Microelectronic Device
Fabrication
Transistor Layers
p-well
n-well
n-channel
transistor
p-channel transistor
p+ substrate
Prof. Dr. Ir. Djoko Hartanto, M.Sc
Arief Udhiarto, S.T,M.T
Electrical Engineering Department
University of Indonesia
Terms and Concepts to be
Covered in this Lesson
•
•
•
•
•
silicon
substrate
monocrystalline
polycrystalline
epitaxial silicon
growth
• polysilicon
• silicon dioxide
• oxide
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
silicon nitride
metal
dopant
doping
concentration
diffusion
field effect
transistor
• source, drain, gate
Terms and Concepts to be
Covered in this Lesson
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
MOS
NMOS technology
n-channel
PMOS technology
p-channel
CMOS technology
p-well
n-well
photoresist
photomask
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
exposure
diffusion
thin films
photolithography
etch
ion implant
polish, CMP
planarization
strips and cleans
test and sort
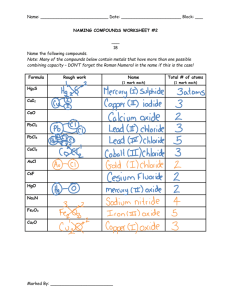
Variations in Dopant
Concentrations
Concentration
P-type
N-type
lightly doped
p-
n-
very lightly doped
p--
n--
heavily doped
p+
n+
very heavily doped
p++
n++
Processing Overview
Steps to Chip IC Fabrication
1. Material Preparation
Convert silicon dioxide to semiconductor-grade silicon
2. Crystal Growth and Wafer Preparation
Convert polysilicon to silicon wafer
Crystal growing
Slice cutting and polishing
Photomask manufacturing
Procesing Overview
3. Wafer Fabrication
a.
b.
c.
d.
Cleaning of surfaces
Growth of epitaxial layer
Thermal oxidation of silicon
Patterning of the various layers
(lithography)
e. Diffusion of impurities into silicon
f. Ion implantation of impurities
Wafer Fabrication
g. Chemical vapor deposition of polycristalline silicon
h. Etching of silicon and GaAs
i. Deposition of insulating layers (silicon oxide or
nitride)
j. Etching of insulating layers (silicon oxide or nitride)
k. Depositon of conductive layers (metal, polysilicon,
other)
l. Alloying (sintering) to form metal-silicon electrical
contact
7
Wafer Fabrication
m. Backgrinding (thinning of wafer by
grinding)
n. Multiprobing (DC electrical testing of each
IC on wafer)
4. Packaging
a. Cutting or breaking of wafers into individual
chips
b. Packaging of individual chips
c. Full AC dan DC electrical testing of
packaged ICs
Fabrication process of a simple metal
oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor
metal connection to gate
doped silicon
polysilicon gate
top nitride
metal connection
to drain
metal connection
to source
field oxide
oxide
gate
source
silicon substrate
oxide
drain
gate oxide
The manufacture of a single MOS
transistor begins with a silicon
substrate.
silicon substrate
A layer of silicon dioxide (field oxide)
provides isolation between devices
manufactured on the same substrate.
field oxide
oxide
silicon substrate
Photoresist provides the means for
transferring the image of a mask onto
the top surface of the wafer.
photoresist
oxide
silicon substrate
Ultraviolet light exposes photoresist
through windows in a photomask.
Ultraviolet Light
Chrome plated
glass mask
Shadow on
photoresist
Exposed area of
photoresist
photoresist
oxide
silicon substrate
Ultraviolet light exposes photoresist
through windows in a photomask.
Ultraviolet Light
Chrome plated
glass mask
Shadow on
photoresist
Exposed area of
photoresist
photoresist
oxide
silicon substrate
Exposed
photoresist
becomes
soluble and can be easily removed
by the develop chemical.
Exposed area of photoresist
Unexposed area
of photoresist
photoresist
oxide
silicon substrate
Unexposed photoresist remains on
surface of oxide to serve as a
temporary protective mask for areas of
the oxide that are not to be etched.
photoresist
photoresist
oxide
silicon substrate
Shadow on
photoresist
Areas of oxide protected by
photoresist remain on the silicon
substrate while exposed oxide is
removed by the etching process.
photoresist
oxide
oxide
siliconsubstrate
substrate
silicon
The photoresist is stripped off -revealing the pattern of the field oxide.
field oxide
oxide
oxide
siliconsubstrate
substrate
silicon
A thin layer of oxide is grown on the
silicon and will later serve as the gate
oxide insulator for the transistor being
constructed.
thin oxide layer
gate oxide
oxide
oxide
silicon substrate
The gate insulator area is defined by
patterning the gate oxide with a
masking and etching process.
gate oxide
oxide
oxide
silicon substrate
Polysilicon is deposited and will
serve as the building material for
the gate of the transistor.
gate oxide
gate oxide
polysilicon
oxide
oxide
silicon substrate
The shape of the gate is defined
by a masking and etching step.
ultra-thin
gate oxide
polysilicon
gate
oxide
gate
gate
silicon substrate
oxide
Dopant ions are selectively implanted
through windows in the photoresist mask.
ion beam
Scanning direction of
ion beam
implanted ions in active
region of transistors
photoresist
Implanted ions in
photoresist to be
removed during
resist strip.
gate
gate
oxide
source
oxide
drain
silicon substrate
The source and drain regions of the
transistor are made conductive by
implanting dopant atoms into
selected areas of the substrate.
doped silicon
gate
gate
oxide
source
oxide
drain
silicon substrate
A layer of silicon nitride is deposited
on top of the completed transistor to
protect it from the environment.
top nitride
gate
source
drain
silicon substrate
Holes are etched into selected
parts of the top nitride where
metal contacts will be formed.
contact holes
gate
source
drain
silicon substrate
Metal is deposited and selectively
etched to provide electrical contacts to
the three active parts of the transistor.
metal contacts
oxide
gate
source
silicon substrate
oxide
drain
Completed structure of a simple MOS
transistor
metal connection to gate
doped silicon
polysilicon gate
top nitride
metal connection
to drain
metal connection
to source
field oxide
oxide
gate
source
silicon substrate
oxide
drain
gate oxide
Manufacturing Areas in Wafer Fab
Wafer Fabrication (front-end)
Bare silicon wafer
Completed product
Test/Sort
Diffusion
Thin Films
Polish
Photo
Etch
Implant
Common Terms in Wafer Fab
• Diffusion
– high temperature processes
– atmospheric - low vacuum pressures
– oxidation, anneal, alloy, deposition, diffusion
• Photolithography
–
–
–
–
patterning process (masking)
photoresist coating
exposure to UV light
develop
Common Terms in Wafer Fab
• Etch
–
–
–
–
selective removal of specific materials
permanent patterning of wafer
low vacuum - high vacuum pressure
RF power, plasma etching
• Ion Implant
– selective doping of specific areas of wafer
– through windows in photoresist or oxide
– high voltage, high vacuum, ion acceleration
Common Terms in Wafer Fab
• Thin Films
– moderate temperatures
– low vacuum - high vacuum pressures
– dielectric films, metals, anneal
• Polish
– chemical mechanical polish (CMP)
– planarization of wafer surface
Common Terms in Wafer Fab
• Strips & Cleans
– dry, plasma resist strip
– wet, chemical cleans using acid solutions and
solvents
• Test/Sort
–
–
–
–
automated testing of each die on wafer
discriminate good from bad
determines a fab’s yield
ship to assembly & packaging
Typical Wafer Flow in CMOS Fab
Diffusion
Test/Sort
Thin Films
Polish
Photo
Etch
Implant
CMOS Inverter Technology
VSS
VDD
Vin
g
Schematic Diagram
s
s
d
d
Vout
VSS
Top view of Transistor
g
VDD
Vin
s
s
d
g
g
d
Vout
polysilicon gate
field oxide
Cross-section of Transistor
p-channel
transistor
p+
source
metal
p+
drain
n-substrate
gate oxide
n-channel
transistor
n+
n+
source
drain
p-well
contact
 0
0