Chapter 4
advertisement

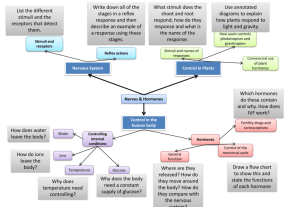
Chapter 4 Extracellular signals: Hormones, cytokines and growth factors Objectives • Understand the general role of Hormones, Cytokines, Growth Factors and Neurotransmitters • Learn the abbreviations for the general molecules in each class • Know one example of a function for each group of signals Hormones • Small water soluble molecules – Cannot cross plasma membrane – Must target cellular receptor – Examples • Histamine • Epinephrine Hormones • Peptide Hormones – – – – Water soluble Stored in vacuoles Pro-peptides Examples • Insulin • Glucagon • LH (luteinizing hormone) • FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) Hormones • Lipophilic molecules (extracellular) – Still need a receptor – Prostaglandins • Synthesized from arachidonic acid – Usually have to do with inflammation Hormones • Lipophilic molecules (intracellular) – Receptors are on the inside of the cell – Steroid hormones – Examples • Testosterone • Progesterone • Thyroxine Hormones • Plant hormones (for Joe!!) – All extracellular signals – Auxin • Young leaves and seeds • Very diverse effects – Cytokinins • Developing seeds – Gibberellins • Young shoots and seeds • Flowering and germination – Abscisic acid • Roots and mature leaves • Stromal closure – Ethylene • Gas • Fruit ripening Cytokines • Very large family of peptides • Range in size from 10-70 kDa Name of Group Examples Notes Interferons IFN-α IFN-β IFN-γ Viral infection response Interleukins IL-1 to IL-35 Some with more than one isoform Cell growth and differentiation Tumor necrosis factors TNFα TNFβ TGFβ Inflammatory response Chemokines MIP-1α NAP-2 RANTES Leukocyte location signals Colony stimulating factors M-CSF G-CSF GM-CSF Development of bone marrow Cytokines • Interleukins – 37 family members – IL-x – Many different sizes – Many different receptors – Many different functions • Immune response and maturation • Can activate themselves or nearby cells Cytokines • Interferons – Type I • IFN-α, INF-β, IFN-Ω – Type II • INF-γ – Anti-tumor properties? • Tumor necrosis factors – TNF-α and TNF-β • Works closely with IFN and causes necrosis of tumors (hence the name!!) Growth Factors • Platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF) – Induces cell migration & proliferation • Fibrosis and arteriosclerosis • Epidermal growth factor (EGF) – Various functions • Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) – Cell proliferation, migration and motility • Proto-oncogenes? Neurotransmitters • Stored in vesicles, released upon Ca2+ stimulation • Small Molecules – Acetylcholine, GABA, dopamine, γ-aminobutyric acid – Glycine, glutamate, ATP and adenosine • Neuropeptides – Substance P, Endorphin, vasopressin