Literary Terms Power Point
advertisement

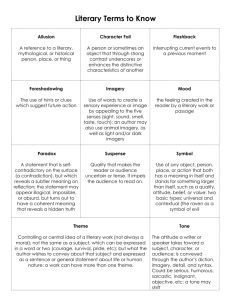
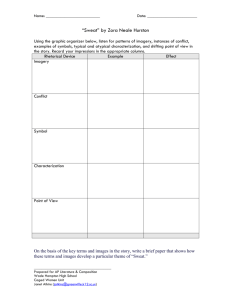
Literary Terms English I Honors Today’s Objectives 9/9/2013 You will be able to: Collaborate with peers to identify & define literary terms Provide examples of literary terms utilizing prior knowledge & information/passages from O.M.A.M Homework: OPEN HOUSE WEDNESDAY YOUR JOB FOR TODAY 9 /9/2013 Count off and group yourselves into tables (yes, that means make a table) with classmates Have all the following materials: your O.M.A.M book, whiteboard, marker (everyone on your team must write at least once) – You are racing the other teams! I want to see who can provide the correct answer. That means write it down quick and hold up your board! Determine the definition of each literary device with your team, write the answer, and hold up your board Provide your own example (write and show) Find and example from O.M.A.M (write and show) Characterization/ Types of Characters Characterization is the art of creating characters for a narrative, including the process of conveying information about them. Characters may be presented by means of description, through their actions, speech, or thoughts. Direct Vs. Indirect Characterization There are two ways an author can convey information about a character: Direct characterization: The author literally tells the audience what a character is like. This may be done via the narrator, another character or by the character him/herself. Indirect characterization: The audience must infer for themselves what the character is like through the character’s thoughts, actions, speech (choice of words, way of talking), looks and interaction with other characters, including other characters’ reactions to that particular person. Write down your answer and hold it up for the following: What type of characterization does Steinbeck use? Flat Character A flat character is a minor character in a work of fiction who does not undergo substantial change or growth in the course of a story. Also referred to as static character, flat characters play a supporting role to the main character. These characters do not represent a fully realistic character, although physical characteristics might be explained. Static character stays the same throughout Round Character A round character in literature is one who has been fully developed. They take on realistic identities and encompass complex characteristics. One who encounters conflict and is changed by it. Dynamic characters change during the unfolding of the story. They learn something, undergo something, or make changes that represents their internal struggles and overcoming them. Symbol/Symbolism An object or person that represents an abstract idea or concept George/Lennie’s Farm Candy’s Dog Rabbits/Mice Please get with your groups from yesterday MAKE SURE YOU ARE IN TABLES! Today’s Objectives 9/10/2013 You will be able to: Collaborate with peers to identify & define literary terms Provide examples of literary terms utilizing prior knowledge & information/passages from O.M.A.M Homework: OPEN HOUSE TOMORROW Let’s Recap…9/10/2013 Characterization – conveying information & types of characters Steinbeck utilizes direct (and indirect) characterization throughout the entire novella Flat & Static INTERCHANGABLE Round & Dynamic Flat: A literary character whose personality can be defined by one or two traits and does not change in the course of the story. Not fully explained by the author (NOT COMPLEX/SAME PERSON) Static: character who undergoes little or no inner change; a character who does not grow or develop – heavier focus on moral/values and changes inside the character, if any (Beliefs REMAIN THE SAME) INTERCHANGABLE Round: character in fiction whose personality, background, motives, and other features are fully explained by the author (Details/Description) Dynamic: a literary or dramatic character who undergoes an important inner change, as a change in personality or attitude - heavier focus on moral/values and changes inside the character (Beliefs CHANGE) Lennie George Curley Carlson Candy Slim Curley’s wife Crooks The Boss SYMBOLS/SYMBOLISM George and Lennie’s Farm The farm represents the possibility of freedom, self-reliance, and protection from the cruelties of the world Candy’s Dog Represents the fate awaiting anyone who has outlived his or her purpose Lennie’s puppy Lennie’s puppy is one of several symbols that represent the victory of the strong over the weak Rabbits also are important because… Theme The overall idea/message of a story or piece of writing Theme Vs. Universal Idea Examples: In Of Mice and Men 1. (Impossibility of) The American Dream 2. Ideal friendship between Males 3. The nature or human existence – strong prey on the weak Imagery and Types Imagery: the formation of mental images, figures, or likenesses of things, a figurative description or illustration. Appeals to the five senses. Words or phrases that use description to create pictures, or images, in the reader’s mind. Visual imagery: Imagery that allows the reader to create a “mental picture” of the scene, event or experience. Often times visual imagery is represented in the form of a simile, metaphor, allusion or literal description. Example: colors, light/darkness, shapes, sizes Auditory Auditory: Imagery that appeals to the reader through sound. Words that are used for auditory imagery imitate or depict sound. Example: voice, music, pitch, rhythm, noise Kinesthetic Words that imitate movement Examples: bend, tumble, stroll, sprint, etc. Tactile Imagery that appeals to the reader’s sense of touch. Words: Hard, soft, wet, heat, warmth, etc. Olfactory Imagery that appeals to the reader’s sense of smell. Words: Fresh, foul, sweet, rancid, etc. On your sticky note… Write your name at the top Today’s Objectives 9/11/2013 You will be able to: Collaborate with peers to identify & define literary terms Provide examples of literary terms utilizing prior knowledge & information/passages from O.M.A.M Homework: O.M.A.M Test FRIDAY Gustatory Imagery that appeals to the reader’s sense of taste. Words: sweet, savory, spicy, sour, etc. Determining passages with imagery… Foreshadowing Foreshadowing is the use of hints or clues to suggest what will happen later in literature FOR EXAMPLE: Foreshadowing plays a large role in indicating that Lennie isn't going to last long. The opening scene introduced a peaceful world, causing the reader to feel happy and content, but at the end of the novella these feelings are washed away . That once beautiful scene plummets into a dark environment. Figurative Language Language that contains or uses figures of speech, especially metaphors, similes, imagery, personification, alliteration, etc. Language that is used to describe one thing in terms of something else—not meant to be taken literally Provide an example for the following: Plot Structure – You tell me! OF Mice and Men Review Passages that represent imagery Passages that foreshadow death Characterization Foreshadowing Theme The purpose of S.T.E.A.L-ing… ____________________is a character who__________________________________________________ What is the purpose: Provides specific information about the character. Summarizes who they are and the purpose that they serve. Used at a quick glance or to dive into character analysis Today’s Objectives 9/16/2013 You will be able to: Identify & define literary terms Understand aspects of writing and apply them in the future Homework: Literary Term Quiz tomorrow! Today’s Objectives 9/17/2013 You will be able to: Understand aspects of writing and apply them in the future Correctly identify literary terms Homework: Enjoy your Tuesday and bring your books tomorrow Motifs Motifs are recurring elements that have symbolic significance in a story. Through its repetition, a motif can help produce other literary aspects such as theme or mood. Usually a symbol or idea ! 1.) Loneliness and Companionship (Which character represents these themes?) 2.) Strength and weakness (Provide an example from the text that relates to this theme) Ambiguity I promise I'll give you a ring tomorrow. “Giving someone a ring" can simply mean calling them on the telephone. But, obviously, the above sentence can also mean giving someone a piece of jewelry worn on the finger. The statement is, therefore, ambiguous. Satire Satire is used to show foolishness or vice in humans, organizations, or even governments, by using sarcasm, ridicule, or irony. Satire can be an entire work that uses satire throughout. EXAMPLE: Austin Powers the movie http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iLKR9tCiwvA Although satire is usually meant to be funny, its greater purpose is often constructive social criticism, using wit as a weapon! Juxtaposition #The placing of elements side by side, leaving it up to the reader to establish connections and impose a meaning. #Juxtaposition is a literary technique in which two or more ideas, places, characters and their actions etc. are placed side by side in a narrative or a poem for the purpose of developing comparisons and contrasts. SAMPLE: John Milton’s “Paradise Lost” is clearly based on the juxtaposition of two characters: God and Satan. Frequently in the poem, the bad qualities of Satan and the good qualities of God are placed side by side and comparison hence made brings to the surface the contrast between the two characters. The juxtaposition in the poem helps us to reach a conclusion that Satan deserved his expulsion from the paradise because of his unwillingness to subjugate to God’s will. Juxtaposition continued… William Shakespeare uses this most commonly in his play “Romeo and Juliet”: “O, she doth teach the torches to burn bright! It seems she hangs upon the cheek of night Like a rich jewel in an Ethiope’s ear;” Here, the radiant face of Juliet is juxtaposed with a black African’s dark skin. Romeo admires Juliet by saying that her face seems brighter than brightly lit torches in the hall. He says that at night her face glows like a bright jewel that shines against the dark skin of an African.