Renaissance Final Notes 2014
advertisement

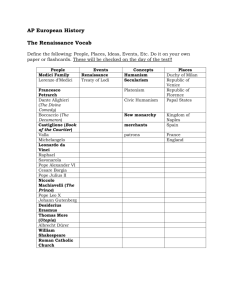
These notes are in the process of being finalized. Student editing ability has been removed. Those of you who did not add information about your topics have had your person deleted from the notes. Mr. Klingman also deleted a few other people that students will not be responsible for on the upcoming test. Please keep up with your study guides and start bringing them in for me to see in tutorial. Also, please begin working on the essay page. If students do not work on the essay page, Mr. Klingman will create the questions without your help. Main Idea I. Italian Renaissance-Beginning Details A. Florence 1. City-State a. A city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state with different laws and ways of life. b. There were numerous Italian city-states. 2. Known as the birthplace of the Italian Renaissance. a. renaissance is a French word meaning rebirth- new beginning b. Renaissance: The revival of art and literature under the influence of classical models in the 14th–16th centuries (1300s-1500s). c. It was a rebirth of culture 1. Culture is a way of life for people in an area. 2. Includes religion, education, food, clothing, and all parts of living in an area. 3. Produced most of the major artists of the Renaissance. a. Leonardo da Vinci b. Michelangelo 4. In the 1400s many wealthy bankers and traders called Florence home. 5. The city-state was controlled by the Medici family who were patrons of the arts. a. Patrons are people who financially support the arts. B. Medici Family 1.The city-state of Florence was ruled by the Medicis. a. They were wealthy bankers and traders. 2. The Medici Family ruled over Florence from 1434 to 1737- at this time, the country was very prosperous 3. The Medici Bank was the most important financial institution of the 15th Century. 4. Cosimo Medici a. Cosimo was the founder of one of the main lines of the Medici Family that ruled over Florence from 1434 to 1537. b. He became the uncrowned ruler of Florence, and during his reign Florence was very prosperous. 1. reign is a period of time a person rules. 2. Cosimo (first main ruler) was uncrowned because he believed the only king was one who wore a crown of thorns. 5. Lorenzo Medici- grandson of Cosimo a. Lorenzo was a patron of the arts b. he was responsible for supporting talents such as Botticelli, Michelangelo, and the young Da Vinci. c. Was called “Lorenzo the Magnificent.” d. Was not as successful as his grandfather Cosimo, and was considered a tyrant. 1. Cruel and unreasonable ruler. C. Humanism 1. Humanism is an intellectual movement at the heart of the Renaissance that focused on education and the classic time of Greece and Rome. 2. The importance of the individual was also emphasized. a. In other words, every person was important. 3. Focus was on the secular world. a. Life outside of the church and the clergy. 1. Clergy refers to ordained leaders of a church. 4. This focus on the secular part of life led to inventions, new discoveries, and a new painting style called perspective. a. Artistic technique used to give paintings and drawings a three-dimensional effect b. Perspective can make the object your drawing look more realistic. 5. A person who practices and believes in the ideals of humanism is a humanist. 6. From the study of classical Greece and Rome, the humanities were studied. a. Subjects such as literature, philosophy, poetry, rhetoric, AND history. 7. Francesco Petrarch was “the Father of humanism.” a. Is mostly remembered for his poetry. b. Many of his poems are directed to a woman named Laura, whom he was in love with. II Art A. Leonardo da Vinci A. Humanist artists showed humanism by painting and sculpting figures from the present, not religious figures from the past. 1. Professions a. He had many professions b. Such as a painter, scientist, architect, sculptor, musician, mathematician, writer, inventor, botanist, engineer, and geologist 3. Art a. Mona Lisa: a Florentine woman with a sleek smile on her face. Displayed in Louvre in Paris. Da Vinci’s largest contribution to Renaissance. b. Last Supper: religious piece that shows Jesus and his disciples the day before the crucifixion. 1. Painted on the wall of Santa Maria delle Grazie dining hall. 2. Da Vinci used different kind of paint (oil) which lead it to decay over time. c. Vitruvian Man: famous study of human proportions based on the statement of the Roman architect Vitruvius that the 'well-shaped man' fits into the perfect shapes of the square and circle." (proportions) d. Perspective is shown in numerous paintings of the Renaissance. 1. It is defined in notes above under Humanism. 4. Inventions a. Flying Machines 1. In his journals he has sketches of machines that allow humans to ‘fly’. 2. He also drew sketches of helicopters and parachutes. b. Water Machines 1. He drew submarines, but refused to share it with the world. 2. He thought they would be used for evil rather than good. 3. He studied properties of water in motion and density. c. Other Machines 1. He drew machines that resemble the modern tank. 2. He drew machines that are now like the machine gun d. Is famous for his notebooks that still exist today. 1. Contain many of his sketches of inventions and other interests such . as art and science. 5. Was fascinated with the human body. a. Studied anatomy frequently. b. Could be considered the first medical examiner. B. Michelangelo 1. Early Years a. He grew up in Florence and his mother died at the age of 6. b. When he was 13 Michelangelo was apprenticed to the most famous painter in Florence, Domenico Ghirlandaio 1. After a year with him, Michelangelo was given the opportunity to live with the Medici Family in Florence. 2. He was advised by a sculptor who looked after the Medici’s Ancient Roman Sculptures. 2. Art a. Mural on the Ceiling of the Sistine Chapel 1. 1508: Michelangelo was asked by Pope Julius II to architecturally design and paint this ceiling 2. Work felt 3-dimensional 3. Includes 9 stories from book of Genesis in the Bible and 12 prophets (Creation- Great Flood) 4. Took 4 years to complete 5. Had to lie on his back to complete his work, at the end of the process 6. Paint dripped into his eyes, sometimes 7. felt pressure from the patron b. Last Judgement a. On Altar Wall of Sistine Chapel. b. Asked by Pope Paul III, after Michelangelo returned to Rome. 3. Sculpture: a. Bacchus 1. Michelangelo’s first surviving large statue, made in Rome in 1496, finished in 1497 b. Pietà 1. In 1498 The Bacchus led to the commission for the Pieta, finished in 1499 and placed in St. Peter’s Basilica (Rome) 2. The Pieta was the first large-scale sculpture by Michelangelo 3. Scene of Mary holding the crucified Jesus in her arms c. David 1. Commission made in 1501 2. This sculpture, to this day, is used as the main example of the Renaissance ideal of perfect humanity 3. David was the main boost of Michelangelo’s career, and is possibly his most famous work d. Tomb of Pope Julius 1. Pope Julius II had commissioned him to paint the Sistine chapel in 1508, and in 1513 he died. 2. When Michelangelo finished the Sistine Chapel, he began the tomb for Pope Julius II 3. On the tomb he carved three figures, Moses (the centerpiece) and two prisoners 4. Tomb placed in the Vatican 4. Architecture a. Michelangelo’s interest in architecture was sparked from working on many sculptures that required architecture to execute. b. Mannerism 1. His style of architecture influenced a period of art called Mannerism ranging from 1510- 1600. a. This is when art was diverging from the traditional classicism of Ancient Greece and Rome b. Into art that used exaggerated proportions and unusual scale and lighting c. Created images focused on beauty, not just natural images. c. San Lorenzo Church: 1. Michelangelo spent much of his career on this church. a. It is the main church of the Medici Family, located in Florence, Italy. b. Constructed in 1418 d. The New Sacristy: 1. 1519-1533 2. Cardinal Giulio de’ Medici commissioned to house the tombs of his recently deceased relatives. 3. The architecture is stone used with traditional Florentine designs around the two tombs on the first two stories 4. With tabernacle windows that join as they go up. 5. Completed with a grand dome on top made to bring in more light. 6. A Sacristy is a chapel where the priest prepares for service. e. The Laurentian Library: 1. Cardinal Giullo de’ Medici also commissioned in 1523 to house the library of his uncle, Lorenzo the Magnificent. 2. The Library has two rooms, the vestibule (entrance hall) and the reading room. a. It is built above where the priests live. 3. Michelangelo did not finish the work on this project because in 1527 the Medici Family was kicked out of Florence, and Michelangelo fled to Rome. f. Saint Peter’s Basilica: 1. Located in Vatican City, a country within Rome. 2. Most significant feature of church is the dome, built by Michelangelo. 3. Originally architect Donato Bramante which Michelangelo redesigned later. 4. His dome served as a model for many other famous structures in history, such as the US Capitol building in Washington, DC. C. Raphael 1. Early Years a. He was trained by his father originally, but his father died when Raphael was 11. b. Raphael became an apprentice of Perugino in Perugia, Italy at the age of 16. c. He used Perugino’s art style for his altar pieces The Crucifixion, The Coronation of the Virgin, and The Marriage of the Virgin. d. He was an apprentice for four years. 2. Famous For a. Raphael was most famous for his painting “Transfiguration”. b. Another one of his famous paintings was “School of Athens” c. his other popular one was the “Sistine Madonna”. d. He also became well known after painting the private library of Pope Julius II. e. Painted numerous works of the Madonna and Madonna with child. D. Donatello 1. Early Years a. Donatello was born in Florence Italy in 1386. 1. His early sculptures were David (out of marble) and Orsanmichele. b. David was made in 1408 and Orsanmichele was made in 1414. 2. Famous For a.His most famous sculptures were St John the Evangelist and David. b. First person to do a sculpture of a lifesize person on horseback. c. His different realistic but classical style of art. III Architecture A. Filippo Brunelleschi 1. He was the first modern architect of the Renaissance, and he rediscovered linear perspective, since all knowledge of it was lost with the Greeks and Romans. a. Linear perspective makes art appear to have space and distance on a flat surface. 2. Filippo’s most famous structure was il duomo (the dome) of the Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore. a. It is very large, and it is made of spiraling brickwork. b. The dome was made without scaffolding or flying buttresses which meant there was nothing inside. 1. So instead he created 2 domes to lower the pressure and prevent the dome from collapsing. 2. He used hoists and cranes of his own design. 3. He also designed buildings such as the Santo Spirito and the Ospedale degli Innocenti (hospital of the innocents). a. The first buildings to have the design of arches supported by columns. IV. Writing A. Niccolo Machiavelli 1. Niccolo’s most famous book called The Prince published in 1513. 2. A famous quote that is still used today comes from ideas written in the book. a. “The End Justifies the Means” 3. The “End Justifies the means” means as a ruler in order to gain power you must do what you have to do, maybe even killing another a. The greatest example of someone who would follow this is a ruler B. Baldassare Castiglione 1. Wrote The Courtier published in 1528 a. Translated into many languages such as Spanish, Latin, English, and German. b. About the Royal court, and manners in the royal court, also wrote about the ideal man. 1. Characteristics of ideal man were: a. Athletic, Good at games, plays musical instrument, knows literature and history, NOT ARROGANT. V. Northern European Renaissance (Beginning) B. Art A. The Great Plague 1. The plague wiped out about one-third of the population of Europe. 2. Also knows as the Black Death 3. Was a reason for the late start of Renaissance in the rest of Europe compared to Italy. 1. Albrecht Durer a. Early Years 1. In his early years, Durer worked in his father’s gold-smithing shop. a. He drew his first self portrait at age 13 and worked towards a life out of Germany to travel to Venice, Italy early on. b. Art 1. He travelled around Germany to gain art experience as soon as his father let him out of his shop. a. He gained knowledge of art from historians and got enough knowledge to know what he should do. b. He is known as the German Leonardo because of his wide interests and he studied Italian artists. 2. He is famous for his self portraits a. In some paintings he makes himself appear to look like Jesus Christ. c. Engravings 1.After he finished up his paintings, he moved on to something called engravings. a. Engravings are where you take a slab of wood about an inch thick, and you carve a design into it with a knife. b. Then you filled the lines with ink and put a sheet of durable paper on the top. c. Then you press the paper down with a stone so the ink makes an impression. d.Two examples of his engravings were Meloncolia and Adam and Eve. 2. This was Durer’s passion that he is remembered for. 2. Jan Van Eyck a. In the 1400s Jan van Eyck was one of the most important Flemish painters. b. He portrayed townspeople as well as religious scenes abound with rich, realistic details. c. Van Eyck painted with tempera, which was a medium that is made with egg. d. He helped make oil paints popular by using them often in his paintings. 1. He used much detail and care when it came to adding light and small details. e. After his death, many people recreated his artwork. f. His most famous piece of art was the altar-piece for the St. Bavon Cathedral. g. Van Eyck was most likely very well educated, because despite the fact from learning mainly Latin and Dutch, he used Hebrew and Greek letters in his painting. 1. He also had the geographical knowledge to paint a map. 3. El Greco a. El Greco’s real name is Dominekos Theotokopoulos. b. He traveled to Venice and studied the works of a few Italian artists. c. In 1570 when El Greco traveled to Rome, he studied with Michelangelo, and Rafael. d. His most famous painting is the Burial of the Count of Orgaz. 1. Took El Greco two years to finish. 2. In this painting you can clearly see El Greco’s many different influences such as the vibrant colors of the Venetian artists, important people of the Renaissance, and the crowding of figures which is a style of European art that originated in Italy. e. El Greco started art in 1560 when he was 19 years old f. El Greco got his name when he traveled to Venice 1. Venetians could not pronounce Dominekos Theotokopoulos, therefore they nicknamed him El Greco, which means the greek. C. Printing Press 1. Johann Gutenberg-German a. An inventor/ craftsman 1. Created the movable type printing press b. Printed first complete edition of the bible in about 1455 c. Books used to be written and copied by hand 1. Only a few thousand books 2. Very inefficient 3. Books were expensive because of the long time it took to write d. He was working on letterpress-mold for each letter that could be put into sentences. e. Wanted to speed up printing process and replace handwriting f. After making the press, he became partners with a wealthy man named Johann Fust 1. first wanted to create the bible since it would sell many copies g. Quickly spread Renaissance ideas throughout Europe. h. It is considered one of the greatest inventions of all time. D. Humanism 1. Difference with Italian a. Emphasis on religious reform 2. Humanities vs. Humanism vs. Humanists a. Humanism- an intellectual movement at the heart of the Renaissance that focused on education and the classics. b. Humanities- the subjects of grammar, rhetoric, poetry, and history 1. Humanities were important to humanists. c. Humanists- people who believed in humanism and the humanities. 3. Desiderius Erasmus a. He was born in Holland. b. Family very religious c. Parents died from plague in 1479 and his brother Peter and him were sent to a monastery 1. He thought monks ruler were unfair. d. He was later ordained a priest. e. He was a humanist and wrote several books including The Praise of Folly. 1. He pokes fun at the church in this book. 2. Says the behavior of the clergy was immoral. a. Making wrong decisions and setting a poor example. f. Martin Luther asked him to be a part reforming the church but he declined. 1. Some historians criticize Erasmus for not joining with Luther, since Erasmus had complaints against the church. g. Translated the Bible into vernacular because he believed everyone should be able to read it. 1. Everyday common language spoken by people. Not Latin 4. Sir Thomas More a. He was a humanist writer. b. More was a friend of Erasmus and wrote A book called Utopia in 1516 1. The book describes an “ideal” society where everyone lives together in peace. c. Now the word Utopia is used to describe perfect societies, but it is implied that the idea is certainly impractical. d. In the ideal place there is no crime, everyone has a job, and it is peaceful. e.He started writing Utopia in Antwerp, Belgium on a diplomatic mission in 1515. f. More was beheaded on July 6th, 1535 for refusing support the marriage of Henry VIII to his second wife. E. Writers 1. William Shakespeare a. Born at the end of the renaissance 1. Northern Renaissance writer 38 plays, 154 sonnets- short poems often written in free verse- poetry that doesn’t necessarily have to rhyme 2. Importance a. Added numerous words and phrases to the english vocabulary. b. Had women in lead roles in his plays and showcased many different kinds of characters. c.Wrote comedies and historical tragedies d. Changed the way plays were written and acted e. Elizabethan London, where there was a high demand for the arts f. Wrote in easy to understand language, expanding the world of theater beyond only the rich and well-taught. 2. Miguel de Cervantes a. Spanish writer b. Wrote Don Quixote 1. A play about knights during Medieval Times. 2. Pokes fun at chivalry a. A code of conduct that knights lived by.