12.3 and 12.4 Filled in notes
advertisement

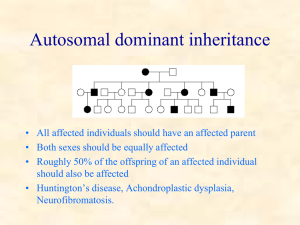
12.3: Modeling Mendel’s Laws Probability • A Punnett square shows the possible outcomes of a cross, but it can also be used to calculate the probability of each outcome. • Probability is the likelihood that a specific event will occur. • Probability can be expressed in words, as a decimal, as a percentage, or as a fraction. • Probability formulas can be used to predict the probabilities that specific alleles will be passed on to offspring. • The possible results of a heterozygous cross are similar to those of flipping two coins at once. Using a Pedigree • A pedigree is a diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations of a family. • Pedigrees can be used to help a family understand a genetic disorder. • A genetic disorder is a disease or disorder that can be inherited. • A pedigree can help answer questions about three aspects of inheritance: sex linkage, dominance, and heterozygosity. • Human generation is longer than 20 years – Must rely on family histories and medical records • Pedigree – diagram that follows the inheritance of a single gene thru several generations in a family (Fig 7-4) – = male, O = Female – connect parents – connect parents to children – children placed from left to right in birth order. – Homo trait shaded in, Hetero trait 1/2 shaded Section 12.4: Beyond Mendelian Heredity Objectives • Are there exceptions to the simple Mendelian pattern of inheritance? • How do heredity and the environment interact to influence phenotype? • How do linked genes affect chromosome assortment and crossover during meiosis? Many Genes, Many Alleles • Most patterns of inheritance are more complex than those that Mendel identified. • The Mendelian inheritance pattern is rare in nature; other patterns include: – polygenic inheritance – incomplete dominance – multiple alleles – codominance. Polygenic character • A character that is influenced or affected by more than one gene • Examples: Eye color, height, and skin color • Most characters are polygenic. Multiple alleles • Genes that have three or more possible alleles • Example: control the ABO blood groups (blood types) in humans. Incomplete Dominance • A condition where an offspring has a phenotype that is intermediate between the two traits of its parents • Example: Snapdragons: red and white with the intermediate trait being pink Codominance • a condition in which both alleles for the same gene are fully expressed. • Example: The genetics of human blood groups Genes Affected by the Environment • Phenotype can be affected by conditions in the environment, such as nutrients and temperature. • In humans, many characters that are partly determined by heredity, such as height, are also affected by the environment. • Many aspects of human personality and behavior are strongly affected by the environment, but genes also play an important role. • Summary The Mendelian inheritance pattern is rare in nature; other patterns include polygenic inheritance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, and codominance. • Phenotype can be affected by conditions in the environment, such as nutrients and temperature. • During meiosis, genes that are close together on the same chromosome are less likely to be separated than genes that are far apart.