MKT 201 - Principles of Marketing
advertisement

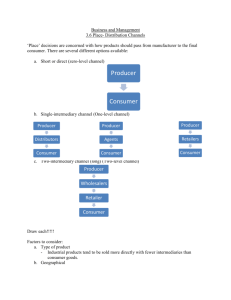
Ch 8/9 Objectives • Recognize the importance of marketing channels and distribution • Understand marketing channels in terms of creating time, place, and possession utilities • Understand some of the complexity of physical distribution What is a Distribution Channel? • A distribution channel consists of the set of people and firms involved in transfer of title to a product as it moves from producer to ultimate consumer or business user. • Every firm wants to have a distribution channel that meets customer's needs and also provides a competitive advantage. Common Marketing Channels for Consumer Products Producer Direct Channel Producer Retailer Channel Producer Wholesaler Channel Wholesalers Consumers Retailers Retailers Consumers Consumers Determining Intensity of Distribution • A firm must decide on the appropriate intensity of distribution for its product. • Intensity is actually a continuum, but three categories are normally used: – Intensive – Selective – Exclusive Intensity-of- Distribution Continuum INTENSIVE Distribution through every reasonable outlet in a market SELECTIVE Distribution through multiple, but not all, reasonable outlets in a market EXCLUSIVE Distribution through a single wholesaling middleman and/or retailer in a market Terms Used for Marketing Intermediaries TERM DESCRIPTION Middleman Any intermediary between manufacturer and enduser markets Agent or Broker Any intermediary with legal authority to act on behalf of the manufacturer Wholesaler An intermediary who sells to other intermediaries, usually to retailers; usually applies to consumer markets Retailer An intermediary who sells to consumers How Intermediaries Minimize Transactions IBM Lynne IBM Lynne Apple Troy Apple Troy Computer City ® HP Compaq Todd Compaq Todd HewlettPackard Diane HewlettPackard Diane Contacts with no intermediaries Contacts with one intermediaries 4 producer x 4 buyers=16 contacts 4 producer + 4 buyers=8 contacts Marketing Channel Functions Performed by Intermediaries Transactional Function Logistical Function -Buying. Purchasing products for resale or as an agent for supply of a product -Selling. Contracting potential customers, promoting products, and soliciting orders -Risk Taking. Assuming business risks in the ownership of inventory that can become obsolete or deteriorate. Facilitating Function Look through this on your own! Channel Terms: • Disintermediation • What is Disintermediation? Terms: • Disintermediation: “The removal of organizations or business process layers responsible for certain intermediary steps in a given value chain” • Show channel “delayering” graphs Rationale for Middlemen • You can eliminate the middleman, but you can’t eliminate the middleman’s function • Benefit both Producers and Retailers “Direct” Distribution • What is it? • For what types of products does it seem to work? • Doesn’t work for all products... “2-Step” Dist. Is Extremely Efficient!!! PRODUCERS A B C D WHOLESALING MIDDLEMAN 1 2 3 4 RETAILERS 5 6 Marketing Channel Management... Formulating channel strategy Design channel structure Select channel members Motivate channel members Coordinate with marketing mix Evaluate member performance Set distribution objectives Specify tasks to be performed by the channel Consider alternative structures Choose optimal structure Channel Conflict Conflict in Marketing Channels 1. Vertical Conflict 2. Horizontal Conflict Don’t worry about this distinction… Conflict is conflict. Channel Conflict: An Internet Example: • Go to the clinique web site: – www.clinique.com Vertical Marketing Systems • Vertical marketing systems are professionally managed and centrally coordinated marketing channels designed to achieve channel economies and maximum marketing impact. • Major types of vertical marketing systems: – corporate – contractual – administered Look at this stuff on your own... Definition of a Supply Chain A Supply Chain is . . . . a sequence of firms that perform activities required to create and deliver a good or service to consumers or industrial users. The Supply Chain • A supply chain differs from a marketing channel in terms of membership. • A supply chain includes suppliers who provide raw material inputs to a manufacturer as well as the wholesalers and retailers who deliver finished goods. PP17-2 The Automotive Supply Chain Supplier Network Raw materials steel aluminum rubber auto manufacturer marketing channel components subassembly assembly transmission suspension GMC Cadillac/Chevy brakes chassis Ford Lincoln/Mercury seats engine Chrysler Dodge/Plymouth Dealer network consumer Types Of Wholesaling Intermediaries Merchant Wholesalers Merchant Wholesalers Full Service Limited Service • General Wholesalers • Cash And Carry Wholesalers • Limited Line Wholesalers • Truck Jobbers • Specialty Line Wholesalers • Drop Shippers • Industrial Distributors • Mail-order Wholesalers • Rack Jobbers