Introduction to Agriculture - Public Schools of Robeson County
advertisement

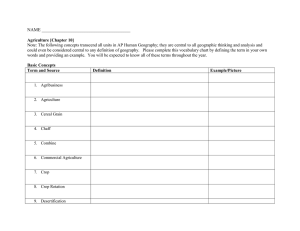
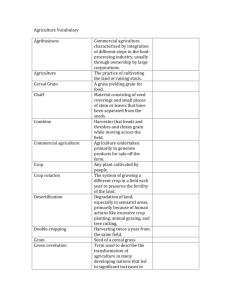
Introduction to Agriculture Understand Global Agriculture Objective 2.01: Understand the history of global agriculture. Agriscience Defined Agriscience- The application of scientific principles and new technologies to agriculture Applied Science vs. Basic Science Basic Sciences Areas of Agriscience The Basic Sciences 1) Biology- The study of living things 2) Chemistry- Deals with elements and simple substances 3) Biochemistry- Focuses on chemistry as it is applied over living things. Fact!!! A United States Department of Agricultural study forecast that job opportunities for graduates in agricultural and life sciences will exceed the graduates available in the coming years. Applied Sciences Definition- The application of one or more of the basic sciences for practical (real life) purposes. • • • • • Aquaculture Agricultural Engineering Animal Science Crop Science Agronomy • • • • Soil Science Biotechnology Horticulture Hydroponics Agriscience Examples • Agronomy – Uses biology and chemistry to produce and control crops • • • • • Cotton Soybeans Tobacco Corn Hay and Turf grass Agriscience Examples • Entomology – Uses biology and chemistry to study insect life • Agriculture Engineering – Uses physics to develop new machines, tools and implements Agriscience Examples • Biotechnology – Uses biology, genetics, and chemistry to modify or change organisms for a useful purpose Scientific Method • Agriculture and other sciences use the Scientific Method to solve problems (we will discuss this more in Objective 3.02) What is Agriculture? • The activities concerned with the production of plants, animals, and related supplies, mechanics, products, processing, and marketing – Production agriculture (farming) only accounts for 1/5th of the total agriculture jobs in the US • USDA refers to agriculture as “agriculture/agribusiness and renewable natural resources. Examples of Agriculture: • Cattle – Production – farmer, cow-calf, feeder steers – Processing – Slaughter facility, rendering, beef, leather – Marketing – Butcher, grocery, steaks – Transportation – Plane, rail, truck – Related Supplies and Services – Veterinarian, feed dealer. Examples of Agriculture • Wheat – Production – farmer, grain – Processing – grain mills, flour – Marketing – bakery, bread – Transportation – grain trucks, rail – Related Supplies and Services – fertilizer dealer, crop scouting, machinery dealer, GPS Examples of Agriculture • Roses – Production – flower grower, roses – Processing/Marketing – harvesters, wholesale and retail florist – Transportation – plane, truck, floral delivery dealer – Related Supplies and Services – glass vase sales, greenhouse manufacturers, floral designers What is Agribusiness? • Refers to commercial firms that have developed with or stemmed out of agriculture – Take a moment to name three agribusinesses in your notes: • • • • • John Deere Monsanto Tractor Supply D.D. McColl’s FCX Examples of Agribusiness: • Farm related – Chemical company, tractor manufacturer, pharmaceutical company (veterinary medicines) • Horticulture related – Landscape or nursery business, seed company, mower manufacturer Renewable Natural Resources • Resources provided by nature that can replace or renew themselves. • Important both economically and for posterity’s sake to maintain life. • Examples – Wildlife – Trees – Fish Progress in Agriculture • Mechanization helps 2% of America’s work force meet the food and fiber needs of our nation • There has been a reduction from 90% of nations populace involved in farming 200 years ago to less than 2% in 2012. – Farms are becoming larger and fewer. Eli Whitney • Invented the cotton gin • 1793 • Transformed cotton to a usable product • Removed cotton seed from cotton fiber Eli Whitney’s Cotton Gin George Washington Carver • Late 1890s • Soil improvement and crop rotation – Use of “legumes” • Crops that “make” their own nitrogen, ie. Peanuts. – Improved soil fertility in the US South. Cyrus McCormick • 1834 • Invented the grain reaper • Cut grains – Cut wheat, oats, and other crops Cutting Grain • With the sickle or reaping hook one man could cut from one-half to one acre in a hard day's work. • The cut grain was later bound by hand The Reaper • While this first machine required only 2 people for operation (a person to ride the horse and a man to rake the cut grain from the platform), it cut as much grain in one day as 12-16 men with reaping hooks. Cast Iron Plow • Invented in the early 1800’s • Thomas Jefferson • Rough surface that dirt stuck to Henry Blair • 1834 – Seed Planter • 1836 – Cotton Planter Steel Moldboard Plow • • • • Invented 1837 John Deere Smoother surface Rich clay soil did not stick to it • Made plowing easier and faster Corn Picker • Invented in 1850 • Edmund Quincy • Helped speed up the harvesting of corn Joseph Glidden • 1874 • Barbed Wire • Dramatically changed raising livestock Milking Machine • Invented in 1878 • Anna Baldwin • Used vacuum suction • Replaced hand milking Thomas Elkins • 1879 • Perishable Food Preservation • Designed a device that helped preserve food by way of refrigeration. Benjamin Holt • Invented in 1904 • Tractor • Replaced the mule as a source of power – Horse power John Sanford • 1987 • Gene gun – Device for injecting cells with genetic information GPS & GIS • 1993 • Tractor based GPS systems together with sophisticated GIS used to gather data • Used for – Soil condition, humidity, temperature and other variables, which system then uses to control such things as intensity of planting, application of fertilizer and pesticides, water schedules, etc. Robotic Milking Machines • • • • Late 1990s First used in Ontario, Canada Reduction in labor High initial cost = disadvantage to small producer Establishment of Land Grant Institutions NCSU NC A&T State University Clemson Definition • An institution designated by its state legislature to receive funding (Morrill Acts of 1862 and 1890) to teach agriculture, military tactics, and the mechanical arts. • Key component is the agricultural experiment station (Hatch Act 1887) Examples • • • • • • North Carolina A&T (1890)- Greensboro, NC North Carolina State University (1887) – Raleigh, NC Clemson University (1889) – Clemson, SC University of Georgia (1785) – Athens, GA University of Tennessee (1794) – Knoxville, TN Virginia Tech University (1872) – Blacksburg, VA Government Agencies Agriculture related Agencies • Established to assist farmers, ranchers, and the general public with information, professional assistance and, in some cases, funding. Examples • USDA (1862) – United States Department of Agriculture – Provides leadership on food, agriculture, natural resources, rural development, nutrition, and related issues based on sound public policy, the best available science, and efficient management. – Branches • • • • NRCS (1935) – Natural Resource Conservation Service APHIS (1972) – Animal Plant and Health Inspection Service NASS (1863) – National Agricultural Statistics Service USFS (1905) – United States Forest Service – Sustain the health, diversity, and productivity of the nation’s forests and grasslands to meet the needs of present and future generations. Examples… • NCCES (1914) – North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service – Help individuals, families, and communities put research based knowledge to work for economic prosperity, environmental stewardship and an improved quality of life. – NCDA&CS – North Carolina Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services. Promote and improve agriculture. Origins of Major Food Crops – Fruits/Vegetables • • • • Peaches – China Tomato – South America Peanut – Peru, South America Sweet potato – Central America Grain, Oil, and Fiber Crops • • • • Corn – Cuba, Mexico Soybeans – Southeast Asia Cotton – Mexico, Africa, Pakistan Wheat – Southwest Asia US Agricultural Production • Regions develop based on a variety of factors including soils, weather, market development, feed availability, etc. High Ranking Regions • Citrus Fruit – Florida, Texas, and California • Corn Belt – Midwestern states • Wheat – Hard Red Spring Wheat – highest protein content, excellent bread wheat, superior milling and baking characteristics • MN, ND, SD, MT, ID, OR, WA, CA – Soft Red Winter Wheat – High yielding, low protein, used for cakes, biscuits, pastries • NC, TN, KY, GA, OH, IN, IL, MO Production Regions… • Spearmint – WA, OR, ID • Floriculture Crops – CA, FL, MI, TX, NC • Beef Cattle – TX, KS, NE, IA, CO, OK, MO, SD • Dairy – MN, WI, MI, OH, PA, NY, VT, NH, MA, ME (CA, ID, TX) • Hogs – NC, IA, IL, IN, MN • Poultry (broilers) – NC, GA, AL, AR, MS, TX NC Agriculture • Mountains • Piedmont • Coastal Plains NC Ag Production by Region • Mountain counties – Christmas Trees, Apples, Trout • Piedmont counties – Greenhouse and nursery crops, broilers, turkeys, dairy • Eastern counties – Hogs, turkeys, broilers, tobacco (flue-cured), sweet potatoes, vegetables, peanuts, cotton, corn, soybeans. Farm Cash Receipts (2011) • $10,000,000,000 ($10B) annually • Livestock, Dairy, and Poultry - 2/3 of all FCR – Broilers and hogs account for nearly ½ of this amount • Crops – 1/3 of all FCR