Echinococcus granulosus (and multilocularis)
advertisement

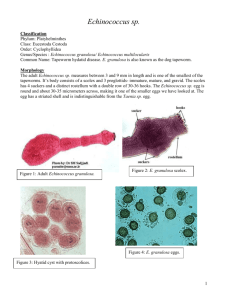
ECHINOCOCCUS (GRANULOSUS AND MULTILOCULARIS) ABDI RAHMAN GULAID INTRODUCTION Echinococcosis: Echinococcosis commomly known as Hydatid Disease or Hydatidosis, is caused by a parasitic cestodes (tapeworms) of the genus Echinococcus. Four species of Echinococcus cause infection in humans are: E. granulosus causes cystic echinococcosis E. multilocularis causes alveolar echinococcosis E. vogeli causes polycystic echinococcosis E. oligarthrus is an extremely rare cause of human echinococcosis. THE GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION Echinococcus granulosus is widely distributed across Canada and more frequent in rural, grazing areas. Echinococcus multilocularis occurs in the northern hemisphere, including central Europe and the northern parts of Europe, Asia, and North America. E. vogeli and E. oligarthrus occur in Central and South America. E.GRANULOSUS HOST & E.MULTILOCULARIS HOST Size E. granulosus Usually 3 to 6 mm long and consist of a scolex with suckers and hooks, as well as at least three proglottid segments. Definitive Adult worm: (adult worm): wolves, coyotes, domestic dogs E. Multilocularis 1.2-3.7 mm long Adult worm: Arctic with two to six and red foxes, proglottic segments. coyotes, sometimes domestic dogs and cats. Intermediate Larval worm: Sheep, Goat, Camel, cattle, Goat, and Horse . Larval worm: rodents (voles, mice, muskrats). Humans TRANSMISSION AND LIFE CYCLE OF ECHINOCOCCUS The Hydatid Tapeworm Life Cycle Diagram 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Adult worm present in intestine of definitive host Eggs passed in feces, ingested by humans or intermediate host Onchosphere penetrates intestinal wall, carried via blood vessels to lodge in organs hydatid cysts develop in liver, lungs, brain, heart After ingestion, the protoscolices attach to the intestine. Ingested protoscolices attach to small intestine and develops into adult worm and the cycle starts all over again. LIFECYCLE: ECHINOCOCCUS EGG IN FECES SYMPTOMS • E. granulosus • Can remain silent for years • It is the enlarging cysts that cause symptoms in organs • Hepatic involvement (75%) (abdominal pain, mass in the hepatic area, biliary duct obstruction) • Pulmonary involvement (chest pain, Cough, hemoptysis) • Brain, bone, and heart (10-20%) • Rupture of cyst (fever, hives, pus, anaphylactic shock, and the cyst spreads throughout body cavity) • E. multilocularis • Affects the liver as a slow growing destructive tumor • Abdominal pain, biliary obstruction, and sometimes metastatic lesions in lungs and brain are common symptoms A SECTION OF HUMAN LUNG SHOWS MULTIPLE PROTOSCOLECES LIBERATED FROM A RUPTURED HYDATID CYST E. MULTILOCULARIS SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF ALVEOLAR HYDATID DISEASE No early symptoms Cysts in multiple body organs Symptoms of liver infestation: upper abdominal pain , weakness , weight loss , chest pain , cough, coughing blood , jaundice Symptoms of brain infestation: Blindness Epilepsy Symptoms of ruptured cysts: Allergic rash Fever DIAGNOSIS • Imaging (CT, MRI, and ultrasound) • Serologic testing (enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescent assay) • Examination of cyst fluid Protoscoleces in a hydatid cyst removed from lung tissue TREATMENT Surgical removal via laparoscopy, can be curative for the treatment of echinococcosis Medication is sometimes effective to keep the cyst from growing back Praziquantel for definitive host (dog) Albendazole, mebendazole intermediate host (sheep, other host) REMOVAL BY SURGERY CONTROL METHOD • interrupt lifecycle by an possible means. • Destroy stray dogs • General education program • Sheep herders should not live closely with their dogs SOURCES - Center of Disease Control. http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/dpdx/html/Echinococcosis.htm journals.cambridge.org/production/action/cjoGetFulltext?fulltex td... by JD SMYTH - 1964 - Cited by 64 - Related articles - www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0166685185900167 by DP McManus - 1985 - Cited by 42 - Related articles - www.springerlink.com/index/MD4LQW968V6TUBPE.pdf by CP Nunes - 2004 - Cited by 12 - Related articles http://www.fao.org/docrep/t1300t/t1300T0m.htm by A. Permin and J.W. Hansen