carbohydrate absorption (post-prandial hyperglycemia) 1. Acarbose Often the defects are multiple and hence the need for combination of the above strategies Dr.Sarma@works Dr.Sarma@works Prevention of Complications Dr.Sarma@works How to prevention Complications of Diabetes ? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Weight reduction Exercise Strict control hyperglycemia Improvement of lipid profile Smoking cessation Treatment of Hypertension Low dose aspirin therapy Early detection by evaluation Dr.Sarma@works Metformin Dr.Sarma@works History 1. 2. 3. 4. Biguanides- used in early medieval timesleguminosa Galega officinalis (goat's rue or French lilac) in Europe 1918-guanidine discovered as active glucose-lowering compound 3 biguanides available for medical use between 1957 & 1960- phenformin, metformin, buformin 1970s- phenformin and buformin withdrawn because of lactic acidosis Dr.Sarma@works Metformin Metabolic actions 1. Reduction of excessive Hepatic Glucose Output 2. Stimulation of insulin-mediated muscle glucose uptake -glycogen synthesis is increased 3. Inhibition of lipolysis and of FFA availability Dr.Sarma@works Metformin Cellular actions 1. Increased insulin binding 2. Stimulation of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity 3. Enhanced glucose transport (GLUT 4) 4. Increased glycogen synthase 5. Doesn't cause hypoglycemia Dr.Sarma@works Actions of Metformin Dr.Sarma@works Metformin Additional actions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Favorable lipid effects Weight loss Increased fibrinolytic activity Decreased platelet aggregability Favorable effect on hypertension Dr.Sarma@works Metformin Preferred choice in 1. Obese diabetics 2. Diabetics with hypertension 3. Diabetics with prominent Dyslipidaemia 4. Patients with IGT Dr.Sarma@works Metformin - Pharmacokinetics Bio-avalability (% of dose) 50% to 60% C max (g/ml) 1.0 to 1.5 t max (in hours) 1.9 to 3.0 Plasma ½ life (t ½) 2.0 to 5.4 Renal clearance (ml/min) 400 to 600 Total clearance (ml/min) 1,300 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin - side effects 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nausea, vomiting, distension Loss of appetite, diarrhoea Skin rashes, urticaria Increase in liver enzymes Rare – Lactic acidosis. Dr.Sarma@works Metformin - contraindications 1. Patients with Type I diabetes 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Patients with hepatic or renal impairment Alcoholic liver disease Chronic obstructive airway disease Congestive heart failure, MI Pregnancy and lactation Peripheral vascular disease Any condition associated with hypoxia In patients > 70 yrs of age. Care while using diuretics concomitantly Dr.Sarma@works 1. Metformin mono therapy in DM 2. Metformin in combination with 1. Glyburide 2. Pioglitazone 3. Insulin 3. Metformin in sec. OHA failure 4. Metformin I.G.T 5. Metformin in P.C.O.D 6. Metformin in Metabolic Syndrome 7. Metformin in obesity Dr.Sarma@works Metformin mono therapy Dr.Sarma@works Metformin - Efficacy NIDDM Pts 29 week therapy Significantly lowers FPG Dr.Sarma@works Metformin - Efficacy NIDDM Pts 29 week therapy Significantly lowers HbA1c Dr.Sarma@works Metformin – Efficacy in microvascular complications 1. 1704 obese type 2 diabetics with FPG > 6 mmol/lit after dietary trial 2. Randomised to metformin to maintain FPG <6 vs “conventional” Rx with diet 3. 10 year follow-up 1. 32% reduction in diabetes related endpoint 2. 42% reduction in diabetes related death 3. 36% reduction in all cause mortality UKPDS trial- Lancet 1998; 352: 837-853 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin combined therapy Dr.Sarma@works Metformin with Glyburide Dr.Sarma@works Metformin – Glyburide Objective To evaluate whether initial treatment with glyburide/metformin tablets is superior to monotherapy with each Design Randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, multicentre Patients 806 treatment naïve type 2diabetics Duration 20 weeks Therapy Placebo, glyburide 2.5 mg, metformin 500 mg, glyburide/metformin 1.25 +250/500 mg, once daily. Garber AJ et al. Diabetes Obes Metab 2002 May;4(3):201-8 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin – Glyburide glyburide/ glyburide/ metformin metformin Placebo Glyburide 1.25/250 mg 2.5/250 mg Metformin 0 -0.2 -0.21 * -0.4 -0.6 -0.8 -1.24 ** -1.0 -1.03 *** -1.2 -1.48 -1.4 P<0.001 * -1.6 P=0.016 * P<0.001 * -1.53 * * P<0.001 ** * *P=0.004 P<0.001 Garber AJ et al. Diabetes Obes Metab 2002 May;4(3):201-8 Week 20 *** Dr.Sarma@works Metformin – Glyburide Conclusions Initial combination treatment with glyburide & metformin tablets produces greater improvements in glycaemic control than either glyburide or metformin alone. The superiority of initial therapy with glyburide + metformin tablets may arise from simultaneous treatment of both pathophysiological defects of type 2 diabetes. Dr.Sarma@works Metformin with Pioglitazone Dr.Sarma@works Metformin – Pioglitazone Design Double blind Randomized placebo controlled clinical trial Duration 16 weeks Patients 328 patients with poorly controlled DM - HbAlc > 8.0%, Rx. Metformin 30 days Later Pioglitazone 30mg + Met (n=168) Placebo + Metformin (n=160) Einhorn D et al Clin Ther 2000 Dec; 22(12): 1395-409 or Dr.Sarma@works Results Compared to placebo combination caused Fall in HbAlc (- 0.83%)* Fall in FPG (-7.7mg/dl)* Fall in TG levels (-18.2%) Rise in HDL +8.7% Decrease in FPG levels occurred as early as 4th weeks * p<0.05 Einhorn D et al Clin Ther 2000 Dec; 22(12): 1395-409 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin – Pioglitazone Open label extension of the study Metformin + 30/45 mg Pioglitazone 154 patients 72 weeks Fall in HbAlc: – 1.36% Fall in FPG: – 63.0 mg/dl Excellent tolerability No hepatotoxicity seen Einhorn D et al Clin Ther 2000 Dec; 22(12): 1395-409 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in Sec. OHA failure Dr.Sarma@works Combination in Sec. OHA failure Design Randomised, open and parallel study Number Fifty-one subjects Patients Type 2 diabetes with secondary oral hypoglycaemic agent failure Therapy 1st phase 36 weeks- Combined therapy of sulphonylureas and nocturnal insulin, with or without metformin 2nd phase Metformin was withdrawn. Tong PC et al. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2002 Aug; 57(2):93-8 Dr.Sarma@works Combination in Sec. OHA failure Subjects on metformin - used less insulin to maintain glycaemic control (13.7+/-6.8 vs. 23.0+/-9.4 U/day, P=0.001) - lower HbA1c values (8.13+/-0.89 v/s 9.05+/1.30%, P=0.003) Withdrawal of metformin therapy caused deterioration in HbA1c (P=0.001) Tong PC et al. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2002 Aug; 57(2):93-8 Dr.Sarma@works Conclusion This study confirms that metformin plays an important role in the success of the combination therapy. The rational use of metformin and sulphonylurea together with insulin will help to improve metabolic control in Type 2 diabetes patients who have secondary drug failure. Tong PC et al. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2002 Aug; 57(2):93-8 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in I. G. T. Dr.Sarma@works IGT to Type 2 DM Plasma glucose level at initial O-GTT, Body mass index Family history of DM, Hypertension Raised basal plasma insulin/ proinsulin Lower post-load insulin/glucose ratio Abnormal lipid profile Abnormal serum creatinine Raman PG et al. Asian J Diabetol 2002 June-July; 4(4): 37-42 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in I G T Design Objective Patients Therapy Duration Randomized double blind To evaluate effect of metformin on glucose metabolism & rate of conversion to DM 70 patients with IGT Placebo (n = 37) or metformin (n= 33) 250 mg three times daily 12 months Li CL et al. Diabet Med 1999 Jun;16(6):477-81 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in PCOD Dr.Sarma@works What is PCOD ? 1. 2. 3. 4. Poly Cystic Ovarian Disease Common form of female infertility Poor conception rates Pregnancy loss rates are high (30-50%) during the 1st trimester Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in PCOD Objective Assess pregnancy outcome pts with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Design Case series, Outpatient. Patients Anovulatory patients (n = 48) with a diagnosis of PCOD enrolled over 15 m. Rx. Metformin started at 500 mg b.i.d. for 6 weeks and increased to 500 mg t.i.d. if no ovulation occurred. Clomiphene citrate 50 mg added if no ovulatory response after 6 wks. Heard MJ et al. Fertil Steril 2002 Apr;77(4):669-73 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin - Effective in PCOD 1. 40% patients resumed spontaneous menses with metformin alone 2. 31% required CC (50 mg) in conjunction with metformin therapy 3. 67% of combination therapy had evidence of ovulation 4. Overall 42% conceived with a median time of 3 m for conception Heard MJ et al. Fertil Steril 2002 Apr;77(4):669-73 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in PCODEarly Pregnancy loss 1. Retrospective study 2. Women with PCOD who became pregnant 3. Duration of enrollment- 4.5 yr , OPD setting 4. Sixty-five women received metformin during pregnancy (metformin group) and 31women did not (control group). Jakubowicz DJ et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002 Feb;87(2):524-9 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin prevents early Preg. loss Early Preg. Loss Rate 41.9 % 50 60 40 P < 0.001 P < 0.002 30 20 10 58.3 % 50 40 30 In prior h/o Miscarriage 20 8.8 % 11.1 % 10 0 0 Metformin Placebo Metformin Jakubowicz DJ et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002 Feb;87(2):524-9 Placebo Dr.Sarma@works Conclusion Metformin administration during pregnancy reduces 1st trimester pregnancy losses in women with Polycystic ovary syndrome. Jakubowicz DJ et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002 Feb;87(2):524-9 Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in Insulin resistance Dr.Sarma@works Metabolic syndrome 1. Exercise 2. Weight reduction 3. Diet modification 4. Control of blood pressure 5. IFG or IGT may be treated with Metformin 250 to 500 mg b.i.d Dr.Sarma@works Insulin Sensitizers 1. Exercise 2. Weight reduction 3. Metformin 4. Glitazones Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in Obesity Dr.Sarma@works Metformin in obesity • In childhood over weight and obesity • Its action of interfering with glucose absorption in the intestine • Anorexio-genic action • No effect on normal blood sugar; non hypoglycemic (only anti hyperglycemic) Dr.Sarma@works Metformin XL vs Plain Design Double blind randomized Patients Type 2 DM on Metformin 500 mg BID for 8 weeks with FPG 200 mg/dl and HbA1c 8.5 % Therapy Plain metformin 500mg BID (n=69) Metformin XL* 1000 mg OD (n=72) Duration 24 weeks Physician’s Desk Reference 2002 Pg. 1083 Dr.Sarma@works Advantages of Metfromin SR Convenience ONCE DAILY dosing simplifies treatment regimen Reduces number of tablets to be consumed To be taken conveniently at - DINNER Compliance Adverse effects such as Nausea / Vomiting (due to gastritis) and diarrhea - less likely with SR Preparation Better tolerated than plain metformin Control Comparable to that of plain metformin b.i.d / t.i.d Dr.Sarma@works Metformin SR with evening meal Evening dosing takes advantage of slow GI transit while patients are sleeping This allows tablet to move slower through GI tract than when patients are awake Dr.Sarma@works DIE Dr.Sarma@works WHO recommendation -Diet CARBOHYDRATES : 50-60% - mainly from complex carbohydrates FATS : 30% - saturated 10% - poly-unsaturated 10% - mono-unsaturated 10% - cholesterol < 300 mg/day PROTEINS : 12-20% SODIUM : < 6 g/day - hypertensive diabetic, < 3 g/day Dr.Sarma@works Managing Diabetes Follow a Healthy Meal Plan Eat Least Eat Moderately Sugar, Fat, Alcohol, Salt Protein Foods Eat More Carbohydrate Foods Eat Most Vegetables Dr.Sarma@works EXERCISE Benefits • • • • • Reduces weight Improves cardiovascular function Increases fitness Increases physical working capacity Improves sense of well-being /quality of life Dr.Sarma@works Let us together win the war against Diabetes Dr.Sarma@works Dr.Sarma@works