The Human Body
advertisement

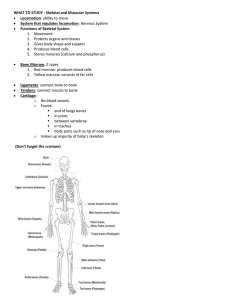
The Human Body • There are over 100 trillion cells in your body. Those cells are organized into tissues. Different tissues are organized into organs. Groups of organs make organ systems. Organ systems make up an organism. There are four basic types of tissues: __________ tissue protects There are four basic types of tissues: Epithelial tissue protects One kind of epithelial tissue is the skin. Epithelial tissue also lines the gut and lungs. Many glands are made of epithelial tissue. There are four basic types of tissues: __________ tissue – supports and defends There are four basic types of tissues: Connective tissue supports and defends Connective Tissue supports and defends. Cells of the immune system – Macrophages and lymphocytes Connective Tissue supports and defends. Cells of the skeletal system – fibroblasts, cartilage, bone Connective Tissue supports and defends. Adipose tissue (fat) , Erythrocytes (red blood cells) There are four basic types of tissues: __________ tissue – sends signals There are four basic types of tissues: Nervous tissue - sends signals Nervous tissue sends signals. Made up of neurons and support cells (also called glial cells) There are four basic types of tissues: __________ tissue – permits movement There are four basic types of tissues: Muscle tissue - permits movement Muscle tissue permits movement. There are three types of muscle tissue: smooth, skeletal and cardiac. Homeostasis- the maintenance of a stable internal environment The body fluid not inside your cells is called extracellular fluid. Because so much exchange occurs across the membranes of cells, extreme changes in the composition or volume of the extracellular fluid can have very serious effects on the cells. To maintain homeostasis, the central nervous system gathers information about what is going on in the body, evaluates this feedback, and issues commands to counteract any change from normal. Most things are controlled by _________ __________. Most things are controlled by negative feedback. Things such as blood pressure, body temperature and pH are compared with their normal values. Anything that causes a change away from the normal value initiates a response from the body that brings it back to normal. An example of negative feedback: The normal body temperature is about 98 degrees Fahrenheit. When you have a fever, your body temperature is above this normal level, and the nervous system detects this change. The brain will then trigger mechanisms such as sweating and dilating the blood vessels in the skin, which lower your temperature back to normal. Some things in the body are controlled by _________ __________, which causes the body to drive the variable even farther away form normal. Some things in the body are controlled by positive feedback, which causes the body to drive the variable even farther away form normal. This happens in childbirth; the pressure of the baby’s head on the lower part of the uterus increases the frequency and intensity of uterine contractions. The Skeletal System There are __________ bones in the adult skeleton. There are 206 bones in the adult skeleton. Skeletal System • A flexible endoskeleton allows the body a wide range of motion while supporting a body of considerable size. • The skeletal system provides a frame work against which the muscles can pull. • It also protects the delicate organs inside the body, such as the brain, lungs, heart. Etc. The human skeleton has two main parts: __________ skeleton – skull, ribcage, backbone __________ skeleton – arms, legs, shoulders, pelvis,etc. The human skeleton has two main parts: Axial skeleton – skull, ribcage, backbone __________ skeleton – arms, legs, shoulders, pelvis,etc. The human skeleton has two main parts: Axial skeleton – skull, ribcage, backbone Appendicular skeleton – arms, legs, shoulders, pelvis,etc. Type of Bones: Flat – ribs, shoulder Type of Bones: Long – arms, legs Type of Bones: Short – feet, wrists Type of Bones: Irregular – vertebrae • Bone is made of calcium-hardened fibers that make it strong yet flexible. It is a living tissue and receives oxygen and nutrients by blood vessels that pass through hollow channels in the bone called ______________________________. • Bones also contain nerve fibers. Bones are surrounded by a tough white membrane called the ________________. • Bone tissue can either be in the form of compact bone or spongy bone. • Bone is made of calcium-hardened fibers that make it strong yet flexible. It is a living tissue and receives oxygen and nutrients by blood vessels that pass through hollow channels in the bone called Haversion canal. • Bones also contain nerve fibers. Bones are surrounded by a tough white membrane called the ________________. • Bone tissue can either be in the form of compact bone or spongy bone. • Bone is made of calcium-hardened fibers that make it strong yet flexible. It is a living tissue and receives oxygen and nutrients by blood vessels that pass through hollow channels in the bone called Haversion canal. • Bones also contain nerve fibers. Bones are surrounded by a tough white membrane called the periosteum. • Bone tissue can either be in the form of compact bone or spongy bone. Haversion canals Two substances that can be found inside bone: • ___________ marrow – produces red blood cells. • ___________ marrow – stores fat. Two substances that can be found inside bone: • Red marrow – produces red blood cells. • Yellow marrow – stores fat. • ____________ is a type of connective tissue that is softer and more flexible than bone. It is the main component of embryonic skeletons. During development, much of it hardens into bone. In adults, cartilage can still be found in the ear, nose, trachea, and at the end of bones to keep them from grinding against each other. • Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that is softer and more flexible than bone. It is the main component of embryonic skeletons. During development, much of it hardens into bone. In adults, cartilage can still be found in the ear, nose, trachea, and at the end of bones to keep them from grinding against each other. __________ - bone tissue is broken down faster than it is replaced. Bones become less dense and brittle. Osteoporosis occurs primarily in females due to the loss of calcium and sex hormones during menopause. Osteoporosis - bone tissue is broken down faster than it is replaced. Bones become less dense and brittle. Osteoporosis occurs primarily in females due to the loss of calcium and sex hormones during menopause. • A __________ is the place at which two bones meet. They can either be immovable (skull), slightly moveable (vertebrae), or freely moveable (knee). • A joint is the place at which two bones meet. They can either be immovable (skull), slightly moveable (vertebrae), or freely moveable (knee). Immoveable joints – (sutures) Slightly moveable – (vertebrae) Freely moveable - (knee) • _____________ - connect bone to bone • ____________ - connect bone to muscle Ligaments – connect bone to bone Tendons – connect bone to muscle http://srs.dl.ac.uk/OTHER/OW/MUSCLE/page2.html Muscular System • There are three kinds of muscles: • ____________ - Appears striated, voluntary movement • ____________ - Walls of internal organs such as the stomach and blood vessels, involuntary movement • ____________ - Only in the heart, appears striated, involuntary There are three kinds of muscles: • Skeletal - Appears striated, voluntary movement • ____________ Walls of internal organs such as the stomach and blood vessels, involuntary movement • ____________ Only in the heart, appears striated, involuntary There are three kinds of muscles: • Skeletal - Appears striated, voluntary movement • Smooth - Walls of internal organs such as the stomach and blood vessels, involuntary movement • ____________ Only in the heart, appears striated, involuntary There are three kinds of muscles: • Skeletal - Appears striated, voluntary movement • Smooth - Walls of internal organs such as the stomach and blood vessels, involuntary movement • Cardiac - Only in the heart, appears striated, involuntary • The skeleton provides a framework against which the muscles can pull. One end of the muscle, the _______, is attached to a bone that remains stationary during the contraction. The other end of the muscle, the _____________, is attached to a bone that moves during the contraction. • The skeleton provides a framework against which the muscles can pull. One end of the muscle, the origin is attached to a bone that remains stationary during the contraction. The other end of the muscle, the _____________, is attached to a bone that moves during the contraction. • The skeleton provides a framework against which the muscles can pull. One end of the muscle, the origin is attached to a bone that remains stationary during the contraction. The other end of the muscle, the insertion, is attached to a bone that moves during the contraction. • _____________ cause the limbs to bend at a joint _____________ cause the limbs to straighten Flexors cause the limbs to bend at a joint • Extensors cause the limbs to straighten • Within each muscle are bundles of smaller muscle fibers called myofibrils. Those myofibrils contain many protein filaments called ________ and __________. • Actin and myosin filaments are arranged into sacromeres, which are the functional unit of contractions. • Within each muscle are bundles of smaller muscle fibers called myofibrils. Those myofibrils contain many protein filaments called actin and myosin • Actin and myosin filaments are arranged into sacromeres, which are the functional unit of contractions. • When a muscle fiber contracts, adjacent myosin and actin filaments slide along one another so that they overlap a great deal and shorten each sarcomere. This explanation of muscle contraction is called the _____________________ theory. • When a muscle fiber contracts, adjacent myosin and actin filaments slide along one another so that they overlap a great deal and shorten each sarcomere. This explanation of muscle contraction is called the Sliding filament theory. The Skin (The Integumentary System) • Skin protects The the Skin body from injury, provides defense against disease, helps regulate temperature, and prevents the body from drying out. The skin is composed of three layers: The Skin • __________-outermost layer of skin; these skin cells are dead and are continually being replaced • __________-middle layer; has many nerve ending, blood vessels, hair follicles and sweat glands • __________ __________-inner layer; stores fat, provides insulation The skin is composed of three layers: The Skin • Epidermis-outermost layer of skin; these skin cells are dead and are continually being replaced • __________-middle layer; has many nerve ending, blood vessels, hair follicles and sweat glands • __________ __________-inner layer; stores fat, provides insulation The skin is composed of three layers: The Skin • Epidermis-outermost layer of skin; these skin cells are dead and are continually being replaced • Dermis-middle layer; has many nerve ending, blood vessels, hair follicles and sweat glands • __________ __________-inner layer; stores fat, provides insulation The skin is composed of three layers: The Skin • Epidermis-outermost layer of skin; these skin cells are dead and are continually being replaced • Dermis-middle layer; has many nerve ending, blood vesse bfhls, hair follicles and sweat glands • Subcutaneous tissue-inner layer; stores fat, provides insulation Some skin disorders: Carcinoma A basal cell carcinoma is a form of skin cancer. Some skin disorders: Acne For reasons no one completely understands, follicles, often called pores, sometimes get blocked. Sebum (oil) which normally drains to the surface gets blocked and bacteria begins to grow. Some skin disorders: malignant melanoma Malignant melanoma is a cancer which usually starts in the skin, either in a mole or in normal-looking skin. Although the number of people who develop melanoma is rising, it is still an uncommon type of cancer. Some skin disorders: Psoriasis Psoriasis is an immune-mediated, genetic disease manifesting in the skin and/or the joints. It is a non-contagious and life-long skin disease that has different forms. Some people may have a spot or two, while others may have extensive coverage on their body. Immune System Immune System The skin and mucous membranes provide the first line of defense. Immune System The second line of defense is provided by several different patrolling cells: __________ kill bacteria one at a time by ingesting them Macrophages kill bacteria one at a time by ingesting them __________ release chemicals that kill nearby bacteria (and themselves) Neutrophils release chemicals that kill nearby bacteria (and themselves) The inflammatory response – expansion of blood vessels at site of injury (causing swelling and redness); Migration of macrophages and neutrophils The temperature response – fevers inhibit bacterial growth Immune System The third line of defense is the IMMUNE SYSTEM!!!! Macrophages – initiate the immune defense by sending an alarm signal Helper T cells – activate killer T cells and B cells Killer T cells – attack and kill infected body cell B cells – use antibodies to label invaders for destruction by macrophages and killer T cell; some become _________cells B cells – use antibodies to label invaders for destruction by macrophages and killer T cell; some become memory cells Autoimmune diseases: In autoimmune diseases, the body cannot distinguish normal body cells from foreign invaders, and the body attacks its own cells Prominent autoimmune diseases afflicting 22 million people in the US, costing more than $100 billion annually to Anemia treat Chronic Fatigue Immune Autoimmune Hepatitis Crohn's Disease Graves' Disease (1.5M) Fibrosis Dysfunction Syndrome SCLERODERMA (300K) SARCOIDOSIS (25K) PSORIASIS (5M) GUILLAIN-BARRÈ (1/100,000) Ulcerative Colitis Raynaud's Phenomenon (1-10% general pop, 25% young women) MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS (200K - 350K) LUPUS (500K) INSULIN DEPENDENT DIABETES (1 M) RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (2M) Allergies are caused by an immune response to a harmless substance. HIV attacks and cripples the immune system by destroying the white blood cells. Endocrine System Endocrine System The endocrine organs secrete _______ Into the blood stream Endocrine System The endocrine organs secrete hormones into the blood stream Endocrine System Pineal Gland secretes the hormone: Melatonincircadian rhythms Endocrine System Pituitary Gland secretes the hormones: •Vasopressinwater reabsorption •Oxytocin-uterine contractions during labor Endocrine System Pituitary Gland secretes the hormones: •Growth hormone-bone and muscle growth •Prolactin-milk production Endocrine System Thyroid secretes the hormones: •Thyroid hormones (T4 & T3)-metabolic activity •Calcitonindecreases blood calcium level Endocrine System Parathyroid secretes the hormone: •Parathyroid hormoneincreases blood calcium Endocrine System Adrenalsecretes the hormone: •Epinephrineincreases heart rate Endocrine System Pancreassecretes the hormones: •Insulin-lowers blood glucose •Glucagonincreases blood glucose Endocrine System Ovary- secretes the hormones: •Estrogenfemale characteristics •Progesteronemaintenance of endometrium Endocrine System Testis- secretes the hormone: •Testosterone -male characteristics Reproductive System Males: The male gonads, called the __________, contain two components: the seminiferous tubules and the interstitial cells. Males: The male gonads, called the testes, contain two components: the seminiferous tubules and the interstitial cells. Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules, while the interstitial cells secrete testosterone and other hormones. The testes are located in an external pouch called the scrotum, which maintains a temperature 2-4oC lower than the body temperature, a condition essential for sperm survival. Scrotum Sperm pass from the seminiferous tubule… Sperm pass from the seminiferous tubule into the epididymis… Sperm pass from the seminiferous tubule into the epididymis then the vas deferens… Sperm pass from the seminiferous tubule into the epididymis then the vas deferens and then to the urethra… Sperm pass from the seminiferous tubule into the epididymis then the vas deferens and then to the urethra and out through the penis. Puberty is between 13-15 years old. Females: The female gonads, called the _______, produces eggs and secrete the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Females: The female gonads, called the ovaries, produces eggs and secrete the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Once a month, an immature egg is released from the ovary into the abdominal cavity and drawn into the fallopian tube. The egg then travels to the __________ , which is the site of fetal development. The egg then travels to the uterus , which is the site of fetal development. The lower end of the uterus is called the cervix, which is connected to the vagina. Puberty is complete by age 13. cervix During ovulation, the wall of the uterus thickens to prepare for pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilized by a sperm, then this thickened layer is shed and blood vessels are broken, which is called menstruation. Human Development The fusion of a sperm and egg is called a __________. The fusion of a sperm and egg is called a zygote. After fertilization the zygote rapidly divides into more cells and continues to travel down the fallopian tube. Around the sixth day after fertilization, the embryo implants in the tissue of the uterus. The growing fetus receives oxygen and nutrients directly from its mother through the __________ and umbilical cord. The growing fetus receives oxygen and nutrients directly from its mother through the placenta and umbilical cord. Circulatory System The circulatory system transports nutrients, wastes, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones. It also distributes heat and maintains body temperature. The circulatory system is composed of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, blood and the heart. Blood leaves the heart through __________, which branch into many smaller arterioles, and then to capillaries. Blood leaves the heart through arteries, which branch into many smaller arterioles, and then to capillaries. In the capillaries, food and oxygen are transferred from the blood to the body cells, and carbon dioxide and wastes are picked up and carried away. Blood returns to the heart through venules and veins. The cardiovascular system is VERY leaky. Fluids are forced out of the thin walls of the capillaries by pressure. This fluid is picked up by the lymphatic tissues and returned to veins. Components of blood: The __________ contains water, metabolite (like glucose and vitamins), wastes, ions (sodium, chloride, etc) and proteins. Components of blood: The plasma contains water, metabolite (like glucose and vitamins), wastes, ions (sodium, chloride, etc) and proteins. Components of blood: The cellular portion of the blood is made up of three different types of cells. __________ blood cells (erythrocytes)- shaped like a float disk, carry oxygen, replaced frequently. Red blood cells (erythrocytes)- shaped like a float disk, carry oxygen, replaced frequently. Anemia is caused by a decrease in the number of red blood cells. ________ blood cells (leukocytes)- used in the immune system for defense. WHITE blood cells (leukocytes)- used in the immune system for defense. Leukemia is caused by an overproduction of white blood cells. __________ - play a key role in blood clotting. Red blood cell White blood cell Platelets (blue)- play a key role in blood clotting. Red blood cell White blood cell The heart is divided into ___________ chambersleft atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, right ventricle. The heart is divided into four chambersleft atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, right ventricle. A small cluster of cells in the right atrium,called the sinoatrial node (SA node), initiate contraction of the heart. The SA node acts as the ___________ of the heart, spontaneously starting contractions with a regular rhythm. The SA node acts as the pacemaker of the heart, spontaneously starting contractions with a regular rhythm. After initiation, the wave of contraction spreads across both atria, is delayed for an instant, and then spreads to the ventricles by the atrioventricular node (AV node) and Bundle of His. Pump your Blood song ♫ From Happy Days Sang by the character Potsie Webber http://www.sitcomso nline.com/happydays. html ♫ ♪Pump, pump, pumps your blood ♫The right atrium’s where the process begins, where the CO2 blood enters the heart. ♫ Through the tricuspid valve, to the right ventricle, the pulmonary artery, and lungs. ♫ Once inside the lungs, it dumps its carbon dioxide and picks up its oxygen supply. ♫ Then it’s back to the heart through the pulmonary vein, through the atrium and left ventricle. ♪ Pump, pump, pumps your blood ♪Pump, pump, pumps your blood ♫ The aortic valve’s, where the Blood leaves the heart, then it's channeled to the rest of the bod ♫ The arteries, arterioles, and capillaries too bring the oxygenated blood to the cells ♫ The tissues and the cells trade off waste and CO2, which is carried through the venules and the veins ♫ Through the larger vena cava to the atrium and lungs, and we're back to where we started in the heart ♪ Pump, pump, pumps your Blood Blood flows through the heart in the following order: vena cava-right atriumtricuspid valve-right ventriclepulmonary valve-pulmonary artery-lungs-pulmonary veinsleft atrium-bicuspid valve-left ventricle-aortic valve-aortabody •Blood pressure is a measure of cardiovascular function. •During the fist part of the heartbeat, the atria are relaxed and filling with blood. This is called the __________ pressure. •Blood pressure is a measure of cardiovascular function. •During the fist part of the heartbeat, the atria are relaxed and filling with blood. This is called the diastolic pressure. •The second part of the heartbeat is when the ventricles contract, pushing blood out into the body. This is called the __________ pressure. •The second part of the heartbeat is when the ventricles contract, pushing blood out into the body. This is called the systolic pressure. Another way to monitor the heart is through measuring the tiny electrical impulses produced by the heart when it contracts. A recording of this is called an __________. Another way to monitor the heart is through measuring the tiny electrical impulses produced by the heart when it contracts. A recording of this is called an electrocardiogram. Hypertension is high blood pressure and can lead to heart damage, stroke, or kidney failure. Atherosclerosis is a buildup of fatty deposits on the inner walls of arteries. Respiratory System Respiratory System Provides your body with a constant supply of oxygen __________ •filters particles, moistens and warms the air Nose •filters particles, moistens and warms the air __________ Upper throat (common tract for both food and air) Pharynx Upper throat (common tract for both food and air) __________ Long tube that carries air to the lungs. (A flap called the epiglottis cover the trachea when you swallow so that food and liquids do not go into your lungs) Trachea Long tube that carries air to the lungs. (A flap called the epiglottis cover the trachea when you swallow so that food and liquids do not go into your lungs) __________ Two branchesone goes to the left lung, one goes to the right lung Bronchi Two branchesone goes to the left lung, one goes to the right lung __________ Millions of tiny sacs where exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs Alveoli Millions of tiny sacs where exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs Breathing is the result of pressure changes that occur inside the thoracic cavity. During inhalation, the __________ contracts and moves downward and the rib cage moves upward and outward. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward and the rib cage moves upward and outward. The air pressure inside the lungs decreases, causing air to rush in. During exhalation, the diaphragm and ribs return to their original position and this compression forces air out of the lungs. As blood flows through the lungs, oxygen is picked up by red blood cells, which contain hemoglobin. Every breath is initiated by the respiratory control center in the brain, which sends signals to the diaphragm to contract. Asthma is a disease in which the bronchioles constrict, making it hard to breathe. Emphysema is caused by cigarette smoking, which damages the alveoli. Lung cancer is caused by abnormal cell growth often due to cigarette smoking. Digestive System Digestion is the process of breaking down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Mouth: Saliva moisten and lubricates the food Saliva contains the enzyme __________ , which begins breakdown of carbohydrates Mouth: Saliva moisten and lubricates the food Saliva contains the enzyme amylase , which begins breakdown of carbohydrates Esophagus: Tube that connects the mouth to the stomach __________ contractions push the food down A sphincter separates esophagus & stomach, preventing acid reflux Esophagus: Tube that connects the mouth to the stomach Peristaltic contractions push the food down A sphincter separates esophagus & stomach, preventing acid reflux Stomach: The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid, which breaks down proteins The mixture of food and gastric juice is churned and becomes __________ Stomach: The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid, which breaks down proteins The mixture of food and gastric juice is churned and becomes chyme Small Intestine: The small intestine is wound upunwound it would be 20 feet long! The SI is lined with fingerlike projections called __________ that increase the surface area and allow for faster absorption of food and water. Small Intestine: The small intestine is wound upunwound it would be 20 feet long! The SI is lined with fingerlike projections called microvilli that increase the surface area and allow for faster absorption of food and water. Small Intestine: Most digestive enzymes are made in the pancreas and secreted into the SI The liver makes bile which is secreted into the SI and helps fat digestion. The complete digestion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins occurs in the SI Small Intestine: Nutrients that are absorbed from the small intestine are sent to the liver, which modifies the nutrients, and detoxifies alcohol Large Intestine: No digestion – just some absorption of ___________ and vitamins Wastes are compacted and sent to the rectum and then out through the anus Large Intestine: No digestion – just some absorption of water and vitamins Wastes are compacted and sent to the rectum and then out through the anus Excretory System Humans eliminate wastes in a process called excretion. Excretion rids the body of nitrogen wastes like ammonia, excessive water, salts, etc. Kidneys: Two small bean-shaped organs located in the lower back Kidneys: Three main sections of the kidney: cortex (outer layer), medulla (inner layer), renal pelvis Kidneys: The kidneys form urine and regulate the amount of water and salt in the blood. Kidney failure is life threatening. Kidneys: Urine produced by the kidneys passes through the ureters and into the urinary bladder. Urine leaves the bladder and exits the __________ Kidneys: Urine produced by the kidneys passes through the ureters and into the urinary bladder. Urine leaves the bladder and exits the Urethra The Nervous System Nerve cells can quickly transmit messages to the body. A nerve cell, or _____________, consists of three basic parts: the cell body, the dendrites, and the axon. Dendrites receive information and send it to the cell body. Then the information travels along a single axon to other cells. Nerve cells can quickly transmit messages to the body. A nerve cell, or neuron consists of three basic parts: the cell body, the dendrites, and the axon. Dendrites receive information and send it to the cell body. Then the information travels along a single axon to other cells. Impulses, known as action potentials, are passed from one nerve to the next. Many nerves are covered by a myelin sheath, which speeds the nerve impulse by allowing ________________ conduction. In multiple sclerosis, the myelin sheath is destroyed, interfering with nerve transmission. Many nerves are covered by a myelin sheath, which speeds the nerve impulse by allowing saltatory conduction. In multiple sclerosis, the myelin sheath is destroyed, interfering with nerve transmission. The _________ Nervous System- The Brain & spinal cord The central Nervous System-The Brain & spinal cord Brain Stem (Medulla) –heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, coughing, sneezing and digestion. Cerebellum – responsible for coordinated movement, balance, posture and muscle tone Hypothalamus – body temperature, appetite, water balance, thirst and blood pressure Thalamus relays information between spinal cord and cerebellum. – Cerebrum (Cerebral Cortex) intellect, memory, language, personality and motor function. – The brain can be divided into four major lobes: occipital, temporal, parietal, and frontal. The __________ Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System –sensory nerves and motor nerves Sensory nerves – gather information about your environment and body conditions and deliver it to the central nervous system. Motor Nerves – transmit information from the central nervous system to muscles and glands Somatic – voluntary muscles (skeletal muscles) Autonomic involuntary muscles (cardiac & smooth muscles) – __________ dominant during times of stress; “fight or flight” – increases blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate; decreases digestion Sympathetic dominant during times of stress; “fight or flight” – increases blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate; decreases digestion __________ – more relaxed state; conserves energy – decreases heartbeat and breathing; increases digestion Parasympathetic – more relaxed state; conserves energy – decreases heartbeat and breathing; increases digestion Special Senses Ear = hearing and equilibrium • Sound waves enter the ear canal and hit the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. • Behind the eardrum are three small bones called ossicles which transmit the vibration to the cochlea. • The cochlea is a fluid-filled chamber with hair cells, which bend and send nerve signals to the brain. Eyes Eyes Sclera – tough outer layer (white of the eye) Cornea – bends and focuses light rays Pupil – where light enters the eye Eyes Iris – controls the amount of light entering the eye (colored part of eye) Lens – focuses light on the rear of the eye Retina – light sensing portion; generates nerve impulses; rods and cones Taste – Taste buds are connected to nerves that send information to the brain. There are four basic taste sensations: salty, sour, sweet, bitter Smell – olfactory receptors line the nose Skin – senses touch, temperature, pain, etc. The End