Famous Microbiologists

Famous Microbiologists
Edward Jenner
1749-1823
British
Vaccine for smallpox created from cowpox
"Vaccination," the word
Jenner invented for his treatment (from the Latin vacca , a cow), was adopted by Pasteur for immunization against any disease.
Louis Pasteur -
“Father of Microbiology”
1822-1895
He solved the mysteries of rabies, anthrax, chicken cholera, and silkworm diseases, and contributed to the development of the first vaccines.
Robert Koch -
“Founder of Microbiology”
German
The Nobel Prize in
Physiology of
Medicine 1905
Koch formulated systematic method for biological research
( Koch's Postulates)
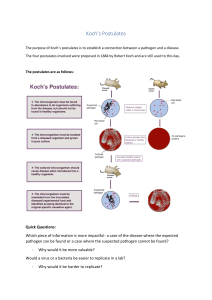
Koch’s Postulates
Pathogen must be found in infected organism.
Pathogen must be isolated & grown in lab
Pathogen grown in lab & introduced to healthy organism must cause the same disease
Injected pathogen must be isolated from the second host
Alexander Fleming
Biologist/Pharmacologist
Scottish
In 1914, he joined British Royal
Army Medical Corps to develop a cure to reduce the number of soldiers dying from infected wounds.
Discovered penicillin in
1928
1930’s other scientists discovered a way to mass produce penicillin
Symbionts
Microorganisms that are harmless or beneficial to other organisms
–
Examples
•
Yeast & bacteria in mouth & throat
•
Bacteria in large intestine
Zoonoses and Vectors
Zoonosis = any disease that can be transmitted from animals to humans.
–
Ex. West Nile, Lyme Disease, Ebola
Vector = transport disease from animal to human
- usually do not get sick themselves ex. Deer Tick is vector for Lyme Disease
Web Sites
http://www.reformation.org/pasteur.html
http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1905/kochbio.htmlhttp://search.nobelprize.org/search/nobel/?q=Alexander+Flemi ng&i=en
http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/immunity/game/ind ex.html
Game above http://www.sjsu.edu/depts/Museum/flemin.html
http://www.accessexcellence.org/RC/AB/BC/Louis_Pasteur.html
http://www.sc.edu/library/spcoll/nathist/jenner.html
http://web.ukonline.co.uk/b.gardner/Koch.htm