Other Methods of Inheritance
advertisement

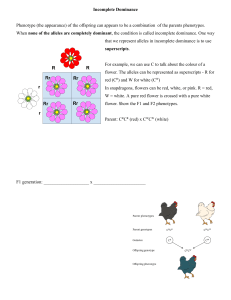
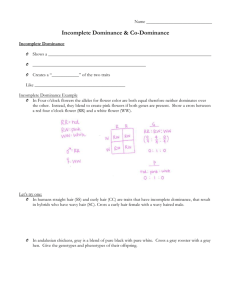
Other Methods of Inheritance: Codominance and Incomplete Dominance The Different Forms of Inheritance Mendel’s Inheritance (Monohybrid + Dihybrid) = Last lesson Incomplete dominance = This lesson Codominance= This lesson Sex linked = Next Lesson Incomplete Dominance Incomplete dominance is another example of how some traits are inherited different from Mendel predicted. In incomplete dominance neither of the two alleles for the same gene can dominate the other. The result is that the phenotype is a blend of both parents This is similar to the old theory of blended inheritance. Incomplete dominance Incomplete Dominance: a condition in which neither of the two alleles for the same gene can completely conceal the presence of the other. As a result, the offspring or heterozygote exhibits a phenotype that is a mixture or somewhere between the a dominant and recessive phenotype. Example: Flower colour of Snapdragons Red Flower x White Flower Pink Flower Practice Incomplete Dominance What would be the result if we crossed two pink snapdragon flowers (CRCW) together. What percentage of the offsrping would be pink? Red? White? Codominance Inheritance a condition in which both alleles for a trait are equally expressed in a heterozygote: both alleles are dominant For example: Roan animal Red Bull x White Cow Roan Calf (has red and white hair) E.g. a Roan animal E.g. 2 Codominance E.g. 3 Codominance Rules Choose ONE letter to represent the trait and always use CAPITALS. (for example: colour of snapdragons, use capital C The two alleles are represented as superscripts (example: R for Red (CR ) and W for White (CW ) Complete the hybrids using the same rules as monohybrids and dihybrids. Heterozygotes (CRCW) will display the intermediate trait (pink flowers) Example The four o’clock flower shows incomplete dominance. A pure red flower is crossed with a pure white flower. Use a punnett square to find the phenotypes and genotypes of the F1 generation and F2 generation Multiple Allele Genes Most genes in the human body are actually controlled by more than 2 alleles = multiple allele genes One common example is human blood type It is controlled by 3 alleles: iA and iB and i Example: Homework Entire class: Examine sample problem on page 246 H.W. # 1-4, 8, 9 (page 247)