Egg Lab and Transport Foldable

Set this up on page 21 in your journal.
There is a copy of this page on your table.
Egg Demo Page 22
Essential Question:
Question Column
How can I demonstrate membrane transport with an egg?
?
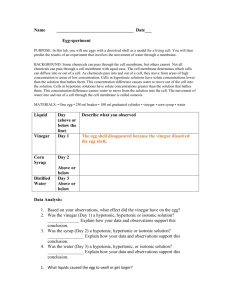
Egg in Vinegar Egg in Syrup Egg in Water
L1 – Describe
L2 – Explain
Hypothesis:
Observation:
Hypothesis:
Observation:
Hypothesis:
Observation:
Diagram: Diagram: Diagram:
*be sure your table of contents is updated
L3 – Why
Colnclusion -
What would happen if I place an egg into vinegar?
Let’s check your eggs!
• Send ONE person from your group to get your egg cup.
• Make observations of the egg and record them in your journal
• This person will pour out the vinegar and GENTLY rinse the egg.
• Place the egg back into your cup and bring it back to your table.
• As a group, make additional observations. What do you notice? How does the egg look different? How is it the same? Write what you see.
• Draw a picture of what the egg looks like now.
• Write a sentence in your Conclusion area about whether your hypothesis was right or wrong.
Now what??
• Use the bottle at your table to cover the egg in syrup
– just barely cover it! Don’t drown it.
• With your group, create a hypothesis about what you think will happen to the egg in syrup overnight ( If I put an egg in syrup, then……… ).
• Send ONE member of your group to put the cup back on the counter.
Foldable Time:
• Title page 20
“Transport Foldables”
Solutions Foldable
• Fold the top of the paper down to make a tab.
• Put a THIN line of glue on your tab, then glue it to the bottom of page 20 (Transport Foldables).
• Write SOLUTIONS (Osmosis) above the paper.
HIGH to
LOW
BELL WORK: Copy and complete the concept map below:
Molecule
Transport LOW to
HIGH
Diffusion
Osmosis
Facilitated
Diffusion uses transport proteins
Active
Transport
Title Page 21: Osmosis
**We’re finishing notes. Only day this week!! **
Watch the video for an intro on what we’re learning about today.
• Cell Video
• Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis .
• Remember: SALT SUCKS
I know that other molecules move too, that’s why we gave the movement of water a special name. This way everyone knows which molecule you’re talking about.
Divide the rest of your page into 3 sections. We’ll fill out each one as we go.
Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic
ISOTONIC means “same strength”
DRAW THIS!
Under the picture, write this:
• equal concentration inside
& outside
• NO VISIBLE CHANGE
• water moves evenly in & out
At the very bottom, write and highlight this:
• ISO = same
HYPERTONIC means “above strength”
DRAW THIS!
Under the picture, write this:
• solute concentration
HIGHER outside the cell
• water moves out of the cell
• CELL WILL SHRINK
At the very bottom, write and highlight this:
• HYPER = HIGH, makes the cell DRY!
HYPOTONIC means “below strength”
DRAW THIS!
Under the picture, write this:
• solute concentration
LOWER outside the cell
• water moves into the cell
• CELL WILL SWELL
At the very bottom, write and highlight this:
• HYPO = LOW, makes the cell GROW!
If the inside of a cell is 95% water, what is the concentration of water in an isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic solution? What is the concentration of solute in each of those cases?
Exit Ticket: On the handout I gave you draw an example of each type of transport with arrows to show how the molecules move.
High
Key:
Blue = water
Pink = Salt (small molecule)
Green = Glucose (large molecule)
Yellow Star = ATP
Red arrow = direction molecule will move
Label the High and Low concentration in red
Low