Exceptions to Mendelian Inheritance
advertisement
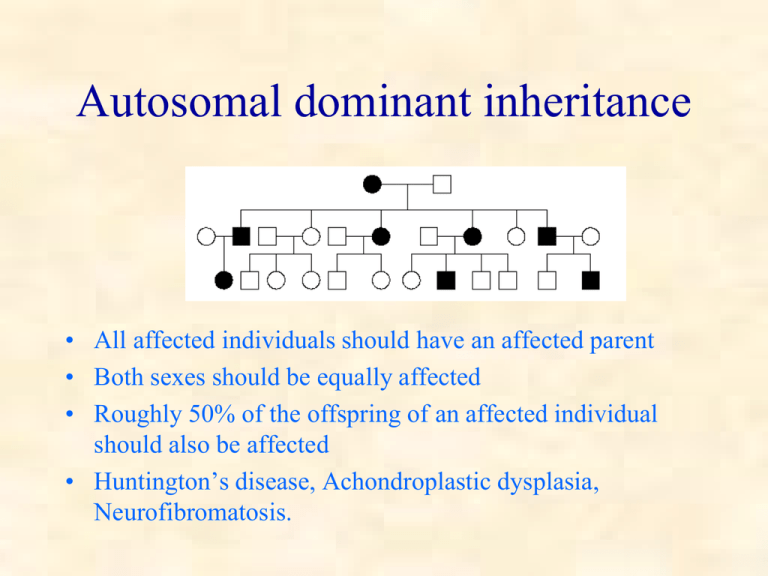
Autosomal dominant inheritance • All affected individuals should have an affected parent • Both sexes should be equally affected • Roughly 50% of the offspring of an affected individual should also be affected • Huntington’s disease, Achondroplastic dysplasia, Neurofibromatosis. A large autosomal dominant pedigree! Autosomal Recessive Inheritance • Usually there is no previous family history • The most likely place to find a second affected child is a sibling of the first Autosomal recessive • Inbreeding increases the chance of observing an autosomal recessive condition • E.g. Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, Tay Sachs disease. Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • Lethal alleles T/+ x T/+ T/T T/+ +/+ 1 : 2 : 1 ratio at conception 0 : 2 : 1 ratio at birth Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • Lethal alleles • Incomplete dominance Familial Hypercholesterolemia +/+ = normal +/- = death as young adult -/- = death in childhood Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • • • • Lethal alleles Incomplete dominance Codominance Silent alleles Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • • • • • Lethal alleles Incomplete dominance Codominance Silent alleles Epistasis The Bombay Phenotype: The ABO blood group genotype cannot be deduced in h/h homozygotes. Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • • • • • • • Lethal alleles Incomplete dominance Codominance Silent alleles Epistasis Pleiotropy genetic heterogeneity Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • • • • • • • Lethal alleles Incomplete dominance Codominance Silent alleles Epistasis Pleiotropy genetic heterogeneity • variable expressivity • incomplete penetrance Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • • • • • • • • • Lethal alleles Incomplete dominance Codominance Silent alleles Epistasis Pleiotropy genetic heterogeneity variable expressivity incomplete penetrance • Anticipation E.g. Myotonic dystrophy Number of CTG repeats 5 phenotype 19 - 30 premutant 50 - 100 mildly affected 2,000 or more severely affected normal Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • • • • • • • • • Lethal alleles Incomplete dominance Codominance Silent alleles Epistasis Pleiotropy genetic heterogeneity variable expressivity incomplete penetrance • Anticipation • germline mosaicism • phenocopies Phocomelia • Incomplete ascertainment • mitochondrial inheritance Mitochondrial inheritance Exceptions to clear cut Mendelian inheritance • • • • • • • • Lethal alleles Incomplete dominance Codominance Silent alleles Epistasis Pleiotropy Genetic heterogeneity Variable expressivity • • • • • • • • Incomplete penetrance Anticipation Reverse anticipation Germline mosaicism Phenocopies Mitochondrial inheritance Uniparental disomy Linkage








