Early Humans Notes
advertisement

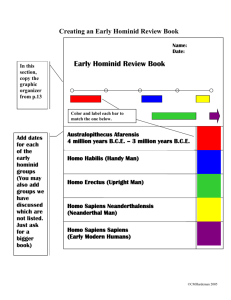
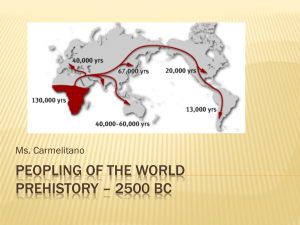
Welcome to 8th grade Social Studies Mr. Crossman The Five Social Studies 1. Def. History The study of past events Ex: World War II Ex: Ex: Democracy in Greece Ex: 2. Def. Geography The study of the earth Ex: Formation of Climates (Biomes) Ex: Deserts Ex: Ex: 3. Def. Sociology The study of human interaction Ex: Foreign Relations Ex: Ex: Teacher to Student Ex: 4. Def. Economics Knowledge about the exchange of goods Ex: Trading System Ex: Ex: Valuable goods/services Ex: 5. Political Science Def. Knowledge of how human order themselves Ex: Dictatorship Ex: Ex: Representative Government Ex: Examining Sources Why is it important to examine sources? Fact, Reasoned Judgments, Opinions Examining Sources Fact – statements that can be proven (proof) Clues - Observations, written records, fossils, etc. Reasoned Judgment – based on fact but has not been proven Clues - Probably, reasonably, possibly, perhaps, etc. Opinion – statement of personal preference Clues - Think, feel, etc. Timeline s There is no year 0 ! Uniform way of measuring the past to the right of year 1 to the left of year 1 Before Christ = B.C. A.D. = Anno Domini Before Common Era = B.C.E. 400 300 200 100 B.C.E. B.C.E. B.C.E. B.C.E. C.E. Distance between years: Same side of year 1 Subtract the # of years ex: 400 B.C.E. to 150 B.C.E. 400 – 150 = 250 years Opposite side of year 1 Add the # of years ex: 100B.C.E. to 200 C.E. 100 + 200 = 300 years C.E. = Common Era 1 C.E. 100 200 300 C.E. C.E. C.E. 400 How to calculate centuries: Find the number of hundred and add 1 (don’t forget your labels) Ex: 356 C.E. = 3 + 1 = 4th Century C.E. 1423 B.C.E. = 14 + 1 = 15th Century B.C.E. 92 C.E. = 0 + 1 = 1st Century C.E. Chapter 2 Introduction: #1 Australopithecus afarensis Time period Description (height, places lived, physical traits) 1 key vocab. term 2 capabilities of your hominid #2 Homo habilis Time period Description (height, places lived, physical traits) 1 key vocab. term 2 capabilities of your hominid #3 Homo erectus Time period Description (height, places lived, physical traits) 1 key vocab. term 2 capabilities of your hominid #4 Homo sapiens neanderthalensis Time period Description (height, places lived, physical traits) 1 key vocab. term 2 capabilities of your hominid #5 Homo sapiens sapiens Time period Description (height, places lived, physical traits) 1 key vocab. term 2 capabilities of your hominid Chapter 2 Introduction: #1 Australopithecus afarensis Bipedal – walked on 2 legs #2 Homo habilis #3 Homo erectus Simple tools – Bone/Stone Used Fire #4 Homo sapiens neanderthalensis #5 Homo sapiens sapiens Community – cared for each other and buried the dead Artwork/Culture Paleolithic Age Means: Old Stone Age Strongest tools: Stone Pre-history – The time before writing About 2 million B.C.E. to 8000 B.C.E. Early Hominids and Humans Neolithic Age Means: New Stone Age Strongest tools: Stone During Pre-history About 8000 B.C.E. to 3000 B.C.E. Agriculture – farming and domestication of animals People began to settle in one place Stable Lifestyle Avoid hunting dangers Discovery and spread of seeds = growing plants Permanent Dwellings Stable life allowed permanent homes Houses had rooms for specific purposes Communities Grow Villages of up to 200 people Population growth Safety in numbers Roles in Community Job specialization – individuals work in one area Workers are more skilled Develops better: pottery, clothing, homes, jewelry, etc. Trade Increases Desire for a better quality of life Humans seek resources from elsewhere Ideas and knowledge spread Civilizations Begin Humans Build First Cities